
Specific detectivity
Encyclopedia
Specific detectivity, or D*, for a photodetector
is a figure of merit
used to characterize performance, equal to the reciprocal of noise-equivalent power
(NEP), normalized per unit area.
Specific detectivity is given by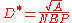 , where
, where 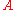 is the area of the photosensitive region of the detector. Its common units are
is the area of the photosensitive region of the detector. Its common units are 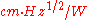 , also called the Jones in honor of R. Clark Jones who defined this magnitude.
, also called the Jones in honor of R. Clark Jones who defined this magnitude.
Given that noise-equivalent power
can be expressed as a function of the responsivity
 (in units of
(in units of 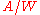 or
or 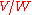 ) and the noise spectral density
) and the noise spectral density
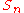 (in units of
(in units of 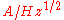 or
or 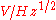 ) as
) as 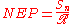 , it's common to see the specific detectivity expressed as
, it's common to see the specific detectivity expressed as 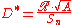 .
.
The unit Jones is now commonly used with the D* figure of merit.
Photodetector
Photosensors or photodetectors are sensors of light or other electromagnetic energy. There are several varieties:*Active pixel sensors are image sensors consisting of an integrated circuit that contains an array of pixel sensors, each pixel containing a both a light sensor and an active amplifier...
is a figure of merit
Figure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
used to characterize performance, equal to the reciprocal of noise-equivalent power
Noise-equivalent power
Noise-equivalent power is a measure of the sensitivity of a photodetector or detector system. It is defined as the signal power that gives a signal-to-noise ratio of one in a one hertz output bandwidth. An output bandwidth of one hertz is equivalent to half a second of integration time. The units...
(NEP), normalized per unit area.
Specific detectivity is given by
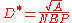 , where
, where  is the area of the photosensitive region of the detector. Its common units are
is the area of the photosensitive region of the detector. Its common units are 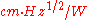 , also called the Jones in honor of R. Clark Jones who defined this magnitude.
, also called the Jones in honor of R. Clark Jones who defined this magnitude.Given that noise-equivalent power
Noise-equivalent power
Noise-equivalent power is a measure of the sensitivity of a photodetector or detector system. It is defined as the signal power that gives a signal-to-noise ratio of one in a one hertz output bandwidth. An output bandwidth of one hertz is equivalent to half a second of integration time. The units...
can be expressed as a function of the responsivity
Responsivity
Responsivity measures the input–output gain of a detector system. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the local slope ....
 (in units of
(in units of 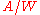 or
or 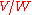 ) and the noise spectral density
) and the noise spectral densityNoise spectral density
In communications, noise spectral density No is the noise power per unit of bandwidth; that is, it is the power spectral density of the noise. It has dimension of power/frequency , whose SI coherent unit is watts per hertz, which is equivalent to watt-seconds or joules...
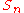 (in units of
(in units of 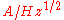 or
or 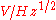 ) as
) as 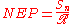 , it's common to see the specific detectivity expressed as
, it's common to see the specific detectivity expressed as 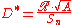 .
.The unit Jones is now commonly used with the D* figure of merit.

