
Semiparametric model
Encyclopedia
In statistics
a semiparametric model is a model that has parametric
and nonparametric components.
A model is a collection of distributions: indexed by a parameter
indexed by a parameter 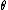 .
.
It may appear at first that semiparametric models include nonparametric models, since they have an infinite dimensional as well as a finite dimensional component. However, a semiparametric model is considered to be "smaller" than a completely nonparametric model because we are often interested only in the finite-dimensional component of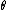 . That is, we are not interested in estimating the infinite-dimensional component. In nonparametric models, by contrast, the primary interest is in estimating the infinite dimensional parameter. Thus the estimation task is statistically harder in nonparametric models.
. That is, we are not interested in estimating the infinite-dimensional component. In nonparametric models, by contrast, the primary interest is in estimating the infinite dimensional parameter. Thus the estimation task is statistically harder in nonparametric models.
These models often use smoothing
or kernels
.
. If we are interested in studying the time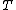 to an event such as death due to cancer or failure of a light bulb, the Cox model specifies the following distribution function for
to an event such as death due to cancer or failure of a light bulb, the Cox model specifies the following distribution function for 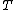 :
: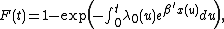
where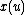 is a known function of time (the covariate vector at time
is a known function of time (the covariate vector at time  ), and
), and 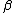 and
and 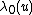 are unknown parameters.
are unknown parameters. 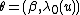 . Here
. Here 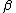 is finite dimensional and is of interest;
is finite dimensional and is of interest; 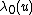 is an unknown non-negative function of time (known as the baseline hazard function) and is often a nuisance parameter. The collection of possible candidates for
is an unknown non-negative function of time (known as the baseline hazard function) and is often a nuisance parameter. The collection of possible candidates for 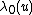 is infinite dimensional.
is infinite dimensional.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
a semiparametric model is a model that has parametric
Parametric statistics
Parametric statistics is a branch of statistics that assumes that the data has come from a type of probability distribution and makes inferences about the parameters of the distribution. Most well-known elementary statistical methods are parametric....
and nonparametric components.
A model is a collection of distributions:
 indexed by a parameter
indexed by a parameter 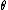 .
.- A parametric model is one in which the indexing parameter is a finite-dimensional vector (in
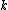 -dimensional Euclidean space for some integer
-dimensional Euclidean space for some integer 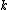 ); i.e. the set of possible values for
); i.e. the set of possible values for 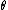 is a subset of
is a subset of 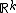 , or
, or 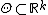 . In this case we say that
. In this case we say that 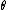 is finite-dimensional.
is finite-dimensional. - In nonparametric models, the set of possible values of the parameter
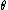 is a subset of some space, not necessarily finite dimensional. For example, we might consider the set of all distributions with mean 0. Such spaces are vector spaces with topological structure, but may not be finite dimensional as vector spaces. Thus,
is a subset of some space, not necessarily finite dimensional. For example, we might consider the set of all distributions with mean 0. Such spaces are vector spaces with topological structure, but may not be finite dimensional as vector spaces. Thus, 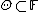 for some possibly infinite dimensional space
for some possibly infinite dimensional space 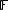 .
. - In semiparametric models, the parameter has both a finite dimensional component and an infinite dimensional component (often a real-valued function defined on the real line). Thus the parameter space
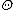 in a semiparametric model satisfies
in a semiparametric model satisfies 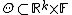 , where
, where 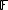 is an infinite dimensional space.
is an infinite dimensional space.
It may appear at first that semiparametric models include nonparametric models, since they have an infinite dimensional as well as a finite dimensional component. However, a semiparametric model is considered to be "smaller" than a completely nonparametric model because we are often interested only in the finite-dimensional component of
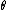 . That is, we are not interested in estimating the infinite-dimensional component. In nonparametric models, by contrast, the primary interest is in estimating the infinite dimensional parameter. Thus the estimation task is statistically harder in nonparametric models.
. That is, we are not interested in estimating the infinite-dimensional component. In nonparametric models, by contrast, the primary interest is in estimating the infinite dimensional parameter. Thus the estimation task is statistically harder in nonparametric models.These models often use smoothing
Smoothing
In statistics and image processing, to smooth a data set is to create an approximating function that attempts to capture important patterns in the data, while leaving out noise or other fine-scale structures/rapid phenomena. Many different algorithms are used in smoothing...
or kernels
Kernel (mathematics)
In mathematics, the word kernel has several meanings. Kernel may mean a subset associated with a mapping:* The kernel of a mapping is the set of elements that map to the zero element , as in kernel of a linear operator and kernel of a matrix...
.
Example
A well-known example of a semiparametric model is the Cox proportional hazards modelProportional hazards models
Proportional hazards models are a class of survival models in statistics. Survival models relate the time that passes before some event occurs to one or more covariates that may be associated with that quantity. In a proportional hazards model, the unique effect of a unit increase in a covariate...
. If we are interested in studying the time
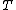 to an event such as death due to cancer or failure of a light bulb, the Cox model specifies the following distribution function for
to an event such as death due to cancer or failure of a light bulb, the Cox model specifies the following distribution function for 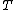 :
: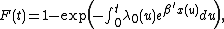
where
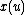 is a known function of time (the covariate vector at time
is a known function of time (the covariate vector at time  ), and
), and 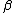 and
and 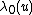 are unknown parameters.
are unknown parameters. 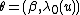 . Here
. Here 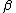 is finite dimensional and is of interest;
is finite dimensional and is of interest; 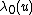 is an unknown non-negative function of time (known as the baseline hazard function) and is often a nuisance parameter. The collection of possible candidates for
is an unknown non-negative function of time (known as the baseline hazard function) and is often a nuisance parameter. The collection of possible candidates for 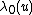 is infinite dimensional.
is infinite dimensional.External links
- Semiparametric Models, in: Nonparametric and Semiparametric models: an introduction (Springer, 2004)

