Solar urticaria
Encyclopedia
Solar urticaria is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light
, induces a case of urticaria
or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria
. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength
of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen
that initiates a breakout.
The agent in the human body responsible for the reaction to radiation, known as the photoallergen, has not yet been identified. The disease itself can be difficult to diagnose properly because it is so similar to other dermatological disorders, such as polymorphic light eruption or PMLE
. The most helpful test is a diagnostic phototest, a specialized test which confirms the presence of an abnormal sunburn reaction. Once recognized, treatment of the disease commonly involves the administration of antihistamines, and desensitization
treatments such as phototherapy. In more extreme cases, the use of immunosuppressive drugs and even plasmapheresis
may be considered.
The initial discovery of the disease is credited to P. Merklen in 1904, but it did not have a name until the suggestion of "solar urticaria" was given by Duke in 1923. However, their research contributed to the study of this uncommon disease. More than one hundred cases have been reported in the past century.
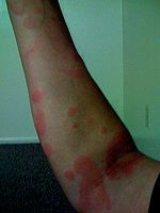
Life with SU can be difficult. Patients are subject to constant itching and pain as within minutes of the initial exposure to UV radiation, a rash will appear. The urticarial reaction begins in the form of pruritus, later progressing to erythema
and edema
in the exposed areas of the skin. If vast areas of the body are affected, the loss of fluid into the skin could lead to light-headedness, headache, nausea and vomiting. Rarely, patients have been reported to experience bronchospasm
. Also, if a large area of the body is suddenly exposed, the person may be subject to an anaphylactic reaction. Once free of exposure, the rash will fade away within several hours.
-mediated hypersensitivity that can be introduced through primary or secondary factors, or induced by exogenous photosensitization. Primary SU is believed to be a type I hypersensitivity
(a mild to severe reaction to an antigen including anaphylaxis
) in which an antigen
, or substance provoking an immune response, is "induced by UV or visible radiation." Secondary SU can occur when a person comes into contact with chemicals such as tar
, pitch
, and dyes. People who use drugs such as benoxaprofen
or patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria
may also contract this secondary form. These items that cause this photosensitivity
are exogenous photosensitizers because they are outside of the body and cause it to have a greater sensitivity to light.
Also, there have been a few unorthodox (unusual) causes of solar urticaria. For those susceptible to visible light, white t-shirts may increase the chances of experiencing an outbreak. In one case, doctors found that the white t-shirt absorbed UVA radiation from the sun and transformed it into visible light which caused the reaction. Another patient was being treated with the antibiotic tetracycline for a separate dermatological disorder and broke out in hives when exposed to the sun, the first case to implicate tetracycline as a solar urticaria inducing agent.
It is not yet known what specific agent in the body brings about the allergic reaction to the radiation. When patients with SU were injected with an irradiated autologous serum, many developed urticaria within the area of injection. When people who did not have SU were injected, they did not demonstrate similar symptoms. This indicates that the reaction is only a characteristic of the patients with solar urticaria and that it is not phototoxic
. It is possible that this photoallergen is located on the binding sites of IgE that are found on the surface of mast cells. The photoallergen is believed to begin its configuration through the absorption of radiation by a chromophore
. The molecule, because of the radiation, is transformed resulting in the formation of a new photoallergen.
Another test known as a phototest is the most useful in identifying solar urticaria. In this test, one centimeter segments of skin are subject to varying amounts of UVA and UVB radiation in order to determine the specific dosage of the certain form of radiation that causes the urticaria
to form. When testing for its less intense form (fixed solar urticaria), phototesting should be conducted only in the areas where the hives have appeared to avoid the possibility of getting false-negative results.
A third form of testing is the photoprovocation test which is used to identify disorders instigated by sun burns. The process of this test involves exposing one area of a patient's arm to certain dosage of UVB radiation and one area on the other arm to a certain dosage of UVA radiation. The amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to is equal to that "received in an hour of midday summer sun." If the procedure produces a rash, then the patient will undergo a biopsy
. Finally, there are laboratory tests which generally involve procedures such as blood, urine, and fecal biochemical tests. In some situations, a skin biopsy
may be performed.
