
Soluble epoxide hydrolase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a soluble epoxide hydrolase or sEH is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are epoxide
and H2O
, whereas its product
is glycol.
The sEH belongs to the hydrolase
family of enzymes, specifically those acting on ether bonds (ether hydrolases). Due to structural similarities, it has been proposed that the sEH evolved from the bacterial haloalkane dehalogenase
. The systematic name of this enzyme class is epoxide hydrolase
. Other names in common use include epoxide hydrase (ambiguous, epoxide hydratase (ambiguous), arene-oxide hydratase (ambiguous), aryl epoxide hydrase (ambiguous), trans-stilbene oxide hydrolase and cytosolic epoxide hydrolase.
metabolism as well as the metabolism of endogenous signalling molecules such as epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
s.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- an epoxide + H2O
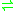 a glycol
a glycol
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are epoxide
Epoxide
An epoxide is a cyclic ether with three ring atoms. This ring approximately defines an equilateral triangle, which makes it highly strained. The strained ring makes epoxides more reactive than other ethers. Simple epoxides are named from the parent compound ethylene oxide or oxirane, such as in...
and H2O
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, whereas its product
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
is glycol.
The sEH belongs to the hydrolase
Hydrolase
In biochemistry, a hydrolase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a chemical bond. For example, an enzyme that catalyzed the following reaction is a hydrolase:-Nomenclature:...
family of enzymes, specifically those acting on ether bonds (ether hydrolases). Due to structural similarities, it has been proposed that the sEH evolved from the bacterial haloalkane dehalogenase
Haloalkane dehalogenase
In enzymology, a haloalkane dehalogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 1-haloalkane and H2O, whereas its two products are primary alcohol and halide....
. The systematic name of this enzyme class is epoxide hydrolase
Epoxide hydrolase
Epoxide hydrolase functions in detoxication during drug metabolism. It converts epoxides to trans-dihydrodiols, which can be conjugated and excreted from the body. Epoxides result from the degradation of aromatic compounds...
. Other names in common use include epoxide hydrase (ambiguous, epoxide hydratase (ambiguous), arene-oxide hydratase (ambiguous), aryl epoxide hydrase (ambiguous), trans-stilbene oxide hydrolase and cytosolic epoxide hydrolase.
Function
This enzyme participates in arachidonic acid metabolism and tetrachloroethene degradation. It is important in xenobioticXenobiotic
A xenobiotic is a chemical which is found in an organism but which is not normally produced or expected to be present in it. It can also cover substances which are present in much higher concentrations than are usual...
metabolism as well as the metabolism of endogenous signalling molecules such as epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid
The Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids or EETs are signaling molecules formed by the action of Cytochrome P450 epoxygenase on 20-carbon essential fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid, from which it is produced by the enzyme epoxygenase....
s.

