In
X-bar theoryX-bar theory is a component of linguistic theory which attempts to identify syntactic features presumably common to all those human languages that fit in a presupposed framework...
in
linguisticsLinguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
,
specifiers, head words, and
complementIn grammar the term complement is used with different meanings. The primary meaning is a word, phrase or clause that is necessary in a sentence to complete its meaning. We find complements that function as an argument and complements that exist within arguments.Both complements and modifiers add...
s together form phrases. Specifiers differ from complements because they are not sisters of the head, but rather sisters of the phrase formed by the head and the complement. In English, some example of specifiers are words such as
the,
no,
some,
every,
John's and
my mother's which can precede
Noun phraseIn grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
s.
Adverbial phraseAn adverbial phrase is a linguistic term for a group of two or more words operating adverbially, when viewed in terms of their syntactic function.Compare the following sentences:*I'll go to bed soon.*I'll go to bed in an hour....
s can be preceded by degree words such as
very,
extremely,
rather and
quite.
These specifiers are so called because they further qualify the category of the head - in these examples nouns and adverbs - in the phrase.
For example:
- My friend likes [Jane Austen's novels] - Jane Austen's specifies novels in this noun phrase
- She is [quite certain of success] - quite specifies certain of success in the adverbial phrase quite certain of success
In recent
transformational grammarIn linguistics, a transformational grammar or transformational-generative grammar is a generative grammar, especially of a natural language, that has been developed in the Chomskyan tradition of phrase structure grammars...
, the term
specifier is not normally used to refer to a type of word or phrase, but rather to a structural position provided by X-bar theory or some derivative thereof. In this usage, a phrase (usually a full XP, though in bare phrase structure it could in theory be an intermediate category) is said to occupy the specifier (SpecXP for short) of a head X.
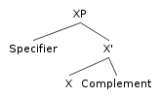
In technical
syntaxIn linguistics, syntax is the study of the principles and rules for constructing phrases and sentences in natural languages....
terminology,
specifier is the sister of X′ in the
X-barX-bar theory is a component of linguistic theory which attempts to identify syntactic features presumably common to all those human languages that fit in a presupposed framework...
schema of
phrase structureIn everyday speech, a phrase may refer to any group of words. In linguistics, a phrase is a group of words which form a constituent and so function as a single unit in the syntax of a sentence. A phrase is lower on the grammatical hierarchy than a clause....
seen in the
tree diagramA concrete syntax tree or parse tree or parsing treeis an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some formal grammar. In a parse tree, the interior nodes are labeled by non-terminals of the grammar, while the leaf nodes are labeled by terminals of the...
below (where XP corresponds to X″):
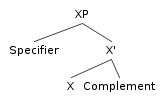
Different form classes can occupy a specifier position, typically determinersA determiner is a noun-modifier that expresses the reference of a noun or noun-phrase in the context, rather than attributes expressed by adjectives...
and possessorsPossession, in the context of linguistics, is an asymmetric relationship between two constituents, the referent of one of which possesses the referent of the other ....
in noun phraseIn grammar, a noun phrase, nominal phrase, or nominal group is a phrase based on a noun, pronoun, or other noun-like word optionally accompanied by modifiers such as adjectives....
s (N″), and an auxiliary verbIn linguistics, an auxiliary verb is a verb that gives further semantic or syntactic information about a main or full verb. In English, the extra meaning provided by an auxiliary verb alters the basic meaning of the main verb to make it have one or more of the following functions: passive voice,...
in a verb phraseIn linguistics, a verb phrase or VP is a syntactic unit composed of at least one verb and the dependents of that verb. One can distinguish between two types of VPs, finite VPs and non-finite VPs . While phrase structure grammars acknowledge both, dependency grammars reject the existence of a...
(V″).
The source of this article is
wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The text of this article is licensed under the
GFDL.