
Shin (letter)
Encyclopedia
Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic (in abjadi order, 13th in modern order).
Its sound value is a voiceless sibilant, ʃ or [s].
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Sigma (which in turn gave Latin and Cyrillic С
), and the letter Sha in the Glagolitic
and Cyrillic scripts .
The South Arabian and Ethiopian
letter Śawt
is also cognate.
shen). The Encyclopaedia Judaica
, 1972, records that it originally represented a composite bow
.
The history of the letters expressing sibilants in the various Semitic alphabets is a bit complicated, due to different mergers between Proto-Semitic phonemes. As usually reconstructed, there are five Proto-Semitic phonemes that evolved into various voiceless sibilants in daughter languages, as follows:
Hebrew spelling:
The Hebrew /s/ version according to the reconstruction shown above is descended from Proto-Semitic }, a phoneme
thought to correspond to a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
/ɬ/, similar to Welsh Ll in "Llandudno".
See also Hebrew phonology
, Śawt
.
The Hebrew letter represents two different phonemes: a sibilant s, like English sour, and a ʃ, like English shoe. The two are distinguished by a dot above the left-hand side of the letter for /s/ and above the right-hand side for /ʃ/.
, Shin represents the number 300.
Shin, as a prefix, bears the same meaning as the relative pronoun
s "that", "which" and "who" in English.
In colloquial Hebrew, Kaph
and Shin together have the meaning of "when". This is a contraction of , ka'asher (as, when).
Shin is also one of the seven letters which receive a special crown (called a tagin) when written in a Sefer Torah
. See Gimmel, Ayin
, Teth
, Nun
, Zayin
, and Tzadi.
According to Judges
12:6, the tribe of Ephraim
could not differentiate between Shin and Sin; when the Gilead
ites were at war with the Ephraimites, they would ask suspected Ephraimites to say the word shibolet; an Ephraimite would say sibolet and thus be exposed. From this episode we get the English word Shibboleth
.
(priest) forms the letter Shin with his hands as he recites the Priestly Blessing
. In the mid 1960s, actor Leonard Nimoy
used a single-handed version of this gesture to create the Vulcan hand salute
for his character, Mr. Spock, on Star Trek
.
The letter Shin is often inscribed on the case containing a mezuzah
, a scroll of parchment with Biblical text written on it. The text contained in the mezuzah is the Shema Yisrael
prayer, which calls the Israelites to love their God with all their heart, soul and strength. The mezuzah is situated upon all the doorframes in a home or establishment. Sometimes the whole word Shaddai will be written.
The Shema Yisrael prayer also commands the Israelites to write God's commandments on their hearts (Deut. 6:6); the shape of the letter Shin mimics the structure of the human heart
: the lower, larger left ventricle
(which supplies the full body) and the smaller right ventricle (which supplies the lungs) are positioned like the lines of the letter Shin.
A religious significance has been applied to the fact that there are three valleys which comprise the city of Jerusalem's geography: the Valley of Ben Hinnom, Tyropoeon Valley, and Kidron Valley
, and that these valleys converge to also form the shape of the letter shin, and that the Temple in Jerusalem
is located where the dagesh (horizontal line) is. This is seen as a fulfillment of passages such as Deuteronomy 16:2 that instructs Jews to celebrate the Pasach at "the place the LORD will choose as a dwelling for his Name" (NIV).
In the Sefer Yetzirah
the letter Shin is King over Fire, Formed Heaven in the Universe, Hot in the Year, and the Head in the Soul.
was an old acronym for the Israeli Department of Internal General Security.
A Shin-Shin Clash is Israeli military
parlance for a battle between two tank divisions (tank in Hebrew is shiryon).
Sh'at haShin (The Shin Hour) is the last possible moment for any action, usually military. Corresponds to the English expression the eleventh hour.
at 15th position.
In Modern Standard Arabic, initial (though, normally diacritics are omitted) ' onMouseout='HidePop("33916")' href="/topics/Arabic_phonology">pronounced
/sa-/) is used as a prefix to imperfective verbs to indicate the future tense
. Arab grammarians generally consider this prefix to be an abbreviation of , meaning (in this sense) "will." Thus sa- prefixed to ("he writes") becomes ("he will write").
represents /s/. It is the 12th letter of the modern alphabet order and is written thus:
represents /ʃ/, and is the 13th letter of the modern alphabet order and is written thus:
, where the use of shin is well-determined, the orthography of sin was never fully resolved.
