
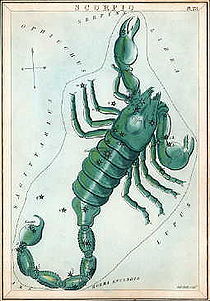
Scorpius
Encyclopedia
Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellation
s of the zodiac
. Its name is Latin
for scorpion
, and its symbol is (Unicode
(Unicode
). It lies between Libra
to the west and Sagittarius
to the east. It is a large constellation located in the southern hemisphere
near the center of the Milky Way
.
(α Sco), β1 Sco
(Graffias), δ Sco
(Dschubba), θ Sco
(Sargas), λ Sco
(Shaula), ν Sco
(Jabbah), ξ Sco
(Girtab), π Sco
(Iclil), σ Sco
(Alniyat), τ Sco
(also known as Alniyat) and υ Sco
(Lesath).
Most of the bright stars are massive members of the nearest OB association: Scorpius-Centaurus
. Its bright stars form a pattern like a longshoreman's hook.
The star δ Sco, after having been a stable 2.3 magnitude
star, flared in July 2000 to 1.9 in a matter of weeks. it has since become a variable star fluctuating between 2.0 and 1.6. This means that at its brightest it is the second brightest star in Scorpius.
U Scorpii
is the fastest known nova
with a period of about 10 years.
ω¹ Scorpii and ω² Scorpii
are an optical double, which can be resolved by the unaided eye. They have contrasting blue and yellow colours.
The star once designated γ Sco (despite being well within the boundaries of Libra) is today known as σ Lib
. Moreover, the entire constellation of Libra
was considered to be claws of Scorpius (Chelae Scorpionis) in Ancient Greek
times, with a set of scales held aloft by Astraea (represented by adjacent Virgo
) being formed from these western-most stars during later Greek times. The division into Libra was formalised during Roman
times.
λ Sco and υ Sco, two stars at the end of the scorpion's tail that appear very close together, are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes.
, this constellation contains many deep sky objects such as the open cluster
s Messier 6 (the Butterfly Cluster
) and Messier 7 (the Ptolemy Cluster
), NGC 6231
(by ζ² Sco), and the globular cluster
s Messier 4
and Messier 80
.
 In Greek Mythology
In Greek Mythology
the myths associated with Scorpio almost invariably also contain a reference to Orion
. According to one of these myths it is written that Orion boasted to goddess Artemis
and her mother, Leto
, that he would kill every animal on the earth. Although Artemis was known to be a hunter herself she offered protection to all creatures. Artemis and her mother Leto sent a scorpion to deal with Orion. The pair battled and the scorpion killed Orion. However, the contest was apparently a lively one that caught the attention of the king of the gods Zeus
, who later raised the scorpion to heaven and afterwards, at the request of Artemis, did the same for Orion to serve as a reminder for mortals to curb their excessive pride. There is also a version that Orion was better than the goddess Artemis but said that Artemis was better than he and so Artemis took a liking to Orion. The god Apollo
, Artemis's twin brother, grew angry and sent a scorpion to attack Orion. After Orion was killed, Artemis asked Zeus to put Orion up in the sky. So every winter Orion hunts in the sky, but every summer he flees as the constellation of the scorpion comes.
In another Greek story involving Scorpio without Orion, Phaeton
(the mortal male offspring of Helios
) went to his father, who had earlier sworn by the River Styx
to give Phaeton anything he should ask for. Phaeton wanted to drive his father's Sun Chariot for a day. Although Helios tried to dissuade his son, Phaeton was adamant. However, when the day arrived, Phaeton panicked and lost control of the white horses that drew the chariot. First, the Earth grew chill as Phaeton flew too high and encountered the celestial scorpion, its deadly sting raised to strike. Alarmed, he dipped the chariot too close, causing the vegetation to burn. By accident, Phaeton turned most of Africa into desert and darkened the skin of the Ethiopian nation until it was black. Eventually, Zeus
was forced to intervene by striking the runaway chariot and Phaeton with a lightning bolt to put an end to its rampage and Phaeton plunged into the River Eridanos
.
Scorpio of the tropical zodiac (October 23 – November 21) differs from the astronomical constellation and the Hindu astrological sign of the sidereal zodiac
(November 16 – December 16). Astronomically, the sun is in Scorpius for just one week, from November 23 – November 30. Much of the difference is due to the constellation Ophiuchus
, which is used by only a few astrologers. Scorpius corresponds to the nakshatras Anuradha
, Jyeshtha
, and Mula
.
