Solar chimney
Encyclopedia
A solar chimney — often referred to as a thermal chimney — is a way of improving the natural ventilation
of building
s by using convection
of air heated by passive solar energy
. A simple description of a solar chimney is that of a vertical shaft utilizing solar energy to enhance the natural stack ventilation through a building.
The solar
chimney
has been in use for centuries, particularly in the Middle east
and Near East
by the Persians
, as well as in Europe
by the Romans
.
. During the day solar energy heats the chimney and the air within it, creating an updraft of air in the chimney. The suction
created at the chimney's base can be used to ventilate and cool the building below. In most parts of the world it is easier to harness wind power
for such ventilation as is done with a Badgir (بادگیر)
, but on hot windless days a Solar chimney can provide ventilation where otherwise there would be none.
There are however a number of solar chimney variations. The basic design elements of a solar chimney are:
A principle
has been proposed for solar power
generation, using a large greenhouse
at the base rather than relying solely on heating the chimney itself. (For further information on this issue, see Solar updraft tower
.)
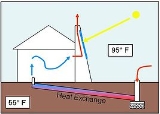
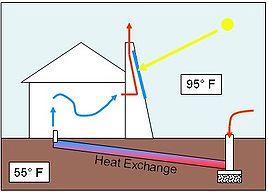
Solar chimneys are painted black so that they absorb the sun's heat more easily and efficiently. When the air inside the chimney is heated, it rises and pulls cold air out from under the ground via the heat exchange tubes.
 Air conditioning and mechanical ventilation have been for decades the standard method of environmental control in many building types, especially offices, in developed countries. Pollution and reallocating energy supplies have led to a new environmental approach in building design. Innovative technologies along with bioclimatic principles and traditional design strategies are often combined to create new and potentially successful design solutions. The solar chimney is one of these concepts currently explored by scientists as well as designers, mostly through research and experimentation.
Air conditioning and mechanical ventilation have been for decades the standard method of environmental control in many building types, especially offices, in developed countries. Pollution and reallocating energy supplies have led to a new environmental approach in building design. Innovative technologies along with bioclimatic principles and traditional design strategies are often combined to create new and potentially successful design solutions. The solar chimney is one of these concepts currently explored by scientists as well as designers, mostly through research and experimentation.
A Solar chimney can serve many purposes. Direct gain warms air inside the chimney causing it to rise out the top and drawing air in from the bottom. This drawing of air can be used to ventilate a home or office, to draw air through a geothermal heat exchange, or to ventilate only a specific area such as a composting toilet.
Natural ventilation can be created by providing vents in the upper level of a building to allow warm air to rise by convection
and escape to the outside. At the same time cooler air can be drawn in through vents at the lower level. Trees may be planted on that side of the building to provide shade for cooler outside air.
This natural ventilation process can be augmented by a solar chimney. The chimney has to be higher than the roof level, and has to be constructed on the wall facing the direction of the sun. Absorption of heat from the sun can be increased by using a glazed surface on the side facing the sun. Heat absorbing material can be used on the opposing side. The size of the heat-absorbing surface is more important than the diameter of the chimney. A large surface area allows for more effective heat exchange with the air necessary for heating by solar radiation. Heating of the air within the chimney will enhance convection, and hence airflow through the chimney. Openings of the vents in the chimney should face away from the direction of the prevailing wind.
To further maximize the cooling effect, the incoming air may be led through underground ducts
before it is allowed to enter the building. The solar chimney can be improved by integrating it with a trombe wall
. The added advantage of this design is that the system may be reversed during the cold season, providing solar heating instead.
A variation of the solar chimney concept is the solar attic
. In a hot sunny climate the attic space is often blazingly hot in the summer. In a conventional building this presents a problem as it leads to the need for increased air conditioning
. By integrating the attic space with a solar chimney, the hot air in the attic can be put to work. It can help the convection in the chimney, improving ventilation.
The use of a solar chimney may benefit natural ventilation and passive cooling strategies of buildings thus help reduce energy use, CO2 emissions and pollution in general. Potential benefits regarding natural ventilation and use of solar chimneys are:
Potential benefits regarding passive cooling may include:
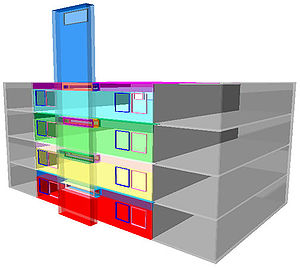
Designed by architects Feilden Clegg Bradley, the BRE offices aim to reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions by 30% from current best practice guidelines and sustain comfortable environmental conditions without the use of air conditioning. The passive ventilation stacks, solar shading, and hollow concrete slabs with embedded under floor cooling are key features of this building. Ventilation and heating systems are controlled by the building management system (BMS) while a degree of user override is provided to adjust conditions to occupants' needs.
