
Source transformation
Encyclopedia
Finding a solution to a circuit can be somewhat difficult without using tricks or methods that make the circuit appear simpler. Circuit solutions are often simplified, especially with mixed sources, by transforming a voltage into a current
source, and vice versa. This process is known as a source transformation, and is an application of Thevenin's theorem
and Norton's theorem
.
in series with a resistance
, and replace it with a current source
in parallel with the same resistance. Remember that Ohms law states that a voltage in a material is equal to the material's resistance times the amount of current through it. Since source transformations are bilateral, one can be derived from the other. Source transformations are not limited to resistive circuits however. They can be performed on a circuit involving capacitors and inductors, as long as the circuit is first put into the frequency domain
. In general, the concept of source transformation is an application of Thevenin's theorem
to a current source
, or Norton's theorem
to a voltage source
.
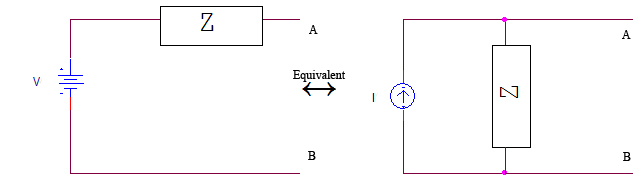
Specifically, source transformations are used to exploit the equivalence of a real current source and a real voltage source, such as a battery
. Application of Thevenin's theorem and Norton's theorem gives the quantities associated with the equivalence. Specifically, suppose we have a real current source I, which is an ideal current source in parallel
with an impedance
. If the ideal current source is rated at I amperes, and the parallel resistor has an impedance Z, then applying a source transformation gives an equivalent real voltage source, which is ideal, and in series
with the impedance. This new voltage source V, has a value equal to the ideal current source's value times the resistance contained in the real current source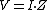 . The impedance component of the real voltage source retains its real current source value.
. The impedance component of the real voltage source retains its real current source value.
In general, source transformations can be summarized by keeping two things in mind:
, it is possible to find the value of the equivalent current source
in parallel with the impedance by dividing the value of the voltage source by the value of the impedance. The converse also applies here: if a current source in parallel with an impedance is present, multiplying the value of the current source with the value of the impedance will result in the equivalent voltage source in series with the impedance. A visual example of what is being done during a source transformation can be seen in Figure 1.
Remember:

Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
source, and vice versa. This process is known as a source transformation, and is an application of Thevenin's theorem
Thévenin's theorem
In circuit theory, Thévenin's theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. For single frequency AC systems the theorem...
and Norton's theorem
Norton's theorem
Norton's theorem for linear electrical networks, known in Europe as the Mayer–Norton theorem, states that any collection of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to an ideal current source, I, in parallel with a single resistor, R...
.
Process
Performing a source transformation is the process of using Ohms Law to take an existing voltage sourceVoltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
in series with a resistance
Resistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
, and replace it with a current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
in parallel with the same resistance. Remember that Ohms law states that a voltage in a material is equal to the material's resistance times the amount of current through it. Since source transformations are bilateral, one can be derived from the other. Source transformations are not limited to resistive circuits however. They can be performed on a circuit involving capacitors and inductors, as long as the circuit is first put into the frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
. In general, the concept of source transformation is an application of Thevenin's theorem
Thévenin's theorem
In circuit theory, Thévenin's theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. For single frequency AC systems the theorem...
to a current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
, or Norton's theorem
Norton's theorem
Norton's theorem for linear electrical networks, known in Europe as the Mayer–Norton theorem, states that any collection of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to an ideal current source, I, in parallel with a single resistor, R...
to a voltage source
Voltage source
In electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
.
Specifically, source transformations are used to exploit the equivalence of a real current source and a real voltage source, such as a battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
. Application of Thevenin's theorem and Norton's theorem gives the quantities associated with the equivalence. Specifically, suppose we have a real current source I, which is an ideal current source in parallel
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
with an impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
. If the ideal current source is rated at I amperes, and the parallel resistor has an impedance Z, then applying a source transformation gives an equivalent real voltage source, which is ideal, and in series
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
with the impedance. This new voltage source V, has a value equal to the ideal current source's value times the resistance contained in the real current source
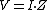 . The impedance component of the real voltage source retains its real current source value.
. The impedance component of the real voltage source retains its real current source value.In general, source transformations can be summarized by keeping two things in mind:
- Ohm's LawOhm's lawOhm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
- Impedances remain the same
Example calculation
Source transformations are easy to perform as long as there is a familiarity with Ohms Law. If there is a voltage source in series with an impedanceElectrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
, it is possible to find the value of the equivalent current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
in parallel with the impedance by dividing the value of the voltage source by the value of the impedance. The converse also applies here: if a current source in parallel with an impedance is present, multiplying the value of the current source with the value of the impedance will result in the equivalent voltage source in series with the impedance. A visual example of what is being done during a source transformation can be seen in Figure 1.
Remember:
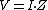


See also
- Ohms Law
- Thévenin's theoremThévenin's theoremIn circuit theory, Thévenin's theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. For single frequency AC systems the theorem...
- current sourceCurrent sourceA current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
- voltage sourceVoltage sourceIn electric circuit theory, an ideal voltage source is a circuit element where the voltage across it is independent of the current through it. A voltage source is the dual of a current source. In analysis, a voltage source supplies a constant DC or AC potential between its terminals for any current...
- electrical impedanceElectrical impedanceElectrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...