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
s of the zodiac
Zodiac
In astronomy, the zodiac is a circle of twelve 30° divisions of celestial longitude which are centred upon the ecliptic: the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year...
. Its name is Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
for scorpion
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arthropod animals of the order Scorpiones within the class Arachnida. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by the pair of grasping claws and the narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back, ending with a venomous stinger...
, and its symbol is
 (Unicode
(UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
). It lies between Libra
Libra (constellation)
Libra is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is . It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east.-Notable features:]...
to the west and Sagittarius
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow...
to the east. It is a large constellation located in the southern hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
near the center of the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
.
Notable features
]Stars
Scorpius contains many bright stars, including AntaresAntares
Antares is a red supergiant star in the Milky Way galaxy and the sixteenth brightest star in the nighttime sky . Along with Aldebaran, Spica, and Regulus it is one of the four brightest stars near the ecliptic...
(α Sco), β1 Sco
Beta Scorpii
Beta Scorpii is a star system in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional names Acrab, Akrab or Elacrab, all come from al-'Aqrab, the Scorpion, for the whole constellation, as well as Graffias, a name it shares with Xi Scorpii...
(Graffias), δ Sco
Delta Scorpii
Delta Scorpii is a star in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional name Dschubba Delta Scorpii (δ Sco, δ Scorpii) is a star in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional name Dschubba Delta Scorpii (δ Sco, δ Scorpii) is a star in the constellation Scorpius. It has the...
(Dschubba), θ Sco
Theta Scorpii
Theta Scorpii is a star in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional name Sargas, of Sumerian origin....
(Sargas), λ Sco
Lambda Scorpii
Lambda Scorpii is the second brightest star system in the constellation Scorpius, and one of the brightest stars in the nighttime sky. It has the Bayer designation λ despite being the second brightest in its constellation...
(Shaula), ν Sco
Nu Scorpii
Nu Scorpii is a star system in the constellation Scorpius.It is at least a quintuple star, probably a septuple, consisting of two close groups that are separated by 41". The brighter group, Nu Scorpii A and B, is split by 1.3" and composed of spectral type B2 subgiants...
(Jabbah), ξ Sco
Xi Scorpii
Xi Scorpii is a star system in the constellation Scorpius. It was also 51 Lib.The Xi Scorpii system consists of at least five stars in two groups separated by 4.67 arcminutes on the sky, corresponding to a distance of at least 8000 astronomical units .The brighter group contains Xi Scorpii A, B,...
(Girtab), π Sco
Pi Scorpii
Pi Scorpii is a triple star system in the constellation Scorpius. It is approximately 459 light years from Earth.Pi Scorpii A is a contact binary of the Beta Lyrae type. Both its members are hot, blue-white B-type dwarfs. Together they have a mean apparent magnitude of +2.89. Their rotation...
(Iclil), σ Sco
Sigma Scorpii
Sigma Scorpii is a star system in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional name Al Niyat, although this name is sometimes also applied to Tau Scorpii, or to the asterism formed by both Sigma and Tau. Sigma Scorpii is 735 light years from the Sun.The primary component of the system,...
(Alniyat), τ Sco
Tau Scorpii
Tau Scorpii is a star in the constellation Scorpius. Tau Scorpii also has the traditional name Alniyat or Al Niyat, which it shares with σ Scorpii. The name derives from the Arabic النياط an-niyāţ meaning "the arteries"....
(also known as Alniyat) and υ Sco
Upsilon Scorpii
Upsilon Scorpii is a star in the constellation Scorpius. It has the traditional name Lesath , from Arabic las'a = "pass of a poisonous animal"; but this is a miscorrection by Scaliger for earlier "Alascha", which came from Arabic al laţkha = "the foggy...
(Lesath).
Most of the bright stars are massive members of the nearest OB association: Scorpius-Centaurus
Scorpius-Centaurus Association
The Scorpius-Centaurus Association is the nearestOB Association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three subgroups The Scorpius-Centaurus Association (sometimes called Sco-Cen or Sco OB2) is the nearestOB Association to the Sun. This stellar association is composed of three...
. Its bright stars form a pattern like a longshoreman's hook.
