
Specific speed
Encyclopedia
Specific speed Ns is a quasi non-dimensional number
used to classify pump
impeller
s as to their type and proportions. In Imperial unit
s it is defined as the speed in revolutions per minute
at which a geometrically similar impeller would operate if it were of such a size as to deliver one gallon per minute against one foot of hydraulic head
. In metric units flow may be in l/s or m³/s and head in m, and care must be taken to state the units used.
Performance is defined as the ratio of the pump or turbine against a reference pump or turbine, which divides the actual performance figure to provide a unitless figure of merit
. The resulting figure would more descriptively be called the "ideal-reference-device-specific performance." This resulting unitless ratio may loosely be expressed as a "speed," only because the performance of the reference ideal pump is linearly dependent on its speed, so that the ratio of [device-performance to reference-device-performance] is also the increased speed the reference device would need to turn, in order to produce the performance, instead of its reference speed of "1 unit."
Specific speed is used in engineering design where it is thought of as an index used to predict desired pump or turbine characteristics; e.g., the general shape of a pump's impeller
. Often it is used to predict the type of pump or turbine required for a design flow rate and head. Once the desired specific speed is known, basic dimensions of the unit's components can be easily calculated.
Several mathematical definitions of specific speed (all of them actually ideal-device-specific) have been created for different devices and applications.
principally through centrifugal force
. Pumps of higher specific speeds develop head partly by centrifugal force and partly by axial force. An axial flow or propeller pump with a specific speed of 10,000 or greater generates its head exclusively through axial forces. Radial impellers are generally low flow/high head designs whereas axial flow impellers are high flow/low head designs.
Centrifugal pump
impellers have specific speed values ranging from 500 to 10,000 (English units), with radial flow pumps at 500-4000, mixed flow at 2000-8000 and axial flow pump
s at 7000-20,000. Values of specific speed less than 500 are associated with positive displacement pumps.
As the specific speed increases, the ratio of the impeller outlet diameter to the inlet or eye diameter decreases. This ratio becomes 1.0 for a true axial flow impeller.
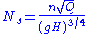
where:
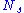 is specific speed (unitless)
is specific speed (unitless) is pump rotational speed (revolutions per seconds)
is pump rotational speed (revolutions per seconds) is flowrate (m³/s) at the point of best efficiency
is flowrate (m³/s) at the point of best efficiency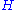 is total head (m) per stage at the point of best efficiency
is total head (m) per stage at the point of best efficiency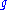 is acceleration due to gravity (m/s²)
is acceleration due to gravity (m/s²)
Note that the units used affect the specific speed value and consistent units should be used for comparisons. Pump specific speed can be calculated using British gallons or using Metric units (m3/s or L/s and metres head), changing the values listed above.
. The higher the net suction specific speed, then the smaller the range of stable operation. The envelope of stable operation is defined in terms of the best efficiency point of the pump.
The net suction specific speed is defined as:
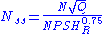
where:
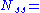 net suction specific speed
net suction specific speed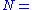 rotational speed of pump in rpm
rotational speed of pump in rpm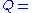 flow of pump in US gallons per minute
flow of pump in US gallons per minute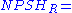 Net positive suction head (NPSH) required in feet at pump's best efficiency point
Net positive suction head (NPSH) required in feet at pump's best efficiency point
Well-designed efficient machines typically use the following values: Impulse turbines have the lowest ns values, typically ranging from 1 to 10, a Pelton wheel is typically around 4, Francis turbine
s fall in the range of 10 to 100, while Kaplan turbine
s are at least 100 or more, all in imperial units.
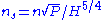 (dimensioned parameter),
(dimensioned parameter),  = rpm
= rpm
where: = angular velocity (radians per second)
= angular velocity (radians per second)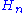 = Net head after turbine and waterway loss (m)
= Net head after turbine and waterway loss (m) = water flow (m³/s)
= water flow (m³/s)
s, the "specific speed" is defined as ns = n√(P)/h5/4
The factor 0.2626 is only required when the specific speed is to be adjusted to English units. In countries which use the metric system, the factor is omitted, and quoted specific speeds are correspondingly larger.