To express an etymological /ś/, a number of dialects chose either sin or samek exclusively, where other dialects switch freely between them (often 'leaning' more often towards one or the other). For example:
Regardless of how it is written, /ś/ in spoken Aramaic seems to have universally resolved to /s/.
Its sound value is a voiceless sibilant, ʃ or [s].
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Sigma (which in turn gave Latin and Cyrillic С
Es (Cyrillic)
Es is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet.It commonly represents the voiceless alveolar fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨s⟩ in "sand".-History:...
), and the letter Sha in the Glagolitic
Glagolitic alphabet
The Glagolitic alphabet , also known as Glagolitsa, is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. The name was not coined until many centuries after its creation, and comes from the Old Slavic glagolъ "utterance" . The verb glagoliti means "to speak"...
and Cyrillic scripts .
The South Arabian and Ethiopian
Ge'ez alphabet
Ge'ez , also called Ethiopic, is a script used as an abugida for several languages of Ethiopia and Eritrea but originated in an abjad used to write Ge'ez, now the liturgical language of the Ethiopian and Eritrean Orthodox Church...
letter Śawt
Sawt
Sawt is a kind of popular music found in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, especially in Kuwait and Bahrain. Sawt is a complex form of urban music, originally performed by 'ud and mirwas , with a violin later supplementing the arrangement.Two men perform the dance, which is called “Zaffan”....
is also cognate.
Origins
The Phoenician letter expressed the continuants of two Proto-Semitic phonemes, and may have been based on a pictogram of a tooth (in modern HebrewHebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
shen). The Encyclopaedia Judaica
Encyclopaedia Judaica
The Encyclopaedia Judaica is a 26-volume English-language encyclopedia of the Jewish people and their faith, Judaism. It covers diverse areas of the Jewish world and civilization, including Jewish history of all eras, culture, holidays, language, scripture, and religious teachings...
, 1972, records that it originally represented a composite bow
Composite bow
A composite bow is a bow made from horn, wood, and sinew laminated together. The horn is on the belly, facing the archer, and sinew on the back of a wooden core. Sinew and horn will store more energy than wood for the same length of bow...
.
The history of the letters expressing sibilants in the various Semitic alphabets is a bit complicated, due to different mergers between Proto-Semitic phonemes. As usually reconstructed, there are five Proto-Semitic phonemes that evolved into various voiceless sibilants in daughter languages, as follows:
| Proto-Semitic | Akkadian Akkadian language Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate... |
Arabic Arabic language Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book... |
Canaanite | Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew Tiberian Hebrew is the extinct canonical pronunciation of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh and related documents in the Roman Empire. This traditional medieval pronunciation was committed to writing by Masoretic scholars based in the Jewish community of Tiberias , in the form of the Tiberian vocalization... |
Aramaic Aramaic language Aramaic is a group of languages belonging to the Afroasiatic language phylum. The name of the language is based on the name of Aram, an ancient region in central Syria. Within this family, Aramaic belongs to the Semitic family, and more specifically, is a part of the Northwest Semitic subfamily,... |
Ge'ez Ge'ez language Ge'ez is an ancient South Semitic language that developed in the northern region of Ethiopia and southern Eritrea in the Horn of Africa... |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| س |  |
||||||||||
| س | 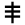 |
||||||||||
| ص | 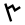 |
||||||||||
| ش |  |
or | |||||||||
| ض | 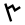 |
||||||||||
Hebrew Shin / Sin
| Orthographic Orthography The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography... variants |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various Print Fonts | Cursive Hebrew |
Rashi Script Rashi script Rashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive... |
||
| Serif | Sans-serif Sans-serif In typography, a sans-serif, sans serif or san serif typeface is one that does not have the small projecting features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. The term comes from the French word sans, meaning "without".... | Monospaced | ||
| ש | ש | ש |  |
 |
Hebrew spelling:
The Hebrew /s/ version according to the reconstruction shown above is descended from Proto-Semitic }, a phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
thought to correspond to a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K...
