
Shikishima class battleship
Encyclopedia
The was a two-ship class
of pre-dreadnought
battleship
s of the Imperial Japanese Navy
designed and built in the UK. The Asahi
is included within the Shikishima-class by some authors, due to commonality of specifications, but it has a completely different silhouette.
convinced the Imperial Japanese Navy of weaknesses in the Jeune Ecole
naval philosophy, and Japan embarked on a program to modernize its fleet with the latest in battleship technology. As with the previous Fuji class battleship
s, Japan lacked the technology and capability to construct its own battleships, and turned again to the United Kingdom
. An order was placed for two vessels in 1896 (Shikishima and Asahi) and one more in 1897 (Hatsuse).
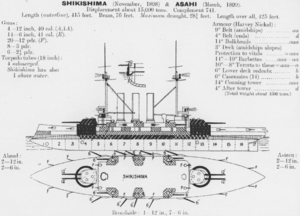 The design of the Shikishima class was a modified version of the Majestic class
The design of the Shikishima class was a modified version of the Majestic class
of the British
Royal Navy
. With a full load displacement of 16,000 tons, the Majestic class ships were considered the largest and most advanced capital ship
s at the time of their construction.
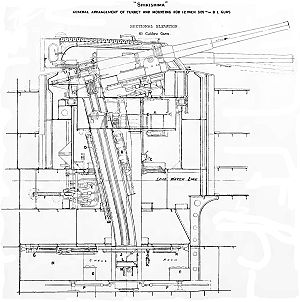 The main battery
The main battery
, on the Shikishima class was the same Elswick
Type 41 12 inch (305 mm) / 40 caliber naval guns used on the Fuji class. These guns were mounted in twin gun turret
s fore and aft.
Secondary armament
on the Shikishima class consisted of fourteen Type 41 6-inch (152 mm)/40-caliber quick firing guns to counter torpedo boat
attacks and were widely spaced on two decks so that a single hit would not disable more than one of them. The guns on the upper deck were enclosed within casemate
s. Tertiary armament consisted of twenty Type 41 3 inch (7.62 cm) /40 caliber naval gun
s, also known as "twelve pounders" and twelve three pounders.
The Shikishima class was also equipped with Whitehead torpedoes, with four tubes below the waterline, and one more on deck.
on the side belt thinning to 6 inches (152 mm) on the upper hull and tapering at both ends. The deck armor was 3 inches (76 mm) thick, with 10 inches (254 mm) around the barbettes and 5 inches (127 mm) around the secondary turrets.
Commissioned on 26 January 1900, Shikishima served with distinction during the Russo-Japanese War
in the naval Battle of Port Arthur
, Battle of the Yellow Sea
and Battle of Tsushima
. After the war, she was de-rated to a Coastal defence ship
, and was used for training duties in various capacities until disarmed in 1922. Her hulk continued to be used as a floating barracks
and training center until 1948.
Commissioned on 18 January 1901, Hatsuse was sunk by a naval mine
on 15 May 1904 off Port Arthur
in one of the greatest naval disasters of the Japanese navy in the Russo-Japanese War.
Ship class
A ship class is a group of ships of a similar design. This is distinct from a ship-type, which might reflect a similarity of tonnage or intended use. For example, the is a nuclear aircraft carrier of the Nimitz class....
of pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleship is the general term for all of the types of sea-going battleships built between the mid-1890s and 1905. Pre-dreadnoughts replaced the ironclad warships of the 1870s and 1880s...
battleship
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of heavy caliber guns. Battleships were larger, better armed and armored than cruisers and destroyers. As the largest armed ships in a fleet, battleships were used to attain command of the sea and represented the apex of a...
s of the Imperial Japanese Navy
Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1869 until 1947, when it was dissolved following Japan's constitutional renunciation of the use of force as a means of settling international disputes...
designed and built in the UK. The Asahi
Japanese battleship Asahi
|-External links:***...
is included within the Shikishima-class by some authors, due to commonality of specifications, but it has a completely different silhouette.
Background
Combat experience in the First Sino-Japanese WarFirst Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War was fought between Qing Dynasty China and Meiji Japan, primarily over control of Korea...
convinced the Imperial Japanese Navy of weaknesses in the Jeune Ecole
Jeune Ecole
The Jeune École was a strategic naval concept developed during the 19th century. It advocated the use of small, powerfully equipped units to combat a larger battleship fleet, and commerce raiders capable of ending the trade of the rival nation...
naval philosophy, and Japan embarked on a program to modernize its fleet with the latest in battleship technology. As with the previous Fuji class battleship
Fuji class battleship
-External links:**...
s, Japan lacked the technology and capability to construct its own battleships, and turned again to the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
. An order was placed for two vessels in 1896 (Shikishima and Asahi) and one more in 1897 (Hatsuse).
Design

Majestic class battleship
The Majestic class was a class of pre-dreadnought battleships, built under the Spencer Programme of 8 December 1893, that sought to counter the growing naval strength of France and the Russian Empire...
of the British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
. With a full load displacement of 16,000 tons, the Majestic class ships were considered the largest and most advanced capital ship
Capital ship
The capital ships of a navy are its most important warships; they generally possess the heaviest firepower and armor and are traditionally much larger than other naval vessels...
s at the time of their construction.