The building utilizes five vertical shafts as an integral part of the ventilation and cooling strategy. The main components of theses stacks are a south facing glass-block wall, thermal mass walls and stainless steel round exhausts rising a few meters above roof level. The chimneys are connected to the curved hollow concrete floor slabs which are cooled via night ventilation. Pipes embedded in the floor can provide additional cooling utilizing groundwater.
On warm windy days air is drawn in through passages in the curved hollow concrete floor slabs. Stack ventilation naturally rising out through the stainless steel chimneys enhances the air flow through the building. The movement of air across the chimney tops enhances the stack effect.
During warm, still days, the building relies mostly on the stack effect while air is taken from the shady north side of the building. Low-energy fans in the tops of the stacks can also be used to improve airflow.
Overnight, control systems enable ventilation paths through the hollow concrete slab removing the heat stored during the day and storing coolth for the following day. The exposed curved ceiling gives more surface area than a flat ceiling would, acting as a cool ‘radiator’, again providing summer cooling.
Research based on actual performance measurements of the passive stacks found that they enhanced the cooling ventilation of the space during warm and still days and may also have the potential to assist night-time cooling due to their thermally massive structure.
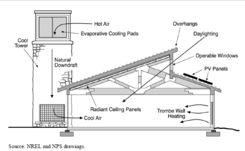 A technology closely related to the solar chimney is the evaporative down-draft cooltower. In areas with a hot, arid climate this approach may contribute to a sustainable way to provide air conditioning
A technology closely related to the solar chimney is the evaporative down-draft cooltower. In areas with a hot, arid climate this approach may contribute to a sustainable way to provide air conditioning
for buildings.
Evaporation of moisture from the pads on top of the Toguna buildings built by the Dogon people of Mali, Africa contribute to the coolness felt by the men who rest underneath. The women's buildings on the outskirts of town are functional as more conventional solar chimneys.
The principle is to allow water to evaporate at the top of a tower, either by using evaporative cooling pads or by spraying water. Evaporation
cools the incoming air, causing a downdraft of cool air that will bring down the temperature inside the building. Airflow can be increased by using a solar chimney on the opposite side of the building to help in venting hot air to the outside. This concept has been used for the Visitor Center of Zion National Park
. The Visitor Center was designed by the High Performance Buildings Research of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory
(NREL).
The principle of the downdraft cooltower has been proposed for solar power generation as well. (See Energy tower for more information.)
Ventilation (architecture)
Ventilating is the process of "changing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality...
of building
Building
In architecture, construction, engineering, real estate development and technology the word building may refer to one of the following:...
s by using convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
of air heated by passive solar energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
. A simple description of a solar chimney is that of a vertical shaft utilizing solar energy to enhance the natural stack ventilation through a building.
The solar
Solar power
Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity and biomass, account for most of the available...
chimney
Chimney
A chimney is a structure for venting hot flue gases or smoke from a boiler, stove, furnace or fireplace to the outside atmosphere. Chimneys are typically vertical, or as near as possible to vertical, to ensure that the gases flow smoothly, drawing air into the combustion in what is known as the...
has been in use for centuries, particularly in the Middle east
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
and Near East
Near East
The Near East is a geographical term that covers different countries for geographers, archeologists, and historians, on the one hand, and for political scientists, economists, and journalists, on the other...
by the Persians
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
, as well as in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
by the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
.
Description
In its simplest form, the solar chimney consists of a black-painted chimneyChimney
A chimney is a structure for venting hot flue gases or smoke from a boiler, stove, furnace or fireplace to the outside atmosphere. Chimneys are typically vertical, or as near as possible to vertical, to ensure that the gases flow smoothly, drawing air into the combustion in what is known as the...
. During the day solar energy heats the chimney and the air within it, creating an updraft of air in the chimney. The suction
Suction
Suction is the flow of a fluid into a partial vacuum, or region of low pressure. The pressure gradient between this region and the ambient pressure will propel matter toward the low pressure area. Suction is popularly thought of as an attractive effect, which is incorrect since vacuums do not...
created at the chimney's base can be used to ventilate and cool the building below. In most parts of the world it is easier to harness wind power
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
for such ventilation as is done with a Badgir (بادگیر)
Windcatcher
A windcatcher is a traditional Persian architectural device used for many centuries to create natural ventilation in buildings. It is not known who first invented the windcatcher, but it still can be seen in many countries today. Windcatchers come in various designs: uni-directional,...
, but on hot windless days a Solar chimney can provide ventilation where otherwise there would be none.