. Physical urticaria arises from physical factors in the environment, which in the case of solar urticaria is UV radiation or light. SU may be classified based on the wavelength of the radiative energy that causes the allergic reaction; known as Harber's classification, six types have been identified in this system. Type I solar urticaria is caused by UVB (ultraviolet B) radiation, with wavelengths ranging from 290–320 nm. Type II is induced by UVA (ultraviolet A) radiation with wavelengths that can range from 320–400 nm. The wavelength range of type III and IV spans from 400 to 500 nm, while type V can be caused by UVB radiation to visible light (280–600 nm). Type VI has only been known to occur at 400 nm.
Another classification distinguishes two types. The first is a hypersensitivity
caused by a reaction to photoallergens located only in people with SU; while the second is caused by photoallergens that can be found in both people with SU and people without it.
A subgroup of solar urticaria, fixed solar urticaria, has also been identified. It is a rare, less intense form of the disease with wheals (swollen areas of the skin) that affect certain, fixed areas of the body. Fixed solar urticaria is induced by a broad spectrum of radiative energy with wavelengths ranging from 300–700 nm.
(PMLE) is the easiest disease to mistake for solar urticaria because the locations of the lesions are similar (the V of the neck and the arms). However, patients with SU are more likely to develop lesions on the face. Also, a reaction with PMLE will take a greater amount of time to appear than with solar urticaria. Lupus erythematosus
has been mistaken for SU; however, lesions from lupus erythematosus will take a longer amount of time to go away. Furthermore, when being tested for the two diseases, patients with SU have a reaction immediately while patients with lupus erythematosus will have a delayed reaction. Patients who have experienced solar urticarial symptoms from a young age could mistakenly be thought to have erythropoietic protoporphyria
. However, the main symptom for this disease is pain and patients with have been found to have abnormal levels of protoporphyrin in their blood while these levels are normal in SU patients. Finally, cholinergic urticaria
, or urticaria induced by heat, can occasionally appear to be solar urticaria because the heat from the sun will cause a person with the disease to have a reaction.
Terfenadine
, an H1 receptor antagonist or medicine that combats the H1 receptor
gene that is associated with many allergic reactions, has been found to be the most potent antihistamine for this particular disease. Patients prescribed 240 milligrams per day have been able to sustain normal exposure to the sun without suffering a reaction. In clinical tests, patients were to found to require up to three times the regular dose of radiation in order to experience the urticarial symptoms.
Patients with less potent forms of solar urticaria such as fixed solar urticaria can be treated with the medication fexofenadine
, which may also be used prophylactically to prevent recurrence.
treatments.
Phototherapy can be used for prevention. Exposure to a certain form of light or UV radiation enables the patient to build up a tolerance and outbreaks can be reduced. This type of treatment is generally conducted in the spring. However, the benefits of this therapy only last for two to three days.
Photochemotherapy, or PUVA
, is considered superior to phototherapy because it produces a longer-lasting tolerance of the radiation that initiates the outbreak. When treatment first begins, the main goal is to build up the patient's tolerance to UVA radiation enough so that they can be outdoors without suffering an episode of solar urticaria. Therefore, treatments are regulated at three per week while constantly increasing the exposure to UVA radiation. Once the patient has reached an adequate level of desensitization, treatments are reduced to once or twice per week.
s such as prednisolone
and ciclosporin
if the patient is suffering from an intense form of solar urticaria. However, the side effects of these medicines can be severe which is why they are reserved for the most extreme of cases.
can be considered. This technique is used to remove the blood plasma or fluid in the red blood cells and then return the cells to the body. It "removes a circulating factor from the blood that may be involved in causing the urticaria," but is still being tested and is not always effective. When the treatment is a success, the patient's photosensitivity
is decreased to the degree that they can undergo PUVA
which can result in the relief of the urticarial outbreaks for an extended period of time. The major setback to this treatment is that the side effects can be severe and may include anaphylactoid reactions.
cases. To put that into a better perspective, since its first documented case in Japan in 1916, over one hundred other instances of the disease have been reported.
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
, induces a case of urticaria
Urticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria
Physical urticaria
Physical urticarias represent a distinct subgroup of the urticarias that are induced by an exogenous physical stimulus rather than occurring spontaneously.The most common form of physical urticaria is dermatographism....
. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen
Allergen
An allergen is any substance that can cause an allergy. In technical terms, an allergen is a non-parasitic antigen capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivity reaction in atopic individuals....
that initiates a breakout.
The agent in the human body responsible for the reaction to radiation, known as the photoallergen, has not yet been identified. The disease itself can be difficult to diagnose properly because it is so similar to other dermatological disorders, such as polymorphic light eruption or PMLE
Polymorphous Light Eruption
Polymorphous light eruption , or polymorphic light eruption , is a skin condition caused by sunlight.- Types :Two subtypes have been described:*Juvenile spring eruption*Benign summer light eruption-Presentation:...
. The most helpful test is a diagnostic phototest, a specialized test which confirms the presence of an abnormal sunburn reaction. Once recognized, treatment of the disease commonly involves the administration of antihistamines, and desensitization
Desensitization (medicine)
For medical purposes, desensitization is a method to reduce or eliminate an organism's negative reaction to a substance or stimulus.For example, if a person with diabetes mellitus has a bad allergic reaction to taking a full dose of beef insulin, the doctor gives the person a very small amount of...
treatments such as phototherapy. In more extreme cases, the use of immunosuppressive drugs and even plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis is the removal, treatment, and return of blood plasma from blood circulation. It is thus an extracorporeal therapy...
may be considered.
The initial discovery of the disease is credited to P. Merklen in 1904, but it did not have a name until the suggestion of "solar urticaria" was given by Duke in 1923. However, their research contributed to the study of this uncommon disease. More than one hundred cases have been reported in the past century.
Signs and symptoms
Generally, the areas affected are exposed skin not usually protected by clothing; however it can also occur in areas covered by clothing. The areas constantly subjected to the sun's rays may only be slightly affected if at all. Parts of the body only thinly covered can potentially be subjected to an outbreak.Life with SU can be difficult. Patients are subject to constant itching and pain as within minutes of the initial exposure to UV radiation, a rash will appear. The urticarial reaction begins in the form of pruritus, later progressing to erythema
Erythema
Erythema is redness of the skin, caused by hyperemia of the capillaries in the lower layers of the skin. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation...
and edema
Edema
Edema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
in the exposed areas of the skin. If vast areas of the body are affected, the loss of fluid into the skin could lead to light-headedness, headache, nausea and vomiting. Rarely, patients have been reported to experience bronchospasm
Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylatoxins...
. Also, if a large area of the body is suddenly exposed, the person may be subject to an anaphylactic reaction. Once free of exposure, the rash will fade away within several hours.
Causes
Solar urticaria is an immunoglobulin EImmunoglobulin E
Immunoglobulin E is a class of antibody that has been found only in mammals. IgE is a monomeric antibody with 4 Ig-like domains...
-mediated hypersensitivity that can be introduced through primary or secondary factors, or induced by exogenous photosensitization. Primary SU is believed to be a type I hypersensitivity
Type I hypersensitivity
Type I hypersensitivity is an allergic reaction provoked by reexposure to a specific type of antigen referred to as an allergen, or to a nonimmunologic stimulus like cold weather or exercise...
(a mild to severe reaction to an antigen including anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is defined as "a serious allergic reaction that is rapid in onset and may cause death". It typically results in a number of symptoms including throat swelling, an itchy rash, and low blood pressure...
) in which an antigen
Antigen
An antigen is a foreign molecule that, when introduced into the body, triggers the production of an antibody by the immune system. The immune system will then kill or neutralize the antigen that is recognized as a foreign and potentially harmful invader. These invaders can be molecules such as...
, or substance provoking an immune response, is "induced by UV or visible radiation." Secondary SU can occur when a person comes into contact with chemicals such as tar
Tar
Tar is modified pitch produced primarily from the wood and roots of pine by destructive distillation under pyrolysis. Production and trade in tar was a major contributor in the economies of Northern Europe and Colonial America. Its main use was in preserving wooden vessels against rot. The largest...
, pitch
Pitch (resin)
Pitch is the name for any of a number of viscoelastic, solid polymers. Pitch can be made from petroleum products or plants. Petroleum-derived pitch is also called bitumen. Pitch produced from plants is also known as resin. Products made from plant resin are also known as rosin.Pitch was...
