
Short chain fatty acid
Encyclopedia
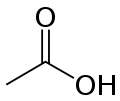
- Acetic acidAcetic acidAcetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
- Propionic acidPropionic acidPropanoic acid is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2COOH. It is a clear liquid with a pungent odor...
- Isobutyric acidIsobutyric acidIsobutyric acid, also known as 2-methylpropanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with structural formula 2-CH-COOH. It is found in the free state in carobs and in the root of Arnica dulcis, and as an ethyl ester in croton oil....
(2-methylpropanoic acid) - Butyric acidButyric acidButyric acid , also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates...
- Isovaleric acid (3-methylbutanoic acid)
- Valeric acidValeric acidValeric acid, or pentanoic acid, is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C5H10O2. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has a very unpleasant odor. It is found naturally in the perennial flowering plant valerian , from which it gets its name. Its...
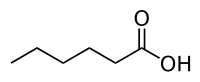
(pentanoic acid) - Caproic acid (hexanoic acid)
Short-chain fatty acids, just as medium chain fatty acids, are taken up directly to the portal vein during lipid digestion, in contrast to long-chain fatty acids, which are packed into chylomicrons and enter lymphatic capillaries
Lymph capillary
Lymph capillaries or lymphatic capillaries are tiny thin-walled vessels that are closed at one end and are located in the spaces between cells throughout the body, except in the central nervous system, and in non-vascular tissues. The main purpose of these vessels is to drain excess tissue fluids...
and enter the blood first at the subclavian vein
Subclavian vein
The subclavian veins are two large veins, one on either side of the body. Their diameter is approximately that of the smallest finger.-Path:Each subclavian vein is a continuation of the axillary vein and runs from the outer border of the first rib to the medial border of anterior scalene muscle...
.
Short-chain fatty acids are produced when dietary fiber
Dietary fiber
Dietary fiber, dietary fibre, or sometimes roughage is the indigestible portion of plant foods having two main components:* soluble fiber that is readily fermented in the colon into gases and physiologically active byproducts, and* insoluble fiber that is metabolically inert, absorbing water as it...
is fermented in the colon
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
.

