Software house
Encyclopedia
A software house is a company whose primary products are software.
All of these may be categorized in one or many of the following :
s found by the testers.
A professional software house normally consists of at least three dedicated sub-teams :
In bigger software houses, greater specialization is employed, and quite often there are also:
The cons:
The pros:
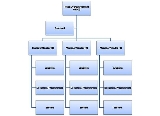
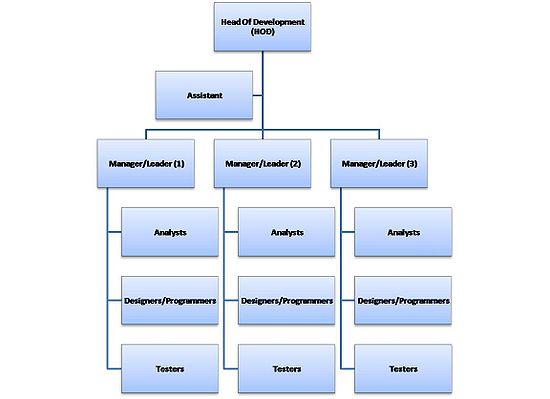 All the teams are fully independent and they work separately on the different projects. The structure is quite simple and all the employees reports to one person, what make the situation quite clear however it is not a good solution in terms of knowledge exchange and optimal usage of human resources.
All the teams are fully independent and they work separately on the different projects. The structure is quite simple and all the employees reports to one person, what make the situation quite clear however it is not a good solution in terms of knowledge exchange and optimal usage of human resources.
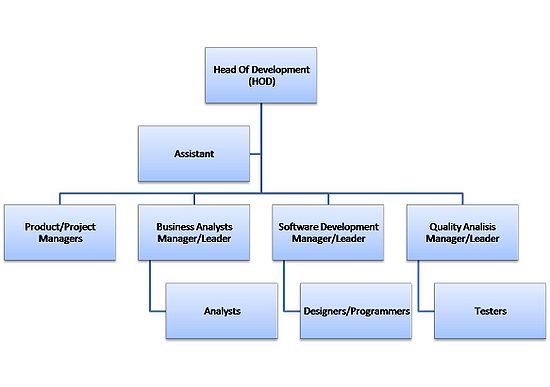 In this model there are dedicated managers/leaders for each main specialization, "renting" their people for particular projects led by product/project managers, who formally or informally buy the people and pay for their time. This leads to each private employee having two bosses – the product/project manager and the specialized "resource" manager. On one hand it optimizes the usage of human resources, on the other hand it may give rise to conflicts about which one manager has priority in the structure.
In this model there are dedicated managers/leaders for each main specialization, "renting" their people for particular projects led by product/project managers, who formally or informally buy the people and pay for their time. This leads to each private employee having two bosses – the product/project manager and the specialized "resource" manager. On one hand it optimizes the usage of human resources, on the other hand it may give rise to conflicts about which one manager has priority in the structure.
There are also a number of variants of these structures, and a number of organizations have this structure spread and split within various departments and units.
There are also some methodologies which combine both, such as the spiral model
, RUP or MSF
.
Each stage ideally takes 30% of the total time, with the remaining 10% in reserve.
The UML
sequence diagram
of interaction between these groups may look like:
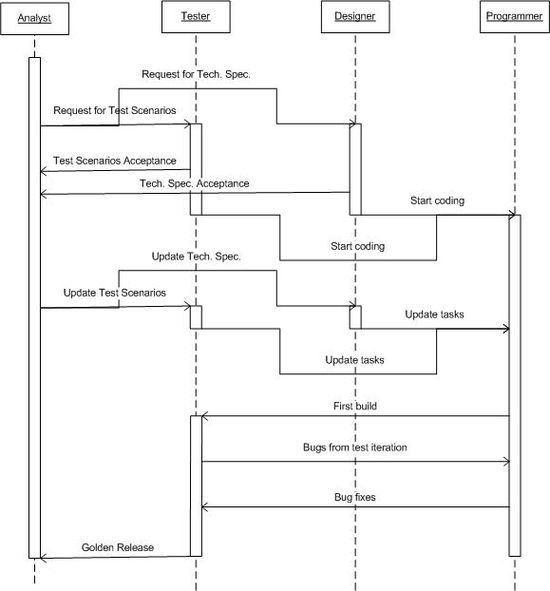 At each stage a different group plays a key role, however each type of role must be involved throughout the whole development process:
At each stage a different group plays a key role, however each type of role must be involved throughout the whole development process:
There are also Application Lifecycle Management
(ALM), which embed some of these functionalities in one package and are used across the groups. They are delivered from various vendors like Borland
, ECM or Compuware
.
