
Space-time block coding based transmit diversity
Encyclopedia
Space-time block coding based transmit diversity (STTD) is a method of transmit diversity
used in UMTS third-generation
cellular systems. STTD is optional in the UTRAN
air interface but mandatory for user equipment (UE
). STTD utilizes space-time block code (STBC) in order to exploit redundancy in multiply transmitted versions of a signal.
STTD is one of numerous open loop transmit diversity schemes which also include Phase Switched Transmit Diversity (PSTD), Time Switched Diversity TSTD, Orthogonal Transmit Diversity (OTD) and Space Time Spreading (STS) [1]. The aim of all of these schemes is to smooth the Rayleigh fading and drop out effects observed when using only a single antenna at both ends of a radio link in a multipath environment. Diversity improves link reliability for each user over time, especially near cell edges (in the absence of soft-handoff), and also the average performance of an ensemble of users at any particular instant. Not being reliant on slow channel-state feedback from the mobile (i.e. user equipment) means that open loop STTD is almost immune to Doppler shifts associated with high UE speeds and is the preferred method for this scenario. However, an open loop transmit diversity scheme must not degrade performance for a user close to the base station where the channels may be line of sight and nearly ideal. Since STTD is an orthogonal coding system this is also guaranteed.
STTD can be applied to single symbols in QAM, CDMA code words, or subcarrier symbols in OFDM and the transmit method has become standardised, especially in 3G cellular wireless [2] as described below. The transmitter coder takes consecutive pairs of data symbols {S1, S2}, normally sent directly from one antenna. For two transmit antennas the symbols {S1, S2} are transmitted unchanged from antenna #1 while simultaneously from antenna #2 is sent the sequence {-S2*, S1*}. At the receiver some linear algebra is needed for decoding. Consider the complex channel gains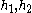 between the TX elements and the single RX element are already known at the receiver. The received signals in the two time slots are
between the TX elements and the single RX element are already known at the receiver. The received signals in the two time slots are
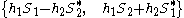 with some added noise
with some added noise 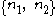 . By conjugating the second received symbol within the receiver, we can write the matrix equation
. By conjugating the second received symbol within the receiver, we can write the matrix equation
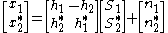
and the least squares solution is to solve for S1 and S2 by matrix inversion:
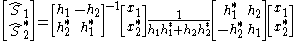
This is called the zero forcing solution. It attempts to drive interference between the symbols to zero by a process of weighting linear combinations of the received signals at the two time samples and works perfectly in the absence of errors and noise.
Note that in the inscrutable 3G specifications, for example TS125.211, a consecutive pair of transmitted QPSK symbols, after coding, interleaving etc., is defined by a logical binary string of four bits:
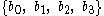 , representing in-phase and quadrature components and
, representing in-phase and quadrature components and 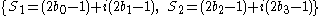 .
.
Here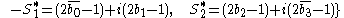 where overbar means logical inversion.
where overbar means logical inversion.
For CDMA, STTD is applied to whole code words rather than consecutive chips. In OFDM applications such as Long Term Evolution (LTE) two transmit element STTD is optionally applied just as above while there is also a 4-element option.
Transmit diversity
Transmit diversity is radio communication using signals that originate from two or more independent sources that have been modulated with identical information-bearing signals and that may vary in their transmission characteristics at any given instant....
used in UMTS third-generation
3G
3G or 3rd generation mobile telecommunications is a generation of standards for mobile phones and mobile telecommunication services fulfilling the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 specifications by the International Telecommunication Union...
cellular systems. STTD is optional in the UTRAN
Utran
Utran is a census town in Surat district in the Indian state of Gujarat.-Geography:Utran is located at . It has an average elevation of 12 metres .-Demographics:...
air interface but mandatory for user equipment (UE
UE (wireless telephone)
In the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System and 3GPP Long Term Evolution , user equipment is any device used directly by an end-user to communicate. It can be a hand-held telephone, a laptop computer equipped with a mobile broadband adapter, or any other device...
). STTD utilizes space-time block code (STBC) in order to exploit redundancy in multiply transmitted versions of a signal.
STTD is one of numerous open loop transmit diversity schemes which also include Phase Switched Transmit Diversity (PSTD), Time Switched Diversity TSTD, Orthogonal Transmit Diversity (OTD) and Space Time Spreading (STS) [1]. The aim of all of these schemes is to smooth the Rayleigh fading and drop out effects observed when using only a single antenna at both ends of a radio link in a multipath environment. Diversity improves link reliability for each user over time, especially near cell edges (in the absence of soft-handoff), and also the average performance of an ensemble of users at any particular instant. Not being reliant on slow channel-state feedback from the mobile (i.e. user equipment) means that open loop STTD is almost immune to Doppler shifts associated with high UE speeds and is the preferred method for this scenario. However, an open loop transmit diversity scheme must not degrade performance for a user close to the base station where the channels may be line of sight and nearly ideal. Since STTD is an orthogonal coding system this is also guaranteed.
STTD can be applied to single symbols in QAM, CDMA code words, or subcarrier symbols in OFDM and the transmit method has become standardised, especially in 3G cellular wireless [2] as described below. The transmitter coder takes consecutive pairs of data symbols {S1, S2}, normally sent directly from one antenna. For two transmit antennas the symbols {S1, S2} are transmitted unchanged from antenna #1 while simultaneously from antenna #2 is sent the sequence {-S2*, S1*}. At the receiver some linear algebra is needed for decoding. Consider the complex channel gains
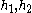 between the TX elements and the single RX element are already known at the receiver. The received signals in the two time slots are
between the TX elements and the single RX element are already known at the receiver. The received signals in the two time slots are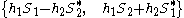 with some added noise
with some added noise 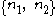 . By conjugating the second received symbol within the receiver, we can write the matrix equation
. By conjugating the second received symbol within the receiver, we can write the matrix equation 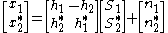
and the least squares solution is to solve for S1 and S2 by matrix inversion:
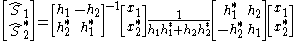
This is called the zero forcing solution. It attempts to drive interference between the symbols to zero by a process of weighting linear combinations of the received signals at the two time samples and works perfectly in the absence of errors and noise.
Note that in the inscrutable 3G specifications, for example TS125.211, a consecutive pair of transmitted QPSK symbols, after coding, interleaving etc., is defined by a logical binary string of four bits:
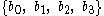 , representing in-phase and quadrature components and
, representing in-phase and quadrature components and 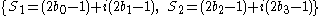 .
. Here
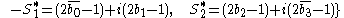 where overbar means logical inversion.
where overbar means logical inversion.For CDMA, STTD is applied to whole code words rather than consecutive chips. In OFDM applications such as Long Term Evolution (LTE) two transmit element STTD is optionally applied just as above while there is also a 4-element option.
See also
- Diversity schemeDiversity schemeIn telecommunications, a diversity scheme refers to a method for improving the reliability of a message signal by using two or more communication channels with different characteristics. Diversity plays an important role in combatting fading and co-channel interference and avoiding error bursts...
- Multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO)
- Space diversity
- Space–time coding (STC)