Armament

Main battery
Generally used only in the terms of naval warfare, the main battery is the primary weapon around which a ship was designed. "Battery" is in itself a common term in the military science of artillery. For example, the United States Navy battleship USS Washington had a main battery of nine guns...
, on the Shikishima class was the same Elswick
Armstrong Whitworth
Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. Headquartered in Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth engaged in the construction of armaments, ships, locomotives, automobiles, and aircraft.-History:In 1847,...
Type 41 12 inch (305 mm) / 40 caliber naval guns used on the Fuji class. These guns were mounted in twin gun turret
Gun turret
A gun turret is a weapon mount that protects the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in many directions.The turret is also a rotating weapon platform...
s fore and aft.
Secondary armament
Battleship secondary armament
The secondary armament of a capital ship are smaller, faster-firing weapons that are typically effective at a shorter range than the main weapons...
on the Shikishima class consisted of fourteen Type 41 6-inch (152 mm)/40-caliber quick firing guns to counter torpedo boat
Torpedo boat
A torpedo boat is a relatively small and fast naval vessel designed to carry torpedoes into battle. The first designs rammed enemy ships with explosive spar torpedoes, and later designs launched self-propelled Whitehead torpedoes. They were created to counter battleships and other large, slow and...
attacks and were widely spaced on two decks so that a single hit would not disable more than one of them. The guns on the upper deck were enclosed within casemate
Casemate
A casemate, sometimes rendered casement, is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired. originally a vaulted chamber in a fortress.-Origin of the term:...
s. Tertiary armament consisted of twenty Type 41 3 inch (7.62 cm) /40 caliber naval gun
QF 12 pounder 12 cwt naval gun
The QF 12 pounder 12 cwt gun was a common calibre naval gun introduced in 1894 and used until the middle of the 20th century. It was produced by Armstrong Whitworth, Elswick and used on Royal Navy warships, and exported to allied countries...
s, also known as "twelve pounders" and twelve three pounders.
The Shikishima class was also equipped with Whitehead torpedoes, with four tubes below the waterline, and one more on deck.
Armor
The Shikishima class vessels were armored using 9 inches (229 mm) of Harvey armorHarvey armor
Harvey armor was a type of steel armor developed in the early 1890s in which the front surfaces of the plates were case hardened. The method for doing this was known as the Harvey process....
on the side belt thinning to 6 inches (152 mm) on the upper hull and tapering at both ends. The deck armor was 3 inches (76 mm) thick, with 10 inches (254 mm) around the barbettes and 5 inches (127 mm) around the secondary turrets.
Propulsion
The engines on the Shikishima class vessels were triple expansion steam engines with water tube boilers and two screws. The engines produced 14500 shp, yielding a design speed of 17 knots (33 km/h); in trials Shikishima achieved 18.7 knots (37 km/h). However, unlike the Majestics side-by-side funnel arrangement, the Shikishima-class had the orthodox three smokestack arrangement along the centerline.Ships in class
- ShikishimaJapanese battleship Shikishima|-External links:**...
Commissioned on 26 January 1900, Shikishima served with distinction during the Russo-Japanese War
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea...
in the naval Battle of Port Arthur
Battle of Port Arthur
The Battle of Port Arthur was the starting battle of the Russo-Japanese War...
, Battle of the Yellow Sea
Battle of the Yellow Sea
The Battle of the Yellow Sea was a major naval engagement of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 August. The battle foiled an attempt by the Russian fleet at Port Arthur to break out and form up with counterparts from...
and Battle of Tsushima
Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima , commonly known as the “Sea of Japan Naval Battle” in Japan and the “Battle of Tsushima Strait”, was the major naval battle fought between Russia and Japan during the Russo-Japanese War...
. After the war, she was de-rated to a Coastal defence ship
Coastal defence ship
Coastal defence ships were warships built for the purpose of coastal defence, mostly during the period from 1860 to 1920. They were small, often cruiser-sized warships that sacrificed speed and range for armour and armament...
, and was used for training duties in various capacities until disarmed in 1922. Her hulk continued to be used as a floating barracks
Barracks
Barracks are specialised buildings for permanent military accommodation; the word may apply to separate housing blocks or to complete complexes. Their main object is to separate soldiers from the civilian population and reinforce discipline, training and esprit de corps. They were sometimes called...
and training center until 1948.
- HatsuseJapanese battleship Hatsuse|-External links:**...
Commissioned on 18 January 1901, Hatsuse was sunk by a naval mine
Naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, an enemy vessel...
on 15 May 1904 off Port Arthur
Lüshunkou
Lüshunkou is a district in the municipality of Dalian, Liaoning province, China. Also called Lüshun City or Lüshun Port, it was formerly known as both Port Arthur and Ryojun....
in one of the greatest naval disasters of the Japanese navy in the Russo-Japanese War.
See also
- Japanese battleship MikasaJapanese battleship Mikasais a pre-Dreadnought battleship of the Imperial Japanese Navy, launched in Britain in 1900. She served as the flagship of Admiral Tōgō Heihachirō during the Battle of the Yellow Sea on 10 August 1904, and the Battle of Tsushima on 27 May 1905 during the Russo-Japanese War. The ship is preserved as...
, another Japanese battleship derived from the Majestic-class