There are however a number of solar chimney variations. The basic design elements of a solar chimney are:
- The solar collector area: This can be located in the top part of the chimney or can include the entire shaft. The orientation, type of glazing, insulation and thermal properties of this element are crucial for harnessing, retaining and utilizing solar gains
- The main ventilation shaft: The location, height, cross section and the thermal properties of this structure are also very important.
- The inlet and outlet air apertures: The sizes, location as well as aerodynamic aspects of these elements are also significant.
A principle
Principle
A principle is a law or rule that has to be, or usually is to be followed, or can be desirably followed, or is an inevitable consequence of something, such as the laws observed in nature or the way that a system is constructed...
has been proposed for solar power
Solar power
Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity and biomass, account for most of the available...
generation, using a large greenhouse
Greenhouse
A greenhouse is a building in which plants are grown. These structures range in size from small sheds to very large buildings...
at the base rather than relying solely on heating the chimney itself. (For further information on this issue, see Solar updraft tower
Solar updraft tower
The solar updraft tower is a renewable-energy power plant. It combines the chimney effect, the greenhouse effect and the wind turbine. Air is heated by sunshine and contained in a very large greenhouse-like structure around the base of a tall chimney, and the resulting convection causes air to...
.)
Solar chimneys are painted black so that they absorb the sun's heat more easily and efficiently. When the air inside the chimney is heated, it rises and pulls cold air out from under the ground via the heat exchange tubes.
Solar chimney and sustainable architecture

A Solar chimney can serve many purposes. Direct gain warms air inside the chimney causing it to rise out the top and drawing air in from the bottom. This drawing of air can be used to ventilate a home or office, to draw air through a geothermal heat exchange, or to ventilate only a specific area such as a composting toilet.
Natural ventilation can be created by providing vents in the upper level of a building to allow warm air to rise by convection
Convection
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids and rheids. It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows nor significant diffusion can take place in solids....
and escape to the outside. At the same time cooler air can be drawn in through vents at the lower level. Trees may be planted on that side of the building to provide shade for cooler outside air.
This natural ventilation process can be augmented by a solar chimney. The chimney has to be higher than the roof level, and has to be constructed on the wall facing the direction of the sun. Absorption of heat from the sun can be increased by using a glazed surface on the side facing the sun. Heat absorbing material can be used on the opposing side. The size of the heat-absorbing surface is more important than the diameter of the chimney. A large surface area allows for more effective heat exchange with the air necessary for heating by solar radiation. Heating of the air within the chimney will enhance convection, and hence airflow through the chimney. Openings of the vents in the chimney should face away from the direction of the prevailing wind.
To further maximize the cooling effect, the incoming air may be led through underground ducts
Earth cooling tubes
A ground-coupled heat exchanger is an underground heat exchanger loop that can capture or dissipate heat to or from the ground. They use the Earth's near constant subterranean temperature to warm or cool air or other fluids for residential, agricultural or industrial uses...
before it is allowed to enter the building. The solar chimney can be improved by integrating it with a trombe wall
Trombe wall
A Trombe wall is a sun-facing wall separated from the outdoors by glass and an air space, which absorbs solar energy and releases it selectively towards the interior at night. The essential idea was first explored by Edward S. Morse and patented by him in 1881...
. The added advantage of this design is that the system may be reversed during the cold season, providing solar heating instead.
A variation of the solar chimney concept is the solar attic
Attic
An attic is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building . Attic is generally the American/Canadian reference to it...
. In a hot sunny climate the attic space is often blazingly hot in the summer. In a conventional building this presents a problem as it leads to the need for increased air conditioning
Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
. By integrating the attic space with a solar chimney, the hot air in the attic can be put to work. It can help the convection in the chimney, improving ventilation.
The use of a solar chimney may benefit natural ventilation and passive cooling strategies of buildings thus help reduce energy use, CO2 emissions and pollution in general. Potential benefits regarding natural ventilation and use of solar chimneys are:

- Improved ventilation rates on still, hot days
- Reduced reliance on wind and wind driven ventilation
- Improved control of air flow though a building
- Greater choice of air intake (i.e. leeward side of building)
- Improved air quality and reduced noise levels in urban areas
- Increased night time ventilation rates
- Allow ventilation of narrow, small spaces with minimal exposure to external elements
Potential benefits regarding passive cooling may include:
- Improved passive cooling during warm season (mostly on still, hot days)
- Improved night cooling rates
- Enhanced performance of thermal mass (cooling, cool storage)
- Improved thermal comfort (improved air flow control, reduced draughts)
Precedent Study: The Environmental Building
The Building Research Establishment (BRE) office building in Garston, Watford, United Kingdom, incorporates solar assisted passive ventilation stacks as part of its ventilation strategy.Designed by architects Feilden Clegg Bradley, the BRE offices aim to reduce energy consumption and CO2 emissions by 30% from current best practice guidelines and sustain comfortable environmental conditions without the use of air conditioning. The passive ventilation stacks, solar shading, and hollow concrete slabs with embedded under floor cooling are key features of this building. Ventilation and heating systems are controlled by the building management system (BMS) while a degree of user override is provided to adjust conditions to occupants' needs.
