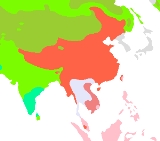
Sino-Tibetan languages
Overview
Language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term 'family' comes from the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a...
comprising, at least, the Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
and the Tibeto-Burman languages
Tibeto-Burman languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Chinese members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken thoughout the highlands of southeast Asia, as well as lowland areas in Burma ....
, including some 250 languages of East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
and parts of South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
. They are second only to the Indo-European languages
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
in terms of the number of native speakers. The internal classification of the family is debated.
In 1823, Julius Klaproth
Julius Klaproth
Julius Heinrich Klaproth , German linguist, historian, ethnographer, author, Orientalist and explorer. As a scholar, he is credited along with Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat, with being instrumental in turning East Asian Studies into scientific disciplines with critical methods.-Chronology:Klaproth was...
suggested a modern-looking classification, nothing similar to which would be proposed again for over a century.
Unanswered Questions