A number of organizations are focused on reaching the optimum level of the Capability Maturity Model
(CMM), where "optimum" does not necessarily mean the highest. There are also other systems such as Carnegie-Mellon University's SEMA, or particular ISO
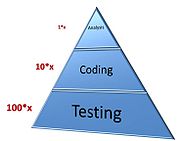
standards. Small software houses will sometimes use less formalized approaches, such as the Joel Test : 12 steps to better code. Each organization works out its own style, which lies somewhere between total technocracy (where all is defined by numbers) and total anarchy (where there are no numbers at all). Whichever way the organization goes, they consider the pyramid describing the cost and risk of introducing change to already-begun development processes:
Types
There are a number of different types of software houses:- Large and well-known companies such as MicrosoftMicrosoftMicrosoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
, SAP AGSAP AGSAP AG is a German software corporation that makes enterprise software to manage business operations and customer relations. Headquartered in Walldorf, Baden-Württemberg, with regional offices around the world, SAP is the market leader in enterprise application software...
, Oracle CorporationOracle CorporationOracle Corporation is an American multinational computer technology corporation that specializes in developing and marketing hardware systems and enterprise software products – particularly database management systems...
, HPHewlett-PackardHewlett-Packard Company or HP is an American multinational information technology corporation headquartered in Palo Alto, California, USA that provides products, technologies, softwares, solutions and services to consumers, small- and medium-sized businesses and large enterprises, including...
, Adobe SystemsAdobe SystemsAdobe Systems Incorporated is an American computer software company founded in 1982 and headquartered in San Jose, California, United States...
, Apple Inc. and Red HatRed HatRed Hat, Inc. is an S&P 500 company in the free and open source software sector, and a major Linux distribution vendor. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina with satellite offices worldwide.... - Companies producing specialized Commercial off-the-shelfCommercial off-the-shelfIn the United States, Commercially available Off-The-Shelf is a Federal Acquisition Regulation term defining a nondevelopmental item of supply that is both commercial and sold in substantial quantities in the commercial marketplace, and that can be procured or utilized under government contract...
(COTS) software, such as PanoramaPanoramaA panorama is any wide-angle view or representation of a physical space, whether in painting, drawing, photography, film/video, or a three-dimensional model....
, HyperionHyperion SolutionsHyperion Solutions Corporation was a business performance management software company, located in Santa Clara, California, USA, which was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2007...
, Siebel SystemsSiebel SystemsSiebel CRM Systems, Inc. was a software company principally engaged in the design, development, marketing, and support of customer relationship management applications. The company was founded by Thomas Siebel in 1993. At first known mainly for its sales force automation products, the company...
, GazitIT, Enigma Technologies - Companies producing software componentsThird-party software componentIn computer programming, a third-party software component is a reusable software component developed to be either freely distributed or sold by an entity other than the original vendor of the development platform...
, such as Developer Express, DundasDundas Data Visualization, Inc.Dundas Data Visualization, Inc. formerly known as Dundas Software Ltd is a commercial software development company with headquarters in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. They are mostly known for their Dundas Components product . Currently Dundas Data Visualization produces Data Visualization and Dashboard...
, ComponentOne and Sohn Software - Application Service ProviderApplication service providerAn application service provider is a business that provides computer-based services to customers over a network. Software offered using an ASP model is also sometimes called On-demand software or software as a service ....
s, such as SalesForce - Companies focused on delivering bespoke software solutions for vertical industries or particular geographical regions
All of these may be categorized in one or many of the following :
- contractual - when the software house is contracted to deliver some particular software from outside (software outsourcingOutsourcingOutsourcing is the process of contracting a business function to someone else.-Overview:The term outsourcing is used inconsistently but usually involves the contracting out of a business function - commonly one previously performed in-house - to an external provider...
) - product development - when it produces ready to use, packaged software; Commercial off-the-shelfCommercial off-the-shelfIn the United States, Commercially available Off-The-Shelf is a Federal Acquisition Regulation term defining a nondevelopmental item of supply that is both commercial and sold in substantial quantities in the commercial marketplace, and that can be procured or utilized under government contract...
Common roles in a software house
Organizing a software house is very specialized type of management skill, where experienced persons can turn the organizational problem into a unique benefit. For example, having sub-teams spread in different time zones may allow a 24-hour company working day, if the teams, systems and procedures are well established. A good example is the test team in time zone 8 hours ahead or behind the development team, who fix software bugSoftware bug
A software bug is the common term used to describe an error, flaw, mistake, failure, or fault in a computer program or system that produces an incorrect or unexpected result, or causes it to behave in unintended ways. Most bugs arise from mistakes and errors made by people in either a program's...
s found by the testers.