The building utilizes five vertical shafts as an integral part of the ventilation and cooling strategy. The main components of theses stacks are a south facing glass-block wall, thermal mass walls and stainless steel round exhausts rising a few meters above roof level. The chimneys are connected to the curved hollow concrete floor slabs which are cooled via night ventilation. Pipes embedded in the floor can provide additional cooling utilizing groundwater.
On warm windy days air is drawn in through passages in the curved hollow concrete floor slabs. Stack ventilation naturally rising out through the stainless steel chimneys enhances the air flow through the building. The movement of air across the chimney tops enhances the stack effect.
During warm, still days, the building relies mostly on the stack effect while air is taken from the shady north side of the building. Low-energy fans in the tops of the stacks can also be used to improve airflow.
Overnight, control systems enable ventilation paths through the hollow concrete slab removing the heat stored during the day and storing coolth for the following day. The exposed curved ceiling gives more surface area than a flat ceiling would, acting as a cool ‘radiator’, again providing summer cooling.
Research based on actual performance measurements of the passive stacks found that they enhanced the cooling ventilation of the space during warm and still days and may also have the potential to assist night-time cooling due to their thermally massive structure.
Passive down-draft cooltower

Air conditioning
An air conditioner is a home appliance, system, or mechanism designed to dehumidify and extract heat from an area. The cooling is done using a simple refrigeration cycle...
for buildings.
Evaporation of moisture from the pads on top of the Toguna buildings built by the Dogon people of Mali, Africa contribute to the coolness felt by the men who rest underneath. The women's buildings on the outskirts of town are functional as more conventional solar chimneys.
The principle is to allow water to evaporate at the top of a tower, either by using evaporative cooling pads or by spraying water. Evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
cools the incoming air, causing a downdraft of cool air that will bring down the temperature inside the building. Airflow can be increased by using a solar chimney on the opposite side of the building to help in venting hot air to the outside. This concept has been used for the Visitor Center of Zion National Park
Zion National Park
Zion National Park is located in the Southwestern United States, near Springdale, Utah. A prominent feature of the park is Zion Canyon, which is 15 miles long and up to half a mile deep, cut through the reddish and tan-colored Navajo Sandstone by the North Fork of the Virgin River...
. The Visitor Center was designed by the High Performance Buildings Research of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory
National Renewable Energy Laboratory
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory , located in Golden, Colorado, is the United States' primary laboratory for renewable energy and energy efficiency research and development. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory is a government-owned, contractor-operated facility; it is funded through...
(NREL).
The principle of the downdraft cooltower has been proposed for solar power generation as well. (See Energy tower for more information.)
See also
|
Solar updraft tower The solar updraft tower is a renewable-energy power plant. It combines the chimney effect, the greenhouse effect and the wind turbine. Air is heated by sunshine and contained in a very large greenhouse-like structure around the base of a tall chimney, and the resulting convection causes air to... Stack effect Stack effect is the movement of air into and out of buildings, chimneys, flue gas stacks, or other containers, and is driven by buoyancy. Buoyancy occurs due to a difference in indoor-to-outdoor air density resulting from temperature and moisture differences. The result is either a positive or... Sustainable architecture Sustainable architecture is a general term that describes environmentally conscious design techniques in the field of architecture. Sustainable architecture is framed by the larger discussion of sustainability and the pressing economic and political issues of our world... Trombe wall A Trombe wall is a sun-facing wall separated from the outdoors by glass and an air space, which absorbs solar energy and releases it selectively towards the interior at night. The essential idea was first explored by Edward S. Morse and patented by him in 1881... Ventilation (architecture) Ventilating is the process of "changing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality... Windcatcher A windcatcher is a traditional Persian architectural device used for many centuries to create natural ventilation in buildings. It is not known who first invented the windcatcher, but it still can be seen in many countries today. Windcatchers come in various designs: uni-directional,... |
External links
- Solar Innovation Ideas - Victorian Solar Innovation Initiative
- Architectural Environmental Analysis - A guide to environmental design
- Sourcebook Passive Solar Design
- Passive Solar Heating & Cooling Manual
- Sustainability at SCU - Tour Sustainable Features - includes simple description and graphic of solar chimney used in a "Green Demonstration Building".
- Ventilation Improved Pit (VIP) Latrines at the award winning Druk White Lotus School, LadakhLadakhLadakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
, IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...