, and dyes. People who use drugs such as benoxaprofen
Benoxaprofen
Benoxaprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. It was marketed by Eli Lilly and Company under the brand name Oraflex in the US and as Opren in Europe. Lilly suspended sales of Oraflex in 1982 after reports from the British government and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration of adverse...
or patients with erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a relatively mild form of porphyria, although very painful, which arises from a deficiency in the enzyme ferrochelatase, leading to abnormally high levels of protoporphyrin in the tissue...
may also contract this secondary form. These items that cause this photosensitivity
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light.- Human medicine :Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn...
are exogenous photosensitizers because they are outside of the body and cause it to have a greater sensitivity to light.
Also, there have been a few unorthodox (unusual) causes of solar urticaria. For those susceptible to visible light, white t-shirts may increase the chances of experiencing an outbreak. In one case, doctors found that the white t-shirt absorbed UVA radiation from the sun and transformed it into visible light which caused the reaction. Another patient was being treated with the antibiotic tetracycline for a separate dermatological disorder and broke out in hives when exposed to the sun, the first case to implicate tetracycline as a solar urticaria inducing agent.
It is not yet known what specific agent in the body brings about the allergic reaction to the radiation. When patients with SU were injected with an irradiated autologous serum, many developed urticaria within the area of injection. When people who did not have SU were injected, they did not demonstrate similar symptoms. This indicates that the reaction is only a characteristic of the patients with solar urticaria and that it is not phototoxic
Phototoxic
Phototoxicity is a chemically induced skin irritation requiring light . The skin response resembles an exaggerated sunburn. The involved chemical may enter into the skin by topical administration or it may reach the skin via systemic circulation following ingestion or parenteral administration...
. It is possible that this photoallergen is located on the binding sites of IgE that are found on the surface of mast cells. The photoallergen is believed to begin its configuration through the absorption of radiation by a chromophore
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color arises when a molecule absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light and transmits or reflects others. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two different molecular orbitals falls...
. The molecule, because of the radiation, is transformed resulting in the formation of a new photoallergen.
Diagnosis
Solar urticaria can be difficult to diagnose, but its presence can be confirmed by the process of phototesting. There are several forms of these tests including photopatch tests, phototests, photoprovocation tests, and laboratory tests. All of these are necessary to determine the exact infliction that the patient is suffering from. Photopatch tests are patch tests conducted when it is believed that a patient is experiencing certain symptoms due to an allergy that will only occur when in contact with sunlight. After the procedure, the patient is given a low dosage of UVA radiation.Another test known as a phototest is the most useful in identifying solar urticaria. In this test, one centimeter segments of skin are subject to varying amounts of UVA and UVB radiation in order to determine the specific dosage of the certain form of radiation that causes the urticaria
Urticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
to form. When testing for its less intense form (fixed solar urticaria), phototesting should be conducted only in the areas where the hives have appeared to avoid the possibility of getting false-negative results.
A third form of testing is the photoprovocation test which is used to identify disorders instigated by sun burns. The process of this test involves exposing one area of a patient's arm to certain dosage of UVB radiation and one area on the other arm to a certain dosage of UVA radiation. The amount of radiation that the patient is exposed to is equal to that "received in an hour of midday summer sun." If the procedure produces a rash, then the patient will undergo a biopsy
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
. Finally, there are laboratory tests which generally involve procedures such as blood, urine, and fecal biochemical tests. In some situations, a skin biopsy
Skin biopsy
Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed and sent to the pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin...
may be performed.
Classification
Solar urticaria, due to its particular features, is considered to be a type of physical urticaria or light sensitivityLight sensitivity
Light sensitivity or photosensitivity is an increase in the reactivity of the skin to sunlight. Apart from vision, human beings have many physiological and psychological responses to light. In rare individuals an atypical response may result in serious discomfort, disease, or injury. Some drugs...
