Spectral slope
Encyclopedia
In astrophysics
and planetary science
, spectral slope, also called spectral gradient , is a measure of dependence of the reflectance on the wavelength
.
In digital signal processing
, it is a measure of how quickly the spectrum of an audio sound tails off towards the high frequencies, calculated using a linear regression
.
spectrum
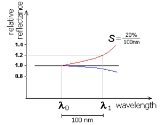
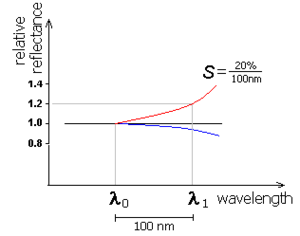
of the reflected sunlight is used to infer physical and chemical properties of the surface of a body. Some objects are brighter (reflect more) in longer wavelengths (red). Consequently, in visible light they will appear redder than objects showing no dependence of reflectance on the wavelength.
The diagram illustrates three slopes:
The slope (spectral gradient) is defined as:

The slope is typically expressed in percentage increase of reflectance (i.e. reflexivity) per unit of wavelength: %/100 nm (or % /1000 Å
)
The slope is mostly used in near infrared part of the spectrum while colour indices
are commonly used in the visible part of the spectrum.
The trans-Neptunian object
Sedna
is a typical example of a body showing a steep red slope (20%/100 nm) while Orcus'
spectrum appears flat in near infra-red.
to the Fourier magnitude spectrum of the signal, which produces a single number indicating the slope of the line-of-best-fit through the spectral data .
Alternative ways to characterise a sound signal's distribution of energy vs frequency include spectral rolloff, spectral centroid
.
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physics of the universe, including the physical properties of celestial objects, as well as their interactions and behavior...
and planetary science
Planetary science
Planetary science is the scientific study of planets , moons, and planetary systems, in particular those of the Solar System and the processes that form them. It studies objects ranging in size from micrometeoroids to gas giants, aiming to determine their composition, dynamics, formation,...
, spectral slope, also called spectral gradient , is a measure of dependence of the reflectance on the wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
.
In digital signal processing
Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
, it is a measure of how quickly the spectrum of an audio sound tails off towards the high frequencies, calculated using a linear regression
Linear regression
In statistics, linear regression is an approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar variable y and one or more explanatory variables denoted X. The case of one explanatory variable is called simple regression...
.

Spectral slope in Astrophysics / Planetary Science
The visible and infraredInfrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
of the reflected sunlight is used to infer physical and chemical properties of the surface of a body. Some objects are brighter (reflect more) in longer wavelengths (red). Consequently, in visible light they will appear redder than objects showing no dependence of reflectance on the wavelength.
The diagram illustrates three slopes:
- a red slope, the reflectance is increasing with the wavelengths
- flat spectrum (in black)
- And a blue slope, the reflectance actually diminishing with the wavelengths
The slope (spectral gradient) is defined as:

- where
 is the reflectance measured with filters F0, F1 having the central wavelengths λ0 and λ1, respectively.
is the reflectance measured with filters F0, F1 having the central wavelengths λ0 and λ1, respectively.
The slope is typically expressed in percentage increase of reflectance (i.e. reflexivity) per unit of wavelength: %/100 nm (or % /1000 Å
Ångström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
)
The slope is mostly used in near infrared part of the spectrum while colour indices
Color index
In astronomy, the color index is a simple numerical expression that determines the color of an object, which in the case of a star gives its temperature...
are commonly used in the visible part of the spectrum.
The trans-Neptunian object
Trans-Neptunian object
A trans-Neptunian object is any minor planet in the Solar System that orbits the Sun at a greater distance on average than Neptune.The first trans-Neptunian object to be discovered was Pluto in 1930...
Sedna
90377 Sedna
90377 Sedna is a trans-Neptunian object discovered in 2003, which was about three times as far from the Sun as Neptune. For most of its orbit it is even further from the Sun, with its aphelion estimated at 960 astronomical units , making it one of the most distant known objects in the Solar System...
is a typical example of a body showing a steep red slope (20%/100 nm) while Orcus'
90482 Orcus
90482 Orcus is a trans-Neptunian object in the Kuiper belt with a large moon. It was discovered on February 17, 2004 by Michael Brown of Caltech, Chad Trujillo of the Gemini Observatory, and David Rabinowitz of Yale University. Precovery images as early as November 8, 1951 were later identified...
spectrum appears flat in near infra-red.
Spectral slope in audio
The spectral "slope" of many natural audio signals (their tendency to have less energy at high frequencies) has been known for many years , and the fact that this slope is related to the nature of the sound source. One way to quantify this is by applying linear regressionLinear regression
In statistics, linear regression is an approach to modeling the relationship between a scalar variable y and one or more explanatory variables denoted X. The case of one explanatory variable is called simple regression...
to the Fourier magnitude spectrum of the signal, which produces a single number indicating the slope of the line-of-best-fit through the spectral data .
Alternative ways to characterise a sound signal's distribution of energy vs frequency include spectral rolloff, spectral centroid
Spectral centroid
The spectral centroid is a measure used in digital signal processing to characterise a spectrum. It indicates where the "center of mass" of the spectrum is...
.

