
Sol-air temperature
Encyclopedia
Sol-air temperature is a variable used to calculate cooling load of a building and determine the total heat gain through exterior surfaces. It is an improvement over
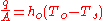
where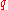 = rate of heat transfer [W]
= rate of heat transfer [W]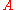 = heat transfer surface area [m²]
= heat transfer surface area [m²]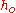 = heat transfer coefficient for radiation (long wave) and convection [W/m²K]
= heat transfer coefficient for radiation (long wave) and convection [W/m²K]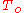 = outdoor surroundings' temperature [°C]
= outdoor surroundings' temperature [°C]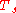 = outside surface temperature [°C]
= outside surface temperature [°C]
This equation only takes into account the temperature differences thus, ignoring solar radiative flux and infrared exchanges from the sky. The Tsol-air was then introduced to accommodate these two parameters.
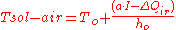
where = solar radiation absortivity of a surface [-]
= solar radiation absortivity of a surface [-]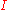 = global solar irradiance [W/m²]
= global solar irradiance [W/m²]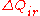 = extra infrared radiation due to difference between the external air temperature and the apparent sky temperature. =
= extra infrared radiation due to difference between the external air temperature and the apparent sky temperature. = 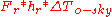 [W/m²]
[W/m²]
and is to be used in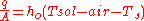
An equivalent, and more useful equation for the net heat loss across the whole construction is:
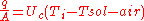
where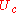 = construction U-value, according to ISO 6946 [W/m²K].
= construction U-value, according to ISO 6946 [W/m²K].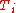 = indoor temperature [°C]
= indoor temperature [°C]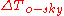 = difference between outside dry-bulb air temperature and sky mean radiant temperature [°C]
= difference between outside dry-bulb air temperature and sky mean radiant temperature [°C]
Expanding the above equation by substituting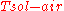 gives the following heat loss equation:
gives the following heat loss equation:
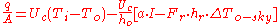
The above equation is used for opaque facades in , and renders intermediate calculation of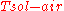 unnecessary. The main advantage of this latter approach is that it avoids the need for a different outdoor temperature node for each facade. Thus, the solution scheme is kept simple, and the solar and sky radiation terms from all facades can be aggregated and distributed to internal temperature nodes as gains/losses.
unnecessary. The main advantage of this latter approach is that it avoids the need for a different outdoor temperature node for each facade. Thus, the solution scheme is kept simple, and the solar and sky radiation terms from all facades can be aggregated and distributed to internal temperature nodes as gains/losses.
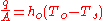
where
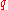 = rate of heat transfer [W]
= rate of heat transfer [W] = heat transfer surface area [m²]
= heat transfer surface area [m²]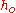 = heat transfer coefficient for radiation (long wave) and convection [W/m²K]
= heat transfer coefficient for radiation (long wave) and convection [W/m²K]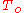 = outdoor surroundings' temperature [°C]
= outdoor surroundings' temperature [°C]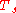 = outside surface temperature [°C]
= outside surface temperature [°C]This equation only takes into account the temperature differences thus, ignoring solar radiative flux and infrared exchanges from the sky. The Tsol-air was then introduced to accommodate these two parameters.
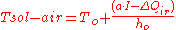
where
 = solar radiation absortivity of a surface [-]
= solar radiation absortivity of a surface [-]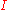 = global solar irradiance [W/m²]
= global solar irradiance [W/m²] = extra infrared radiation due to difference between the external air temperature and the apparent sky temperature. =
= extra infrared radiation due to difference between the external air temperature and the apparent sky temperature. = 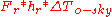 [W/m²]
[W/m²]and is to be used in
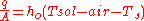
An equivalent, and more useful equation for the net heat loss across the whole construction is:
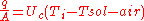
where
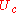 = construction U-value, according to ISO 6946 [W/m²K].
= construction U-value, according to ISO 6946 [W/m²K].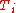 = indoor temperature [°C]
= indoor temperature [°C] = difference between outside dry-bulb air temperature and sky mean radiant temperature [°C]
= difference between outside dry-bulb air temperature and sky mean radiant temperature [°C]Expanding the above equation by substituting
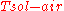 gives the following heat loss equation:
gives the following heat loss equation: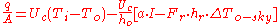
The above equation is used for opaque facades in , and renders intermediate calculation of
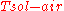 unnecessary. The main advantage of this latter approach is that it avoids the need for a different outdoor temperature node for each facade. Thus, the solution scheme is kept simple, and the solar and sky radiation terms from all facades can be aggregated and distributed to internal temperature nodes as gains/losses.
unnecessary. The main advantage of this latter approach is that it avoids the need for a different outdoor temperature node for each facade. Thus, the solution scheme is kept simple, and the solar and sky radiation terms from all facades can be aggregated and distributed to internal temperature nodes as gains/losses.