A professional software house normally consists of at least three dedicated sub-teams :
- business analystBusiness analystA Business Analyst analyzes the organization and design of businesses, government departments, and non-profit organizations; BAs also assess business models and their integration with technology.-Levels:...
s who define the business needs of the market - software designers/programmerProgrammerA programmer, computer programmer or coder is someone who writes computer software. The term computer programmer can refer to a specialist in one area of computer programming or to a generalist who writes code for many kinds of software. One who practices or professes a formal approach to...
s who create the technical specification and write the software - software testers who are responsible for the whole process of quality managementQuality managementThe term Quality management has a specific meaning within many business sectors. This specific definition, which does not aim to assure 'good quality' by the more general definition , can be considered to have four main components: quality planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality...
In bigger software houses, greater specialization is employed, and quite often there are also:
- technical writerTechnical writerA technical writer is a professional writer who designs, creates, and maintains technical documentation...
s who write all the documentationSoftware documentationSoftware documentation or source code documentation is written text that accompanies computer software. It either explains how it operates or how to use it, and may mean different things to people in different roles....
such as user guideUser guideA user guide or user's guide, also commonly known as a manual, is a technical communication document intended to give assistance to people using a particular system...
s - release specialists who are responsible for building the whole product and software versioning
- graphic designerGraphic designerA graphic designer is a professional within the graphic design and graphic arts industry who assembles together images, typography or motion graphics to create a piece of design. A graphic designer creates the graphics primarily for published, printed or electronic media, such as brochures and...
s who are particularly important in the gaming industry and elsewhere. They are normally responsible for the design of the graphical user interfaceGraphical user interfaceIn computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
. - maintenance engineers who are behind two, three or more lines of support
- consultants responsible for making the solution operational, especially if some specialist knowledge is necessary. Examples of this include: building multidimensional cubes in business intelligence software, integrating with existing solutions, and implementing business scenarios in Business Process ManagementBusiness process managementBusiness process management is a holistic management approach focused on aligning all aspects of an organization with the wants and needs of clients. It promotes business effectiveness and efficiency while striving for innovation, flexibility, and integration with technology. BPM attempts to...
software.
The cons:
- people are not focused so much on the specialization
- each person must be very flexible and have the ability to play each role (not each person is willing to do that)
- the approach is possible just for smaller, less formalized organizations
The pros:
- each person has full knowledge about the full production cycle
- people are doing various tasks what makes especially young people excited about their work
- there is a very good possibility to manage the work load especially in crisis situations like "all hands on pump"
Structure
The manager of a software house is usually called the Head Of Development (HOD), and reports to the stakeholders. He or she leads the sub-teams directly or via the managers/leaders depending on the size of the organization. Usually teams of up to 10 person are the most operational. In bigger organizations, there are in general two models of the hierarchy:

There are also a number of variants of these structures, and a number of organizations have this structure spread and split within various departments and units.
Methodologies
Software house may use a number of various methodologies to produce the code. These can include:- the waterfall modelWaterfall modelThe waterfall model is a sequential design process, often used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through the phases of Conception, Initiation, Analysis, Design, Construction, Testing, Production/Implementation and Maintenance.The waterfall...
, including project management methodologies like PRINCE2PRINCE2PRojects IN Controlled Environments 2 is a structured project management method endorsed by the UK government as the project management standard for public projects. The methodology encompasses the management, control and organisation of a project...
or PMBoK - agile software developmentAgile software developmentAgile software development is a group of software development methodologies based on iterative and incremental development, where requirements and solutions evolve through collaboration between self-organizing, cross-functional teams...
, such as Extreme ProgrammingExtreme ProgrammingExtreme programming is a software development methodology which is intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements...
and SCRUMScrumScrum can refer to:* Scrum , a rugby restart after an interruption* Media scrum , similar to a rugby scrum, occurs when public figures, such as politicians, are surrounded by a group of journalists and are asked questions in an impromptu or loosely organized manner* Scrum , an agile software...
There are also some methodologies which combine both, such as the spiral model
Spiral model
The spiral model is a software development process combining elements of both design and prototyping-in-stages, in an effort to combine advantages of top-down and bottom-up concepts. Also known as the spiral lifecycle model , it is a systems development method used in information technology...
