
Siemens (unit)
Encyclopedia
The siemens is the SI
derived unit
of electric conductance and electric admittance
. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance
and impedance
respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm
, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term siemens is used both for the singular and plural. The 14th General Conference on Weights and Measures
approved the addition of the siemens as an SI derived unit
in 1971.
R, the conductance G is defined as

where I is the electric current through the object and V is the voltage
(electrical potential difference) across the object.
The unit siemens for the conductance G is defined by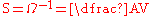
where Ω is the ohm
, A is the ampere
, and V is the volt
.
For a device with a conductance of one siemens, the electric current through the device will increase by one ampere for every increase of one volt of electric potential difference across the device.
Example: The conductance of a resistor with resistance six ohms is G = 1/(6 Ω) ≈ 0.167 S ≈ 167 mS.
.
backwards and is written with an upside-down capital Greek
letter Omega: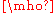 , Unicode symbol U+2127 . According to Maver the term mho was suggested by Sir William Thomson. The mho was officially renamed to the siemens, replacing the old meaning of the unit siemens, at a conference in 1881.
, Unicode symbol U+2127 . According to Maver the term mho was suggested by Sir William Thomson. The mho was officially renamed to the siemens, replacing the old meaning of the unit siemens, at a conference in 1881.
The term siemens, as it is an SI unit, is used universally in science and often in electrical applications, while mho is still used primarily in electronic applications. Two reasons are usually given for using mho instead of siemens in electronic applications:
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
derived unit
SI derived unit
The International System of Units specifies a set of seven base units from which all other units of measurement are formed, by products of the powers of base units. These other units are called SI derived units, for example, the SI derived unit of area is square metre , and of density is...
of electric conductance and electric admittance
Admittance
In electrical engineering, the admittance is a measure of how easily a circuit or device will allow a current to flow. It is defined as the inverse of the impedance . The SI unit of admittance is the siemens...
. Conductance and admittance are the reciprocals of resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
and impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
respectively, hence one siemens is equal to the reciprocal of one ohm
Ohm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
, and is sometimes referred to as the mho. In English, the term siemens is used both for the singular and plural. The 14th General Conference on Weights and Measures
General Conference on Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures is the English name of the Conférence générale des poids et mesures . It is one of the three organizations established to maintain the International System of Units under the terms of the Convention du Mètre of 1875...
approved the addition of the siemens as an SI derived unit
SI derived unit
The International System of Units specifies a set of seven base units from which all other units of measurement are formed, by products of the powers of base units. These other units are called SI derived units, for example, the SI derived unit of area is square metre , and of density is...
in 1971.
Definition
For a conducting or semiconducting element with electrical resistanceElectrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
R, the conductance G is defined as

where I is the electric current through the object and V is the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
(electrical potential difference) across the object.
The unit siemens for the conductance G is defined by

where Ω is the ohm
Ohm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
, A is the ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
, and V is the volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
.
For a device with a conductance of one siemens, the electric current through the device will increase by one ampere for every increase of one volt of electric potential difference across the device.
Example: The conductance of a resistor with resistance six ohms is G = 1/(6 Ω) ≈ 0.167 S ≈ 167 mS.
Historical/Deprecated
Since 1860 to the middle of 20th century, siemens or siemens mercury unit, was the unit of electrical resistance. It was defined as the resistance of a mercury column 1 meter long and uniform 1 mm2 cross sectional area at 0 degrees Celsius. It was equivalent to 0.953 ohm approximately. Officially, it ceased usage after 1881, but was widely used in telegraph and telephone services until World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
.
Mho
Mho is an alternate, non-SI unit of conductivity which is equivalent to 1 siemens. Mho is derived from spelling ohmOhm
The ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.- Definition :The ohm is defined as a resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1 ampere,...
backwards and is written with an upside-down capital Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
letter Omega:
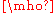 , Unicode symbol U+2127 . According to Maver the term mho was suggested by Sir William Thomson. The mho was officially renamed to the siemens, replacing the old meaning of the unit siemens, at a conference in 1881.
, Unicode symbol U+2127 . According to Maver the term mho was suggested by Sir William Thomson. The mho was officially renamed to the siemens, replacing the old meaning of the unit siemens, at a conference in 1881.The term siemens, as it is an SI unit, is used universally in science and often in electrical applications, while mho is still used primarily in electronic applications. Two reasons are usually given for using mho instead of siemens in electronic applications:
- The inverted Omega and the mho, while not an official SI abbreviation, has the advantage of being less likely to be confused with a variable than the letter S when doing algebraic calculations by hand, where the usual typographical distinctions (such as italic for variables and Roman for unit names) are difficult to maintain. Likewise, it is difficult to distinguish the symbol S from the lower case s where second is meant, potentially causing confusion.
- The term siemens could be confused with the large multinational electronics company SiemensSiemensSiemens may refer toSiemens, a German family name carried by generations of telecommunications industrialists, including:* Werner von Siemens , inventor, founder of Siemens AG...
.