/ɬ/, similar to Welsh Ll in "Llandudno".
See also Hebrew phonology
Hebrew phonology
This article is about the phonology of the Hebrew language based on the Israeli dialect. It deals with current phonology and phonetics as well as with historical developments thereof, including geographical variants....
, Śawt
Sawt
Sawt is a kind of popular music found in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, especially in Kuwait and Bahrain. Sawt is a complex form of urban music, originally performed by 'ud and mirwas , with a violin later supplementing the arrangement.Two men perform the dance, which is called “Zaffan”....
.
Sin and Shin Dot
| Sin and Shin dot | |
|---|---|
| IPA | s, ʃ |
| Transliteration Romanization of Hebrew Hebrew uses the Hebrew alphabet with optional vowel points. The romanization of Hebrew is the use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Hebrew words.... |
s, sh |
| English example | sought, shot |
| Sin Dot | |
| The word Israel in Hebrew Hebrew language Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such... , Yisrael. The upper left hand dot on the Sin is a Sin dot. |
|
| Shin Dot | |
| The Hebrew Hebrew language Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such... word yesh, there is. The upper right hand dot on the Shin is a Shin dot. |
|
| Other niqqud | |
| Shva Shva Shva or, in Biblical Hebrew, Sh'wa is a Hebrew niqqud vowel sign written as two vertical dots "ְ" underneath a letter. In Modern Hebrew, it indicates either the phoneme or the complete absence of a vowel , whereas in Hebrew prescriptive linguistics, four grammatical entities are differentiated:... Hiriq Zeire Segol Patach Kamatz Holam Dagesh Mappiq Shuruk Kubutz Rafe Sin/Shin Dot |
|
The Hebrew letter represents two different phonemes: a sibilant s, like English sour, and a ʃ, like English shoe. The two are distinguished by a dot above the left-hand side of the letter for /s/ and above the right-hand side for /ʃ/.
| | Name | | Symbol | | IPA International Phonetic Alphabet The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic... |
| Transliteration Transliteration Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another... |
| Example | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sin dot (left) | /s/ | s | sour | ||||||
| Shin dot (right) | /ʃ/ | sh | shop | ||||||
Unicode encoding
| Glyph | Unicode | Name |
|---|---|---|
| U+05C1 | SHIN DOT | |
| U+05C2 | SIN DOT |
Significance
In gematriaGematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
, Shin represents the number 300.
Shin, as a prefix, bears the same meaning as the relative pronoun
Relative pronoun
A relative pronoun is a pronoun that marks a relative clause within a larger sentence. It is called a relative pronoun because it relates the relative clause to the noun that it modifies. In English, the relative pronouns are: who, whom, whose, whosever, whosesoever, which, and, in some...
s "that", "which" and "who" in English.
In colloquial Hebrew, Kaph
Kaph
Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet...
and Shin together have the meaning of "when". This is a contraction of , ka'asher (as, when).
Shin is also one of the seven letters which receive a special crown (called a tagin) when written in a Sefer Torah
Sefer Torah
A Sefer Torah of Torah” or “Torah scroll”) is a handwritten copy of the Torah or Pentateuch, the holiest book within Judaism. It must meet extremely strict standards of production. The Torah scroll is mainly used in the ritual of Torah reading during Jewish services...
. See Gimmel, Ayin
Ayin
' or ' is the sixteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic . It is the twenty-first letter in the new Persian alphabet...
, Teth
Teth
' is the ninth letter of many Semitic abjads , including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Tet , Syriac and Arabic ; it is 9th in abjadi order and 16th in modern Arabic order....
, Nun
Nun (letter)
Nun is the fourteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . It is the third letter in Thaana , pronounced as "noonu"...
, Zayin
Zayin
Zayin is the seventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic , Hebrew , Syriac and Perso-Arabic alphabet...
, and Tzadi.
According to Judges
Book of Judges
The Book of Judges is the seventh book of the Hebrew bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its title describes its contents: it contains the history of Biblical judges, divinely inspired prophets whose direct knowledge of Yahweh allows them to act as decision-makers for the Israelites, as...
12:6, the tribe of Ephraim
Ephraim
Ephraim ; was, according to the Book of Genesis, the second son of Joseph and Asenath. Asenath was an Egyptian woman whom Pharaoh gave to Joseph as wife, and the daughter of Potipherah, a priest of On. Ephraim was born in Egypt before the arrival of the children of Israel from Canaan...
could not differentiate between Shin and Sin; when the Gilead
Gilead
In the Bible "Gilead" means hill of testimony or mound of witness, , a mountainous region east of the Jordan River, situated in the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan. It is also referred to by the Aramaic name Yegar-Sahadutha, which carries the same meaning as the Hebrew . From its mountainous character...
ites were at war with the Ephraimites, they would ask suspected Ephraimites to say the word shibolet; an Ephraimite would say sibolet and thus be exposed. From this episode we get the English word Shibboleth
Shibboleth
A shibboleth is a custom, principle, or belief distinguishing a particular class or group of people, especially a long-standing one regarded as outmoded or no longer important...
.
In Judaism
Shin also stands for the word Shaddai, a name for God. Because of this, a kohenKohen
A Kohen is the Hebrew word for priest. Jewish Kohens are traditionally believed and halachically required to be of direct patrilineal descent from the Biblical Aaron....
(priest) forms the letter Shin with his hands as he recites the Priestly Blessing
Priestly Blessing
The Priestly Blessing, , also known in Hebrew as Nesiat Kapayim, , or Dukhanen , is a Jewish prayer recited by Kohanim during certain Jewish services...
. In the mid 1960s, actor Leonard Nimoy
Leonard Nimoy
Leonard Simon Nimoy is an American actor, film director, poet, musician and photographer. Nimoy's most famous role is that of Spock in the original Star Trek series , multiple films, television and video game sequels....
used a single-handed version of this gesture to create the Vulcan hand salute
Vulcan salute
The Vulcan salute is a hand gesture consisting of a raised hand, palm forward with the fingers parted between the middle and ring finger, and the thumb extended. Often, the famous line, "Live long and prosper", is said after it. The salute was devised and popularised by Leonard Nimoy, who...
for his character, Mr. Spock, on Star Trek
Star Trek: The Original Series
Star Trek is an American science fiction television series created by Gene Roddenberry, produced by Desilu Productions . Star Trek was telecast on NBC from September 8, 1966, through June 3, 1969...
.
The letter Shin is often inscribed on the case containing a mezuzah
Mezuzah
A mezuzah is usually a metal or wooden rectangular object that is fastened to a doorpost of a Jewish house. Inside it is a piece of parchment inscribed with specified Hebrew verses from the Torah...
, a scroll of parchment with Biblical text written on it. The text contained in the mezuzah is the Shema Yisrael
Shema Yisrael
Shema Yisrael are the first two words of a section of the Torah that is a centerpiece of the morning and evening Jewish prayer services...
prayer, which calls the Israelites to love their God with all their heart, soul and strength. The mezuzah is situated upon all the doorframes in a home or establishment. Sometimes the whole word Shaddai will be written.
The Shema Yisrael prayer also commands the Israelites to write God's commandments on their hearts (Deut. 6:6); the shape of the letter Shin mimics the structure of the human heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
: the lower, larger left ventricle
Ventricle
Ventricle may refer to:* Ventricle , the pumping chambers of the heart* Ventricular system in the brain* Ventricle of the larynx, a structure in the larynx* Stomach of the gastrointestinal tract...
(which supplies the full body) and the smaller right ventricle (which supplies the lungs) are positioned like the lines of the letter Shin.
A religious significance has been applied to the fact that there are three valleys which comprise the city of Jerusalem's geography: the Valley of Ben Hinnom, Tyropoeon Valley, and Kidron Valley
Kidron Valley
The Kidron Valley is the valley on the eastern side of The Old City of Jerusalem which features significantly in the Bible...
