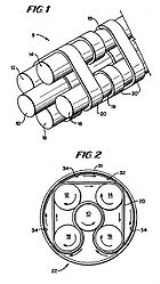
Scrollerwheel
Encyclopedia
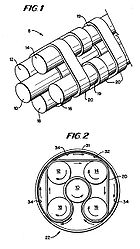
Rolamite
Rolamite is a technology for very low friction bearings developed by Sandia National Laboratories in the 1960s. Invented by Sandia engineer Donald F. Wilkes and patented by him on June 24, 1969 these devices use a stressed metal band and counter rotating rollers within an enclosure to create a...
linear bearings (developed at Sandia National Labs in the late 1960s), and like them, they display only rolling friction, and not the kinetic friction inherent in most mechanical bearings.
The rollers can have a cross section
Cross section (geometry)
In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
in a variety of shapes other than circular, such as: ovoids (which with a single ovoid roller as the central roller, or one of the outer rollers, results in a cam
Cam
A cam is a rotating or sliding piece in a mechanical linkage used especially in transforming rotary motion into linear motion or vice-versa. It is often a part of a rotating wheel or shaft that strikes a lever at one or more points on its circular path...
med motion), various varieties of superellipse
Superellipse
A superellipse is a geometric figure defined in the Cartesian coordinate system as the set of all points withwhere n, a and b are positive numbers....
s and Reuleaux triangle
Reuleaux triangle
A Reuleaux triangle is, apart from the trivial case of the circle, the simplest and best known Reuleaux polygon, a curve of constant width. The separation of two parallel lines tangent to the curve is independent of their orientation...
s.
Advantages
Unlike conventional rolling-element bearingRolling-element bearing
A rolling-element bearing, also known as a rolling bearing, is a bearing which carries a load by placing round elements between the two pieces...
s, they do not require lubrication. Consequentially, they can be employed in environments hostile to lubricated bearings: underwater, in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
(where grease will boil) and at elevated temperatures.
They can be constructed from a wide variety of materials.
Disadvantages
Scrollerwheels cannot have an aspect ratioAspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
(diameter compared to thickness) as high as conventional mechanical bearings.