. Physical urticaria arises from physical factors in the environment, which in the case of solar urticaria is UV radiation or light. SU may be classified based on the wavelength of the radiative energy that causes the allergic reaction; known as Harber's classification, six types have been identified in this system. Type I solar urticaria is caused by UVB (ultraviolet B) radiation, with wavelengths ranging from 290–320 nm. Type II is induced by UVA (ultraviolet A) radiation with wavelengths that can range from 320–400 nm. The wavelength range of type III and IV spans from 400 to 500 nm, while type V can be caused by UVB radiation to visible light (280–600 nm). Type VI has only been known to occur at 400 nm.
Another classification distinguishes two types. The first is a hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. These reactions may be damaging, uncomfortable, or occasionally fatal. Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized state of the host. The four-group classification...
caused by a reaction to photoallergens located only in people with SU; while the second is caused by photoallergens that can be found in both people with SU and people without it.
A subgroup of solar urticaria, fixed solar urticaria, has also been identified. It is a rare, less intense form of the disease with wheals (swollen areas of the skin) that affect certain, fixed areas of the body. Fixed solar urticaria is induced by a broad spectrum of radiative energy with wavelengths ranging from 300–700 nm.
Differential diagnosis
Polymorphous light eruptionPolymorphous Light Eruption
Polymorphous light eruption , or polymorphic light eruption , is a skin condition caused by sunlight.- Types :Two subtypes have been described:*Juvenile spring eruption*Benign summer light eruption-Presentation:...
(PMLE) is the easiest disease to mistake for solar urticaria because the locations of the lesions are similar (the V of the neck and the arms). However, patients with SU are more likely to develop lesions on the face. Also, a reaction with PMLE will take a greater amount of time to appear than with solar urticaria. Lupus erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is a category for a collection of diseases with similar underlying problems with immunity . Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs...
has been mistaken for SU; however, lesions from lupus erythematosus will take a longer amount of time to go away. Furthermore, when being tested for the two diseases, patients with SU have a reaction immediately while patients with lupus erythematosus will have a delayed reaction. Patients who have experienced solar urticarial symptoms from a young age could mistakenly be thought to have erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Erythropoietic protoporphyria is a relatively mild form of porphyria, although very painful, which arises from a deficiency in the enzyme ferrochelatase, leading to abnormally high levels of protoporphyrin in the tissue...
. However, the main symptom for this disease is pain and patients with have been found to have abnormal levels of protoporphyrin in their blood while these levels are normal in SU patients. Finally, cholinergic urticaria
Cholinergic urticaria
Cholinergic urticaria is a subcategory of physical urticaria that is a skin rash brought on by a hypersensitive reaction to body heat...
, or urticaria induced by heat, can occasionally appear to be solar urticaria because the heat from the sun will cause a person with the disease to have a reaction.
Antihistamines
Histamines are proteins associated with many allergic reactions. When the UV radiation or light comes in contact with a person with solar urticaria, histamine is released from mast cells. When this occurs, the permeability of vessels near the area of histamine release is increased. This allows blood fluid to enter the vessels and cause inflammation. Antihistamines suppress the activity of the histamine.Terfenadine
Terfenadine
Terfenadine is an antihistamine formerly used for the treatment of allergic conditions. It was brought to market by Hoechst Marion Roussel and marketed under various brand names including Seldane in the United States, Triludan in the United Kingdom, and Teldane in Australia...
, an H1 receptor antagonist or medicine that combats the H1 receptor
H1 receptor
The H1 receptor is a histamine receptor belonging to the family of Rhodopsin like G-protein-coupled receptors. This receptor, which is activated by the biogenic amine histamine, is expressed throughout the body, to be specific, in smooth muscles, on vascular endothelial cells, in the heart, and in...
gene that is associated with many allergic reactions, has been found to be the most potent antihistamine for this particular disease. Patients prescribed 240 milligrams per day have been able to sustain normal exposure to the sun without suffering a reaction. In clinical tests, patients were to found to require up to three times the regular dose of radiation in order to experience the urticarial symptoms.
Patients with less potent forms of solar urticaria such as fixed solar urticaria can be treated with the medication fexofenadine
Fexofenadine
Fexofenadine is an antihistamine drug used in the treatment of hayfever and similar allergy symptoms...
, which may also be used prophylactically to prevent recurrence.