, RUP or MSF
MSF
MSF may refer to:* Mail Summary File , file extension used by Earthlink, Mozilla Thunderbird, and Netscape mail clients to store folder data in Mork.* Marvel Super Heroes vs...
.
Product life cycle
Regardless of the methodology used, the product life cycle always consists of at least three stages:- Design – including both the business and technical specification
- Coding – the development itself
- Testing – the quality management
Each stage ideally takes 30% of the total time, with the remaining 10% in reserve.
The UML
Unified Modeling Language
Unified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
sequence diagram
Sequence diagram
A sequence diagram in Unified Modeling Language is a kind of interaction diagram that shows how processes operate with one another and in what order. It is a construct of a Message Sequence Chart....
of interaction between these groups may look like:

- Analysts, after completing the business specification, manage the changing business situation to minimize the possibility of change over time. They also support both programmers and testers during the whole development process to ensure that the final product fulfills the business needs specified at the start. The process ideally puts business analysts as the key players during final delivery of the solution to the customer, as they are best placed to provide the best business layer.
- Programmers do the technical specification during the design phase, which is why they are called programmers/designers, and during testing time they fix bugs.
- Testers complete the test scenarios during the design phase, and evaluate them during the coding phase
Systems and procedures
Well-run software houses possess various systems and procedures implemented and working internally across all the sub-teams. These include:Business Analysts
- Modeling tools like Sparx Enterprise ArchitectEnterprise Architect (Visual Modeling Platform)Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a visual modeling and design tool based on the OMG UML. The platform supports: the design and construction of software systems; modeling business processes; and modeling industry based domains...
or IBMIBMInternational Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
Rational Rose
Programmers
- Version Control Systems and software versioning procedures
- Code analysis tools and coding standards, validated manually or automatically
- Deployment mechanisms
Testers
- Bug tracking systemBug tracking systemA bug tracking system is a software application that is designed to help quality assurance and programmers keep track of reported software bugs in their work. It may be regarded as a type of issue tracking system....
s - Test automationTest automationTest automation is the use of software to control the execution of tests, the comparison of actual outcomes to predicted outcomes, the setting up of test preconditions, and other test control and test reporting functions...
tools - Performance and stress test tools
Project/Product managers
- Enterprise Project ManagementEnterprise Project ManagementEnterprise Project Management , in broad terms, is the field of organizational development that supports organizations in managing integrally and adapting themselves to the changes of a transformation....
(EPM) systems and procedures - Product Portfolio Management (PPM)
- Change management systems and procedures
There are also Application Lifecycle Management
Application Lifecycle Management
Application Lifecycle Management is a continuous process of managing the life of an application through governance, development and maintenance...
(ALM), which embed some of these functionalities in one package and are used across the groups. They are delivered from various vendors like Borland
Borland
Borland Software Corporation is a software company first headquartered in Scotts Valley, California, Cupertino, California and finally Austin, Texas. It is now a Micro Focus subsidiary. It was founded in 1983 by Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, Mogens Glad and Philippe Kahn.-The 1980s:...
, ECM or Compuware
Compuware
Compuware Corporation is a software company with products aimed at the information technology departments of large businesses. The company's services also include testing, development, professional services automation, project and portfolio management, cloud-based collaboration and performance...
.
Efficiency audits
Well-established software houses typically have some way of measuring their own efficiency. This is usually done by defining the set of key performance indicators (KPI), such as- The average number of bugs done by the developer per unit of time or source lines of codeSource lines of codeSource lines of code is a software metric used to measure the size of a software program by counting the number of lines in the text of the program's source code...
- The number of bugs found by tester per test cycle
- The average number of test cycles until Zero Bug Bounce (ZBB)
- The average time of test cycle
- Estimated time of task comparing to the real time of the task (exactitude of planning)
- Number of corrections to the baseline
A number of organizations are focused on reaching the optimum level of the Capability Maturity Model
Capability Maturity Model
The Capability Maturity Model is a development model that was created after study of data collected from organizations that contracted with the U.S. Department of Defense, who funded the research. This model became the foundation from which CMU created the Software Engineering Institute...
(CMM), where "optimum" does not necessarily mean the highest. There are also other systems such as Carnegie-Mellon University's SEMA, or particular ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
standards. Small software houses will sometimes use less formalized approaches, such as the Joel Test : 12 steps to better code. Each organization works out its own style, which lies somewhere between total technocracy (where all is defined by numbers) and total anarchy (where there are no numbers at all). Whichever way the organization goes, they consider the pyramid describing the cost and risk of introducing change to already-begun development processes:


