
Sigma Octantis
Encyclopedia
Sigma Octantis is a magnitude
5.6 star in the constellation Octans
most notable for being the current South Star. Sigma Octantis is approximately 270 light years from Earth, and is classified as a giant
, with a spectral type of F0 III. It is a Delta Scuti variable
, with magnitude varying by about 0.03 magnitudes over 2.3 hours.
Sigma Octantis is the dimmest star to be represented on a national flag. It appears on the flag of Brazil
, symbolising the Brazilian Federal District
.
Its position near the southern celestial pole makes it the southern hemisphere
's pole star
, whence its occasional name, Polaris Australis.
, the current North Star. To an observer in the southern hemisphere, Sigma Octantis appears almost motionless and all the other stars in the Southern sky appear to rotate around it. It is part of a small "half hexagon" shape. It is over a degree away from the true south pole, and the south celestial pole is moving away from it due to precession of the equinoxes
.
 At magnitude 5.5, Sigma Octantis is barely visible to the naked eye, making it a rather poor pole star, especially by comparison with the much brighter and more easily visible Polaris
At magnitude 5.5, Sigma Octantis is barely visible to the naked eye, making it a rather poor pole star, especially by comparison with the much brighter and more easily visible Polaris
. Because of this, the Crux
constellation is often preferred for determining the position of the South Celestial Pole.
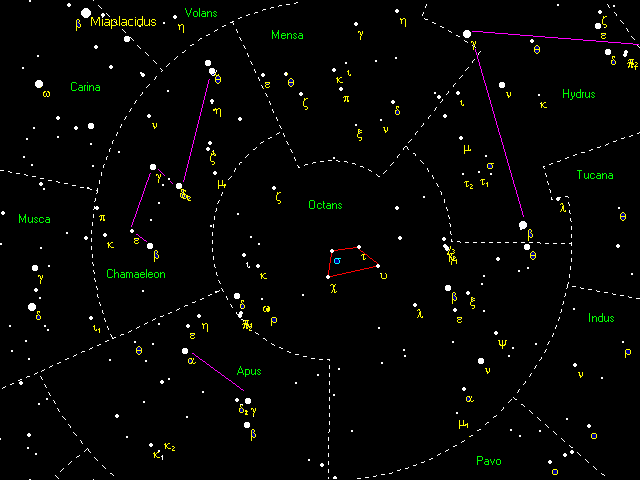
Once Sigma Octantis' approximate position has been determined, either by the major stars in Octans or using the Southern Cross method, it can be positively verified using an asterism
. Sigma, Chi, Tau and Upsilon Octantis are all stars of around magnitude 5.5, and form the distinctive shape of a trapezoid
.
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
5.6 star in the constellation Octans
Octans
Octans is a faint constellation the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the eighth part of a circle, but it is named after the octant, a navigational instrument. The constellation was devised by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in the eighteenth century....
most notable for being the current South Star. Sigma Octantis is approximately 270 light years from Earth, and is classified as a giant
Giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main sequence star of the same surface temperature. Typically, giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 solar radii and luminosities between 10 and 1,000 times that of the Sun. Stars still more luminous than giants are...
, with a spectral type of F0 III. It is a Delta Scuti variable
Delta Scuti variable
A Delta Scuti variable is a variable star which exhibits variations in its luminosity due to both radial and non-radial pulsations of the star's surface. Typical brightness fluctuations are from 0.003 to 0.9 magnitudes in V over a period of a few hours, although the amplitude and period of the...
, with magnitude varying by about 0.03 magnitudes over 2.3 hours.
Sigma Octantis is the dimmest star to be represented on a national flag. It appears on the flag of Brazil
Flag of Brazil
The national flag of Brazil is a blue disc depicting a starry sky spanned by a curved band inscribed with the national motto, within a yellow rhombus, on a green field. Brazil officially adopted this design for its national flag on November 19, 1889, replacing the flag of the second Empire of Brazil...
, symbolising the Brazilian Federal District
Brazilian Federal District
The Federal District is set apart for Brasília, the capital of Brazil. Located in a region called Planalto Central, or Central Plateau, the Federal District is divided in 29 administrative regions. Brasilia - place where the three branches of the Federal Government are located - is the main...
.
Its position near the southern celestial pole makes it the southern hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
's pole star
Pole star
The term "Pole Star" usually refers to Polaris, which is the current northern pole star, also known as the North Star.In general, however, a pole star is a visible star, especially a prominent one, that is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation; that is, a star whose apparent...
, whence its occasional name, Polaris Australis.
Southern pole star
Sigma Octantis is the southern pole star, whose counterpart to PolarisPolaris
Polaris |Alpha]] Ursae Minoris, commonly North Star or Pole Star, also Lodestar) is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is very close to the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star....
, the current North Star. To an observer in the southern hemisphere, Sigma Octantis appears almost motionless and all the other stars in the Southern sky appear to rotate around it. It is part of a small "half hexagon" shape. It is over a degree away from the true south pole, and the south celestial pole is moving away from it due to precession of the equinoxes
Precession of the equinoxes
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In particular, it refers to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation, which, like a wobbling top, traces out a pair of cones joined...
.
Locating Sigma Octantis

Polaris
Polaris |Alpha]] Ursae Minoris, commonly North Star or Pole Star, also Lodestar) is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor. It is very close to the north celestial pole, making it the current northern pole star....
. Because of this, the Crux
Crux
Crux is the smallest of the 88 modern constellations, but is one of the most distinctive. Its name is Latin for cross, and it is dominated by a cross-shaped asterism that is commonly known as the Southern Cross.-Visibility:...
constellation is often preferred for determining the position of the South Celestial Pole.
Once Sigma Octantis' approximate position has been determined, either by the major stars in Octans or using the Southern Cross method, it can be positively verified using an asterism
Asterism (astronomy)
In astronomy, an asterism is a pattern of stars recognized on Earth's night sky. It may form part of an official constellation, or be composed of stars from more than one. Like constellations, asterisms are in most cases composed of stars which, while they are visible in the same general direction,...
. Sigma, Chi, Tau and Upsilon Octantis are all stars of around magnitude 5.5, and form the distinctive shape of a trapezoid
Trapezoid
In Euclidean geometry, a convex quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides is referred to as a trapezoid in American English and as a trapezium in English outside North America. A trapezoid with vertices ABCD is denoted...
.