Desensitization
This form of treatment is meant to reduce the intensity or altogether eliminate the allergic reactions people have by gradually increasing exposure to the form of radiation that brings about the reaction. In the case of solar urticaria, phototherapy and photochemotherapy are the two major desensitizationDesensitization (medicine)
For medical purposes, desensitization is a method to reduce or eliminate an organism's negative reaction to a substance or stimulus.For example, if a person with diabetes mellitus has a bad allergic reaction to taking a full dose of beef insulin, the doctor gives the person a very small amount of...
treatments.
Phototherapy can be used for prevention. Exposure to a certain form of light or UV radiation enables the patient to build up a tolerance and outbreaks can be reduced. This type of treatment is generally conducted in the spring. However, the benefits of this therapy only last for two to three days.
Photochemotherapy, or PUVA
PUVA
PUVA is a psoralen + UVA treatment for eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease and vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides. The psoralen is applied or taken orally to sensitize the skin, then the skin is exposed to UVA. Long term use has been associated with higher rates of skin cancer.Psoralens are...
, is considered superior to phototherapy because it produces a longer-lasting tolerance of the radiation that initiates the outbreak. When treatment first begins, the main goal is to build up the patient's tolerance to UVA radiation enough so that they can be outdoors without suffering an episode of solar urticaria. Therefore, treatments are regulated at three per week while constantly increasing the exposure to UVA radiation. Once the patient has reached an adequate level of desensitization, treatments are reduced to once or twice per week.
Immunosuppression
Doctors will sometimes prescribe immunosuppressive drugImmunosuppressive drug
Immunosuppressive drugs or immunosuppressive agents are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. They are used in immunosuppressive therapy to:...
s such as prednisolone
Prednisolone
Prednisolone is the active metabolite of prednisone, which is also used as a drug.-Uses:Prednisolone is a corticosteroid drug with predominant glucocorticoid and low mineralocorticoid activity, making it useful for the treatment of a wide range of inflammatory and auto-immune conditions such as...
and ciclosporin
Ciclosporin
Ciclosporin , cyclosporine , cyclosporin , or cyclosporin A is an immunosuppressant drug widely used in post-allogeneic organ transplant to reduce the activity of the immune system, and therefore the risk of organ rejection...
if the patient is suffering from an intense form of solar urticaria. However, the side effects of these medicines can be severe which is why they are reserved for the most extreme of cases.
Plasmapheresis
In more extreme cases, plasmapheresisPlasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis is the removal, treatment, and return of blood plasma from blood circulation. It is thus an extracorporeal therapy...
can be considered. This technique is used to remove the blood plasma or fluid in the red blood cells and then return the cells to the body. It "removes a circulating factor from the blood that may be involved in causing the urticaria," but is still being tested and is not always effective. When the treatment is a success, the patient's photosensitivity
Photosensitivity
Photosensitivity is the amount to which an object reacts upon receiving photons, especially visible light.- Human medicine :Sensitivity of the skin to a light source can take various forms. People with particular skin types are more sensitive to sunburn...
is decreased to the degree that they can undergo PUVA
PUVA
PUVA is a psoralen + UVA treatment for eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease and vitiligo, and mycosis fungoides. The psoralen is applied or taken orally to sensitize the skin, then the skin is exposed to UVA. Long term use has been associated with higher rates of skin cancer.Psoralens are...
which can result in the relief of the urticarial outbreaks for an extended period of time. The major setback to this treatment is that the side effects can be severe and may include anaphylactoid reactions.
Epidemiology
In the United States, only about 4% of patients with photosensitive disorders are reported to have been diagnosed with solar urticaria. Internationally, the number is slightly larger at 5.3%. Solar urticaria may occur in all races but studies monitoring 135 African Americans and 110 Caucasians with photodermatoses found that 2.2% of the African Americans had SU and 8% of the Caucasians had the disease showing that Caucasians have a better chance of getting the disease. Globably 3.1 per 100,000 people are affected and females are more likely to be affected than males. The age ranges anywhere from 10–70 years old, but the average age is 35 and cases have been reported with children that are still in infancy. Solar urticaria accounts for less than one percent of the many documented urticariaUrticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
cases. To put that into a better perspective, since its first documented case in Japan in 1916, over one hundred other instances of the disease have been reported.