The star δ Sco, after having been a stable 2.3 magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
star, flared in July 2000 to 1.9 in a matter of weeks. it has since become a variable star fluctuating between 2.0 and 1.6. This means that at its brightest it is the second brightest star in Scorpius.
U Scorpii
U Scorpii
U Scorpii is one of only 10 known recurring nova in our galaxy. Located near the northern edge of the constellation Scorpius it normally has a magnitude of 18, but reaches a magnitude of about 8 during outbursts...
is the fastest known nova
Nova
A nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion in a star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of a white dwarf star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner...
with a period of about 10 years.
ω¹ Scorpii and ω² Scorpii
Omega Scorpii
The Bayer designation Omega Scorpii is shared by two stars, ω¹ Scorpii and ω² Scorpii, in the constellation Scorpius. They are separated by 0.24° on the sky...
are an optical double, which can be resolved by the unaided eye. They have contrasting blue and yellow colours.
The star once designated γ Sco (despite being well within the boundaries of Libra) is today known as σ Lib
Sigma Librae
Sigma Librae is a star in the constellation Libra. It has the traditional names Brachium , Cornu , and Zubenalgubi ....
. Moreover, the entire constellation of Libra
Libra (constellation)
Libra is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for weighing scales, and its symbol is . It is fairly faint, with no first magnitude stars, and lies between Virgo to the west and Scorpius to the east.-Notable features:]...
was considered to be claws of Scorpius (Chelae Scorpionis) in Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
times, with a set of scales held aloft by Astraea (represented by adjacent Virgo
Virgo (constellation)
Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for virgin, and its symbol is . Lying between Leo to the west and Libra to the east, it is the second largest constellation in the sky...
) being formed from these western-most stars during later Greek times. The division into Libra was formalised during Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
times.
λ Sco and υ Sco, two stars at the end of the scorpion's tail that appear very close together, are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes.
Deep sky objects
Due to its location on the Milky WayMilky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
, this constellation contains many deep sky objects such as the open cluster
Open cluster
An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist...
s Messier 6 (the Butterfly Cluster
Butterfly Cluster
The Butterfly Cluster is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. Its name derives from the vague resemblance of its shape to a butterfly....
) and Messier 7 (the Ptolemy Cluster
Ptolemy Cluster
Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius....
), NGC 6231
NGC 6231
NGC 6231 is an open cluster located near Zeta Scorpii. Zeta1 is a member of this star cluster....
(by ζ² Sco), and the globular cluster
Globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is...
s Messier 4
Messier 4
Messier 4 or M4 is a globular cluster in the constellation of Scorpius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1746 and catalogued by Charles Messier in 1764. It was the first globular cluster in which individual stars were resolved.-Visibility:M4 is conspicuous in even the smallest of...
and Messier 80
Messier 80
Messier 80 is a globular cluster in the constellation Scorpius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781....
.
Mythology

Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
the myths associated with Scorpio almost invariably also contain a reference to Orion
Orion (mythology)
Orion was a giant huntsman in Greek mythology whom Zeus placed among the stars as the constellation of Orion....
. According to one of these myths it is written that Orion boasted to goddess Artemis
Artemis
Artemis was one of the most widely venerated of the Ancient Greek deities. Her Roman equivalent is Diana. Some scholars believe that the name and indeed the goddess herself was originally pre-Greek. Homer refers to her as Artemis Agrotera, Potnia Theron: "Artemis of the wildland, Mistress of Animals"...
and her mother, Leto
Leto
In Greek mythology, Leto is a daughter of the Titans Coeus and Phoebe. The island of Kos is claimed as her birthplace. In the Olympian scheme, Zeus is the father of her twins, Apollo and Artemis, the Letoides, which Leto conceived after her hidden beauty accidentally caught the eyes of Zeus...
, that he would kill every animal on the earth. Although Artemis was known to be a hunter herself she offered protection to all creatures. Artemis and her mother Leto sent a scorpion to deal with Orion. The pair battled and the scorpion killed Orion. However, the contest was apparently a lively one that caught the attention of the king of the gods Zeus
Zeus
In the ancient Greek religion, Zeus was the "Father of Gods and men" who ruled the Olympians of Mount Olympus as a father ruled the family. He was the god of sky and thunder in Greek mythology. His Roman counterpart is Jupiter and his Etruscan counterpart is Tinia.Zeus was the child of Cronus...