, and that these valleys converge to also form the shape of the letter shin, and that the Temple in Jerusalem
Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem or Holy Temple , refers to one of a series of structures which were historically located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, the current site of the Dome of the Rock. Historically, these successive temples stood at this location and functioned as the centre of...
is located where the dagesh (horizontal line) is. This is seen as a fulfillment of passages such as Deuteronomy 16:2 that instructs Jews to celebrate the Pasach at "the place the LORD will choose as a dwelling for his Name" (NIV).
In the Sefer Yetzirah
Sefer Yetzirah
Sefer Yetzirah is the title of the earliest extant book on Jewish esotericism, although some early commentators treated it as a treatise on mathematical and linguistic theory as opposed to Kabbalah...
the letter Shin is King over Fire, Formed Heaven in the Universe, Hot in the Year, and the Head in the Soul.
Sayings with Shin
The Shin-BetBet (letter)
Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of many Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet , Aramaic, Hebrew , Phoenician and Syriac...
was an old acronym for the Israeli Department of Internal General Security.
A Shin-Shin Clash is Israeli military
Israel Defense Forces
The Israel Defense Forces , commonly known in Israel by the Hebrew acronym Tzahal , are the military forces of the State of Israel. They consist of the ground forces, air force and navy. It is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and has no civilian jurisdiction within Israel...
parlance for a battle between two tank divisions (tank in Hebrew is shiryon).
Sh'at haShin (The Shin Hour) is the last possible moment for any action, usually military. Corresponds to the English expression the eleventh hour.
Arabic šīn/sīn
In the Arabic alphabet, is at the original (21st) position in Abjadi order. A letter variant takes the place of SamekhSamekh
Samekh or Simketh is the fifteenth letter in many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Hebrew, and Aramaic, representing . The Arabic alphabet, however, uses a letter based on Phoenician šin to represent ; however, that glyph takes Samekh's place in the traditional Abjadi order of the Arabic...
at 15th position.
In Modern Standard Arabic, initial (though, normally diacritics are omitted) ' onMouseout='HidePop("33916")' href="/topics/Arabic_phonology">pronounced
Arabic phonology
While many languages have numerous dialects that differ in pronunciation, the Arabic language is more properly described as a continuum of varieties. This article deals primarily with Modern Standard Arabic, which is the standard variety shared by educated speakers throughout Arabic-speaking regions...
/sa-/) is used as a prefix to imperfective verbs to indicate the future tense
Future tense
In grammar, a future tense is a verb form that marks the event described by the verb as not having happened yet, but expected to happen in the future , or to happen subsequent to some other event, whether that is past, present, or future .-Expressions of future tense:The concept of the future,...
. Arab grammarians generally consider this prefix to be an abbreviation of , meaning (in this sense) "will." Thus sa- prefixed to ("he writes") becomes ("he will write").
represents /s/. It is the 12th letter of the modern alphabet order and is written thus:
represents /ʃ/, and is the 13th letter of the modern alphabet order and is written thus:
Aramaic Shin/Sin
In AramaicAramaic language
Aramaic is a group of languages belonging to the Afroasiatic language phylum. The name of the language is based on the name of Aram, an ancient region in central Syria. Within this family, Aramaic belongs to the Semitic family, and more specifically, is a part of the Northwest Semitic subfamily,...
, where the use of shin is well-determined, the orthography of sin was never fully resolved.
To express an etymological /ś/, a number of dialects chose either sin or samek exclusively, where other dialects switch freely between them (often 'leaning' more often towards one or the other). For example:
| ʿaśar "ten" |
Old Aramaic | Imperial Aramaic | Middle Aramaic | Palestinian Aramaic | Babylonian Aramaic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrian Inscriptions | Idumaean Ostraca, Egyptian, Egyptian-Persian, Ezra | Qumran | Galilean | Gaonic, Jewish Babylonian Aramaic | |
| Tell Halaf | (none recorded) | Palmyrene, Syriac | Zoar, Christian Palestinian Aramaic | Mandaic | |
| both | (none recorded) | (none recorded) | (none recorded) | Targum Jehonathan, Original Manuscript Archival Texts, Palestinian Targum (Genizah), Samaritan | Late Jewish Literary Aramaic |
Regardless of how it is written, /ś/ in spoken Aramaic seems to have universally resolved to /s/.