Turbine calculations:
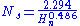
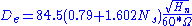
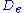 = Runner diameter (m)
= Runner diameter (m)
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
used to classify pump
Pump
A pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps...
impeller
Impeller
An impeller is a rotor inside a tube or conduit used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid.- Impellers in pumps :...
s as to their type and proportions. In Imperial unit
Imperial unit
The system of imperial units or the imperial system is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act of 1824, which was later refined and reduced. The system came into official use across the British Empire...
s it is defined as the speed in revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute is a measure of the frequency of a rotation. It annotates the number of full rotations completed in one minute around a fixed axis...
at which a geometrically similar impeller would operate if it were of such a size as to deliver one gallon per minute against one foot of hydraulic head
Hydraulic head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of water pressure above a geodetic datum. It is usually measured as a water surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance of a piezometer...
. In metric units flow may be in l/s or m³/s and head in m, and care must be taken to state the units used.
Performance is defined as the ratio of the pump or turbine against a reference pump or turbine, which divides the actual performance figure to provide a unitless figure of merit
Figure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
. The resulting figure would more descriptively be called the "ideal-reference-device-specific performance." This resulting unitless ratio may loosely be expressed as a "speed," only because the performance of the reference ideal pump is linearly dependent on its speed, so that the ratio of [device-performance to reference-device-performance] is also the increased speed the reference device would need to turn, in order to produce the performance, instead of its reference speed of "1 unit."
Specific speed is used in engineering design where it is thought of as an index used to predict desired pump or turbine characteristics; e.g., the general shape of a pump's impeller
Impeller
An impeller is a rotor inside a tube or conduit used to increase the pressure and flow of a fluid.- Impellers in pumps :...
. Often it is used to predict the type of pump or turbine required for a design flow rate and head. Once the desired specific speed is known, basic dimensions of the unit's components can be easily calculated.
Several mathematical definitions of specific speed (all of them actually ideal-device-specific) have been created for different devices and applications.
Pump specific speed
Low-specific speed radial flow impellers develop hydraulic headHydraulic head
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of water pressure above a geodetic datum. It is usually measured as a water surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance of a piezometer...
principally through centrifugal force
Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force can generally be any force directed outward relative to some origin. More particularly, in classical mechanics, the centrifugal force is an outward force which arises when describing the motion of objects in a rotating reference frame...
. Pumps of higher specific speeds develop head partly by centrifugal force and partly by axial force. An axial flow or propeller pump with a specific speed of 10,000 or greater generates its head exclusively through axial forces. Radial impellers are generally low flow/high head designs whereas axial flow impellers are high flow/low head designs.
Centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pump
A centrifugal pump is a rotodynamic pump that uses a rotating impeller to create flow by the addition of energy to a fluid. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used to move liquids through piping...
impellers have specific speed values ranging from 500 to 10,000 (English units), with radial flow pumps at 500-4000, mixed flow at 2000-8000 and axial flow pump
Axial flow pump
An axial flow pump, or AFP, is a common type of pump that essentially consists of a propeller in a pipe. The propeller can be driven directly by a sealed motor in the pipe or mounted to the pipe from the outside or by a right-angle drive shaft that pierces the pipe.The main advantage of an AFP is...
s at 7000-20,000. Values of specific speed less than 500 are associated with positive displacement pumps.
As the specific speed increases, the ratio of the impeller outlet diameter to the inlet or eye diameter decreases. This ratio becomes 1.0 for a true axial flow impeller.
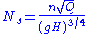
where:
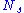 is specific speed (unitless)
is specific speed (unitless) is pump rotational speed (revolutions per seconds)
is pump rotational speed (revolutions per seconds) is flowrate (m³/s) at the point of best efficiency
is flowrate (m³/s) at the point of best efficiency is total head (m) per stage at the point of best efficiency
is total head (m) per stage at the point of best efficiency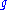 is acceleration due to gravity (m/s²)
is acceleration due to gravity (m/s²)Note that the units used affect the specific speed value and consistent units should be used for comparisons. Pump specific speed can be calculated using British gallons or using Metric units (m3/s or L/s and metres head), changing the values listed above.
Net suction specific speed
The net suction specific speed is mainly used to see if there will be problems with cavitation during the pump's operation on the suction side . It is defined by centrifugal and axial pumps' inherent physical characteristics and operating point . The net suction specific speed of a pump will define the range of operation in which a pump will experience stable operation. The higher the net suction specific speed, then the smaller the range of stable operation. The envelope of stable operation is defined in terms of the best efficiency point of the pump.
