
Spectral flatness
Encyclopedia
Spectral flatness or tonality coefficient, also known as Wiener entropy, is a measure used in digital signal processing
to characterize an audio spectrum
. Spectral flatness, measured in decibels, provides a way to quantify how tone
-like a sound is, as opposed to being noise
-like. The meaning of tonal in this context is in the sense of the amount of peaks or resonant structure in a power spectrum, as opposed to flat spectrum of a white noise
. A high spectral flatness indicates that the spectrum has a similar amount of power in all spectral bands – this would sound similar to white noise, and the graph of the spectrum would appear relatively flat and smooth. A low spectral flatness indicates that the spectral power is concentrated in a relatively small number of bands – this would typically sound like a mixture of sine wave
s, and the spectrum would appear "spiky".
The spectral flatness is calculated by dividing the geometric mean
of the power spectrum by the arithmetic mean
of the power spectrum, i.e.:
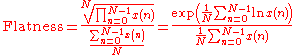
where x(n) represents the magnitude of bin number n
. Note that a single (or more) empty bin yields a flatness of 0, so this measure is most useful when bins are generally not empty.
The spectral flatness can also be measured within a specified subband, rather than across the whole band.
standard, in which it is labelled"AudioSpectralFlatness" .
In birdsong
research, it has been used as one of the features measured on birdsong audio, when testing similarity between two excerpts.
Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
to characterize an audio spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
. Spectral flatness, measured in decibels, provides a way to quantify how tone
Pitch (music)
Pitch is an auditory perceptual property that allows the ordering of sounds on a frequency-related scale.Pitches are compared as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies,...
-like a sound is, as opposed to being noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
-like. The meaning of tonal in this context is in the sense of the amount of peaks or resonant structure in a power spectrum, as opposed to flat spectrum of a white noise
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
. A high spectral flatness indicates that the spectrum has a similar amount of power in all spectral bands – this would sound similar to white noise, and the graph of the spectrum would appear relatively flat and smooth. A low spectral flatness indicates that the spectral power is concentrated in a relatively small number of bands – this would typically sound like a mixture of sine wave
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
s, and the spectrum would appear "spiky".
The spectral flatness is calculated by dividing the geometric mean
Geometric mean
The geometric mean, in mathematics, is a type of mean or average, which indicates the central tendency or typical value of a set of numbers. It is similar to the arithmetic mean, except that the numbers are multiplied and then the nth root of the resulting product is taken.For instance, the...
of the power spectrum by the arithmetic mean
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
of the power spectrum, i.e.:
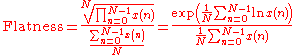
where x(n) represents the magnitude of bin number n
Histogram
In statistics, a histogram is a graphical representation showing a visual impression of the distribution of data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable and was first introduced by Karl Pearson...
. Note that a single (or more) empty bin yields a flatness of 0, so this measure is most useful when bins are generally not empty.
The spectral flatness can also be measured within a specified subband, rather than across the whole band.
Applications
This measurement is one of the many audio descriptors used in the MPEG-7MPEG-7
MPEG-7 is a multimedia content description standard. It was standardized in ISO/IEC 15938 . This description will be associated with the content itself, to allow fast and efficient searching for material that is of interest to the user. MPEG-7 is formally called Multimedia Content Description...
standard, in which it is labelled
In birdsong
Birdsong
Birdsong may refer to:* Bird vocalization, the sounds of birds* Birdsong , a 1993 novel by Sebastian Faulks* Birdsong, Arkansas, USA* Birdsong , a channel on the UK Digital One digital radio multiplex...
research, it has been used as one of the features measured on birdsong audio, when testing similarity between two excerpts.

