Service Oriented Device Architecture
Encyclopedia
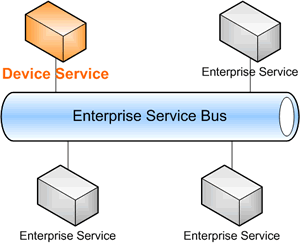
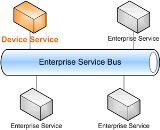
The purpose of Service Oriented Device Architecture (SODA) is to enable devices to be connected to a service-oriented architecture
Service-oriented architecture
In software engineering, a Service-Oriented Architecture is a set of principles and methodologies for designing and developing software in the form of interoperable services. These services are well-defined business functionalities that are built as software components that can be reused for...
(SOA). Currently, developers connect enterprise services to an enterprise service bus
Enterprise service bus
An enterprise service bus is a software architecture model used for designing and implementing the interaction and communication between mutually interacting software applications in Service Oriented Architecture...
(ESB) using the various web service
Web service
A Web service is a method of communication between two electronic devices over the web.The W3C defines a "Web service" as "a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network". It has an interface described in a machine-processable format...
standards that have evolved since the advent of XML
XML
Extensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
in 1998. With SODA, developers are able to connect devices to the ESB and users can access devices in exactly the same manner that they would access any other web service.
External links
- Service Oriented Device Architecture, IEEE Pervasive Computing September 2006
- Presentation at EclipseCon 2007