, who later raised the scorpion to heaven and afterwards, at the request of Artemis, did the same for Orion to serve as a reminder for mortals to curb their excessive pride. There is also a version that Orion was better than the goddess Artemis but said that Artemis was better than he and so Artemis took a liking to Orion. The god Apollo
Apollo
Apollo is one of the most important and complex of the Olympian deities in Greek and Roman mythology...
, Artemis's twin brother, grew angry and sent a scorpion to attack Orion. After Orion was killed, Artemis asked Zeus to put Orion up in the sky. So every winter Orion hunts in the sky, but every summer he flees as the constellation of the scorpion comes.
In another Greek story involving Scorpio without Orion, Phaeton
Phaëton
In Greek mythology, Phaëton or Phaethon was the son of Helios and the Oceanid Clymene. Alternate, less common genealogies make him a son of Clymenus by Merope, of Helios and Rhode or of Helios and Prote....
(the mortal male offspring of Helios
Helios
Helios was the personification of the Sun in Greek mythology. Homer often calls him simply Titan or Hyperion, while Hesiod and the Homeric Hymn separate him as a son of the Titans Hyperion and Theia or Euryphaessa and brother of the goddesses Selene, the moon, and Eos, the dawn...
) went to his father, who had earlier sworn by the River Styx
Styx
In Greek mythology the Styx is the river that forms the boundary between the underworld and the world of the living, as well as a goddess and a nymph that represents the river.Styx may also refer to:-Popular culture:...
to give Phaeton anything he should ask for. Phaeton wanted to drive his father's Sun Chariot for a day. Although Helios tried to dissuade his son, Phaeton was adamant. However, when the day arrived, Phaeton panicked and lost control of the white horses that drew the chariot. First, the Earth grew chill as Phaeton flew too high and encountered the celestial scorpion, its deadly sting raised to strike. Alarmed, he dipped the chariot too close, causing the vegetation to burn. By accident, Phaeton turned most of Africa into desert and darkened the skin of the Ethiopian nation until it was black. Eventually, Zeus
Zeus
In the ancient Greek religion, Zeus was the "Father of Gods and men" who ruled the Olympians of Mount Olympus as a father ruled the family. He was the god of sky and thunder in Greek mythology. His Roman counterpart is Jupiter and his Etruscan counterpart is Tinia.Zeus was the child of Cronus...
was forced to intervene by striking the runaway chariot and Phaeton with a lightning bolt to put an end to its rampage and Phaeton plunged into the River Eridanos
Eridanos (mythology)
The river Eridanos or Eridanus is a river mentioned in Greek mythology. Virgil considered it one of the rivers of Hades in his Aeneid VI, 659.-Ancient references:...
.
Origins
The Babylonians called this constellation MUL.GIR.TAB - the 'Scorpion', the signs can be literally read as 'the (creature with) a burning sting'. The Claws of the Scorpion were also known as the Scales in Babylonia.Astrology
The Western astrological signAstrological sign
Astrological signs represent twelve equal segments or divisions of the zodiac. According to astrology, celestial phenomena reflect or govern human activity on the principle of "as above, so below", so that the twelve signs are held to represent twelve basic personality types or characteristic modes...
Scorpio of the tropical zodiac (October 23 – November 21) differs from the astronomical constellation and the Hindu astrological sign of the sidereal zodiac
Sidereal astrology
Sidereal and tropical are astronomical terms used to describe two different definitions of a "year". They are also used as terms for two systems of ecliptic coordinates used in astrology....
(November 16 – December 16). Astronomically, the sun is in Scorpius for just one week, from November 23 – November 30. Much of the difference is due to the constellation Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century...
, which is used by only a few astrologers. Scorpius corresponds to the nakshatras Anuradha
Anuradha
Anuradha may be:*A disciple and a cousin of Gautama Buddha, see Anuruddha*a lunar mansion in Hindu astrology, see Anuradha *a film, see Anuradha...
, Jyeshtha
Jyeshtha (nakshatra)
Jyeshtha is the 18th nakshatra or lunar mansion in Vedic astrology associated with the heart of the constellation Scorpii , and the stars α , σ, and τ ....
, and Mula
Mula (astrology)
Mula is the 19th nakshatra or lunar mansion in Vedic astrology and corresponds to the stars ε, ζ, η, θ, ι, κ, υ, λ, μ and ν Scorpii in the tail/sting of Scorpius. The symbol of Mula is a bunch of roots tied together or an 'elephant goad' and the Deity associated with it is Niriti, god of...
.