The net suction specific speed is defined as:
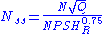
where:
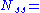 net suction specific speed
net suction specific speed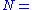 rotational speed of pump in rpm
rotational speed of pump in rpm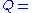 flow of pump in US gallons per minute
flow of pump in US gallons per minute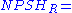 Net positive suction head (NPSH) required in feet at pump's best efficiency point
Net positive suction head (NPSH) required in feet at pump's best efficiency pointTurbine specific speed
The specific speed value (radian/second) for a turbine is the speed of a geometrically similar turbine which would produce one unit of the specific speed of a turbine is given by the manufacturer (along with other ratings) and will always refer to the point of maximum efficiency. This allows accurate calculations to be made of the turbine's performance for a range of heads.Well-designed efficient machines typically use the following values: Impulse turbines have the lowest ns values, typically ranging from 1 to 10, a Pelton wheel is typically around 4, Francis turbine
Francis turbine
The Francis turbine is a type of water turbine that was developed by James B. Francis in Lowell, Massachusetts. It is an inward-flow reaction turbine that combines radial and axial flow concepts....
s fall in the range of 10 to 100, while Kaplan turbine
Kaplan turbine
The Kaplan turbine is a propeller-type water turbine which has adjustable blades. It was developed in 1913 by the Austrian professor Viktor Kaplan, who combined automatically adjusted propeller blades with automatically adjusted wicket gates to achieve efficiency over a wide range of flow and...
s are at least 100 or more, all in imperial units.
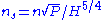 (dimensioned parameter),
(dimensioned parameter),  = rpm
= rpm where:
 = angular velocity (radians per second)
= angular velocity (radians per second)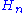 = Net head after turbine and waterway loss (m)
= Net head after turbine and waterway loss (m) = water flow (m³/s)
= water flow (m³/s)-
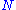 = Wheel speed (rpm)
= Wheel speed (rpm) -
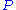 = Power (kW)
= Power (kW) -
 = Water head (m)
= Water head (m)
English units
Expressed in English unitEnglish unit
English units are the historical units of measurement used in England up to 1824, which evolved as a combination of the Anglo-Saxon and Roman systems of units...
s, the "specific speed" is defined as ns = n√(P)/h5/4
- where n is the wheel speed in rpm
- P is the power in horsepowerHorsepowerHorsepower is the name of several units of measurement of power. The most common definitions equal between 735.5 and 750 watts.Horsepower was originally defined to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses in continuous operation. The unit was widely adopted to measure the...
- h is the water head in feet
Metric units
Expressed in metric units, the "specific speed" is ns = 0.2626 n√(P)/h5/4- where n is the wheel speed in rpm
- P is the power in kilowatts
- h is the water head in meters
The factor 0.2626 is only required when the specific speed is to be adjusted to English units. In countries which use the metric system, the factor is omitted, and quoted specific speeds are correspondingly larger.
Example
Given a flow and head for a specific hydro site, and the RPM requirement of the generator, calculate the specific speed. The result is the main criteria for turbine selection or the starting point for analytical design of a new turbine. Once the desired specific speed is known, basic dimensions of the turbine parts can be easily calculated.Turbine calculations:
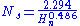
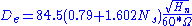
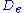 = Runner diameter (m)
= Runner diameter (m)See also
- PumpPumpA pump is a device used to move fluids, such as liquids, gases or slurries.A pump displaces a volume by physical or mechanical action. Pumps fall into three major groups: direct lift, displacement, and gravity pumps...
- Net positive suction headNPSHNPSH is an initialism for Net Positive Suction Head. In any cross-section of a generic hydraulic circuit, the NPSH parameter shows the difference between the actual pressure of a liquid in a pipeline and the liquid's vapor pressure at a given temperature.NPSH is an important parameter to take into...
- Best efficiency point
- Water turbineWater turbineA water turbine is a rotary engine that takes energy from moving water.Water turbines were developed in the 19th century and were widely used for industrial power prior to electrical grids. Now they are mostly used for electric power generation. They harness a clean and renewable energy...

