
Sidereus Nuncius
Encyclopedia
New Latin
The term New Latin, or Neo-Latin, is used to describe the Latin language used in original works created between c. 1500 and c. 1900. Among other uses, Latin during this period was employed in scholarly and scientific publications...
by Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei
Galileo Galilei , was an Italian physicist, mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher who played a major role in the Scientific Revolution. His achievements include improvements to the telescope and consequent astronomical observations and support for Copernicanism...
in March 1610. It was the first scientific treatise based on observations made through a telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
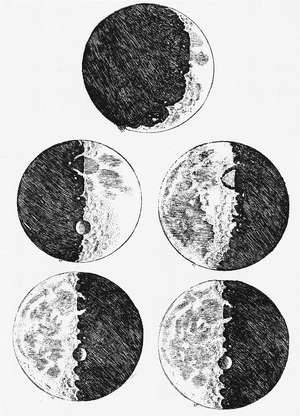
. It contains the results of Galileo's early observations of the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
, the star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s, and the moons of Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
.
Galileo improved the construction of a telescope, which he used to observe the night sky and the moon. In his observations of the Moon, Galileo observed that the line separating lunar day from night (the terminator) was smooth where it crossed the darker regions of the moon, but quite irregular where it crossed the brighter areas. From this observation, he deduced that the darker regions are flat, low-lying areas, while the brighter regions are rough and covered with mountains. Based on the distance of sunlit mountaintops from the terminator, he estimated that the lunar mountains were at least 4 miles in height. This contradicted Aristotelean
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
cosmology, which held that since the heavens were more perfect than the earth, the heavenly bodies must be perfectly smooth spheres.
In observing the stars, Galileo reported that he saw at least ten times as many stars through the telescope as with the naked eye, and he published star charts of the belt of Orion
Orion (constellation)
Orion, often referred to as The Hunter, is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous, and most recognizable constellations in the night sky...
and the Pleiades
Pleiades (star cluster)
In astronomy, the Pleiades, or Seven Sisters , is an open star cluster containing middle-aged hot B-type stars located in the constellation of Taurus. It is among the nearest star clusters to Earth and is the cluster most obvious to the naked eye in the night sky...
showing some of the newly observed stars. Also, when he observed some of the "nebulous" stars in the Ptolemaic
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
star catalogue, he saw that rather than being cloudy, they were made of many small stars. From this, he deduced that the nebulae, and the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
itself, were collections of stars too small and far away to be resolved into individual stars by the naked eye.
In the last portion of Sidereus Nuncius, Galileo reported his discovery of four objects that appeared to form a straight line of stars near Jupiter. He gave illustrations of the relative positions of Jupiter and its moons as they appeared nightly from late January through early March 1610. From the fact that they changed their relative positions from night to night, but always appeared in the same straight line near Jupiter, he deduced that they were four bodies in orbit around Jupiter.
At the time of its publication, Galileo was a mathematician at the university of Padua
Padua
Padua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
, and had recently received a lifetime contract for his work in building more powerful telescopes. He desired to return to Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
, and in hopes of gaining patronage there, he dedicated Sidereus Nuncius to Cosimo II de' Medici, fourth Grand Duke of Tuscany, and he named the four moons of Jupiter he had discovered the "Medicean stars". Since then, his effort at naming the moons has failed, for they are now referred to as the "Galilean moons
Galilean moons
The Galilean moons are the four moons of Jupiter discovered by Galileo Galilei in January 1610. They are the largest of the many moons of Jupiter and derive their names from the lovers of Zeus: Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. Ganymede, Europa and Io participate in a 1:2:4 orbital resonance...
".
Albert Van Helden, professor of history at Rice University
Rice University
William Marsh Rice University, commonly referred to as Rice University or Rice, is a private research university located on a heavily wooded campus in Houston, Texas, United States...
, published an English translation of the Sidereus Nuncius in 1989 (ISBN 978-0226279039). A copy of the original edition is a valuable rare book and can reach £180,000 as of 2010.
External links
- Sidereus Nuncius 1610. From Rare Book RoomRare Book RoomRare Book Room is an educational website for the repository of digitally scanned rare books made freely available to the public.Starting around 1996 the California based company Octavo began scanning rare and important books from libraries around the world. These scans were done at extremely high...
. Photographed first edition. - Sidereus Nuncius, in Latin, HTML format. From LiberLiber.
- Linda Hall Library has a scanned first edition, as well as a scanned pirated edition from Frankfurt, also from 1610.

