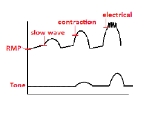
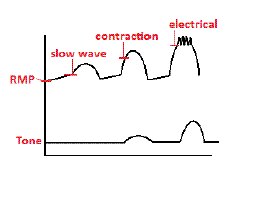
Slow wave threshold
Encyclopedia
In physiology
, the slow-wave threshold is the potential which must be reached before a slow wave can be propagated in smooth muscle
. Slow waves cause no smooth muscle contraction.
and Substance P
) and inhibitory (vasoactive intestinal peptide
and nitric oxide
) compounds.
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, the slow-wave threshold is the potential which must be reached before a slow wave can be propagated in smooth muscle
Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two sub-groups; the single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit smooth muscle tissues, the autonomic nervous system innervates a single cell within a sheet or bundle and the action potential is propagated by...
. Slow waves cause no smooth muscle contraction.

Gastrointestinal smooth muscle
In gastrointestinal smooth muscle, the slow-wave threshold can be altered by input from endogenous and exogenous innervation, as well as excitatory (acetylcholineAcetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
and Substance P
Substance P
In the field of neuroscience, substance P is a neuropeptide: an undecapeptide that functions as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. It belongs to the tachykinin neuropeptide family. Substance P and its closely related neuropeptide neurokinin A are produced from a polyprotein precursor...
) and inhibitory (vasoactive intestinal peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide also known as the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP is a peptide hormone containing 29 amino acid residues that is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain...
and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
) compounds.

