
Spectral sensitivity
Encyclopedia
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
or other signal, as a function of the frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
or wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of the signal.
In visual
Color vision
Color vision is the capacity of an organism or machine to distinguish objects based on the wavelengths of the light they reflect, emit, or transmit...
neuroscience
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system. Traditionally, neuroscience has been seen as a branch of biology. However, it is currently an interdisciplinary science that collaborates with other fields such as chemistry, computer science, engineering, linguistics, mathematics,...
, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics of the photopigment
Photopigment
Photopigments are unstable pigments that undergo a chemical change when they absorb light. The term is generally applied to the non-protein chromophore moiety of photosensitive chromoproteins, such as the pigments involved in photosynthesis and photoreception...
s in the rod cell
Rod cell
Rod cells, or rods, are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in less intense light than can the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Named for their cylindrical shape, rods are concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On...
s and cone cell
Cone cell
Cone cells, or cones, are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that are responsible for color vision; they function best in relatively bright light, as opposed to rod cells that work better in dim light. If the retina is exposed to an intense visual stimulus, a negative afterimage will be...
s in the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
of the eye
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
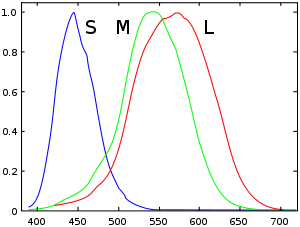
. It is known that the rod cells are more suited to scotopic vision
Scotopic vision
Scotopic vision is the vision of the eye under low light conditions. The term comes from Greek skotos meaning darkness and -opia meaning a condition of sight...
and cone cells to photopic vision
Photopic vision
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions. In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher visual acuity and temporal resolution than available with scotopic vision.The human eye uses three types...
, and that they differ in their sensitivity to different wavelengths of light.
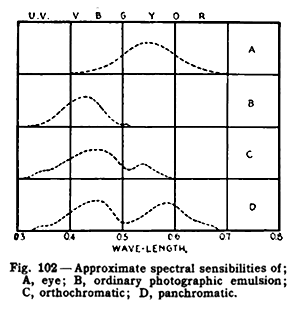
In photography
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
, film and sensors are often described in terms of their spectral sensitivity, to supplement their characteristic curves
Sensitometry
Sensitometry is the scientific study of light-sensitive materials, especially photographic film. The study has its origins in the work by Ferdinand Hurter and Vero Charles Driffield with early black-and-white emulsions...
that describe their responsivity
Responsivity
Responsivity measures the input–output gain of a detector system. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the local slope ....
. For X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
films, the spectral sensitivity is chosen to be appropriate to the phosphors that respond to X-rays, rather than being related to human vision.
In sensor
Sensor
A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. For example, a mercury-in-glass thermometer converts the measured temperature into expansion and contraction of a liquid which can be read on a calibrated...
systems, where the output is easily quantified, the responsivity
Responsivity
Responsivity measures the input–output gain of a detector system. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the local slope ....
can be extended to be wavelength dependent, incorporating the spectral sensitivity. When the sensor system is linear, its spectral sensitivity and spectral responsivity can both be decomposed with similar basis functions. When a system's responsivity is a fixed monotonic nonlinear function, that nonlinearity can be estimated and corrected for, to determine the spectral sensitivity from spectral input–output data via standard linear methods.
The responses of the rod and cone cells of the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
, however, have a very context-dependent (coupled) nonlinear response, which complicates the analysis of their spectral sensitivities from experimental data. In spite of these complexities, however, the conversion of light energy spectra to the effective stimulus, the excitation of the photopigment
Photopigment
Photopigments are unstable pigments that undergo a chemical change when they absorb light. The term is generally applied to the non-protein chromophore moiety of photosensitive chromoproteins, such as the pigments involved in photosynthesis and photoreception...
, is quite linear, and linear characterizations such as spectral sensitivity are therefore quite useful in describing many properties of color vision
Color vision
Color vision is the capacity of an organism or machine to distinguish objects based on the wavelengths of the light they reflect, emit, or transmit...
.
Spectral sensitivity is sometimes expressed as a quantum efficiency
Quantum efficiency
Quantum efficiency is a quantity defined for a photosensitive device such as photographic film or a charge-coupled device as the percentage of photons hitting the photoreactive surface that will produce an electron–hole pair. It is an accurate measurement of the device's electrical sensitivity to...
, that is, as probability of getting a quantum reaction, such as a captured electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
, to a quantum of light, as a function of wavelength. In other contexts, the spectral sensitivity is expressed as the relative response per light energy, rather than per quantum, normalized to a peak value of 1, and a quantum efficiency is used to calibrate the sensitivity at that peak wavelength. In some linear applications, the spectral sensitivity may be expressed as a spectral responsivity
Responsivity
Responsivity measures the input–output gain of a detector system. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the local slope ....
, with units such as ampere
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
s per watt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
.

