
Sphaerotheca castagnei
Encyclopedia
Sphaerotheca castagnei is a species of ascomycete fungi in the Erysiphaceae
family. A plant pathogen, it causes a form of Powdery mildew
.
is abundant and persistent or sometimes inconspicuous, occurring on either side or both sides of the infected leaves. The perithecia are abundant, scattered or somewhat aggregated, small, usually about 75 µm
long, but varying from 60–100 µm. The texture is soft, surface uneven, reticulations very large and irregular, 20–30 µm. The appendages are long, stout, usually colored throughout, but sometimes colorless, flexuous, somewhat uneven in width, and more or less interwoven with the mycelium. The ascus
is rather small, elliptical or suborbicular in shape.
and antheridium
, which are formed where two neighboring hypha
e approach, each contain a single nucleus. The cell wall between these organs is dissolved at the time of fertilization and the male and female nuclei unite and a fresh wall is laid down between the two organs.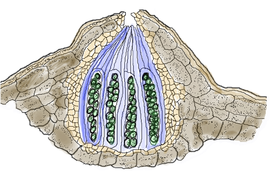 Now the wall of the future perithecium beings to form by the development of a number of upright hyphal branches around the oogonium, forming a pseudo-parenchymatous tissue, while the other branches later absorbed grow into the interior of the developing perithecium, while the outer cell walls become flattened and darker in color. Like other species in Sphaerotheca, S. castagnei contains only a single ascus
Now the wall of the future perithecium beings to form by the development of a number of upright hyphal branches around the oogonium, forming a pseudo-parenchymatous tissue, while the other branches later absorbed grow into the interior of the developing perithecium, while the outer cell walls become flattened and darker in color. Like other species in Sphaerotheca, S. castagnei contains only a single ascus
. The the cell in which the egg nucleus develops and is fertilized (the carpogonium) elongates, divides and a curved row of 5 or 6 cells is formed. The penultimate cell of this row contains two large nuclei, while the other cells of the row have one nucleus each. The young ascus develops from this penultimate cell in which the two nuclei fuse following a rapid increase in the size of the ascus, which presses against the inner wall cells of the perithecium and absorbs them. The nucleus of the ascus finally divides three times, producing the nuclei of the eight ascospores, which subsequently are formed by free cell formation. From the half-grown perithecium there arise hyphae which grow out as the appendages. These appendages serve to attach the perithecia to plants.
. This is accomplished by the appearance of a vertical slit in the perithecium from which the ascus protrudes, swelling to several times the diameter of the perithecium. The walls of the ascus become rigid, the ascospores collect at the apex, eventually being discharged forcibly through the slit. Sometimes an ascus slips out of the perithecium, bursting open to discharge the spores.
Erysiphaceae
The Erysiphaceae are fungal family of the order Erysiphales. The family contains many of the powdery mildews.-Genera:*Arthrocladiella*Blumeria*Brasiliomyces*Bulbomicrosphaera*Bulbouncinula*Caespitotheca...
family. A plant pathogen, it causes a form of Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of fungi in the order Erysiphales. It is one of the easier diseases to spot, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the...
.
Description
The myceliumMycelium
thumb|right|Fungal myceliaMycelium is the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, thread-like hyphae. The mass of hyphae is sometimes called shiro, especially within the fairy ring fungi. Fungal colonies composed of mycelia are found in soil and on or within many other...
is abundant and persistent or sometimes inconspicuous, occurring on either side or both sides of the infected leaves. The perithecia are abundant, scattered or somewhat aggregated, small, usually about 75 µm
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
long, but varying from 60–100 µm. The texture is soft, surface uneven, reticulations very large and irregular, 20–30 µm. The appendages are long, stout, usually colored throughout, but sometimes colorless, flexuous, somewhat uneven in width, and more or less interwoven with the mycelium. The ascus
Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
is rather small, elliptical or suborbicular in shape.
Development of the perithecium
The oogoniumOogonium
"Oogonium" may refer to either a primordial oocyte in a female fetus or the female gametangium of certain thallophytes.-in the fetus:Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells...
and antheridium
Antheridium
An antheridium or antherida is a haploid structure or organ producing and containing male gametes . It is present in the gametophyte phase of lower plants like mosses and ferns, and also in the primitive vascular psilotophytes...
, which are formed where two neighboring hypha
Hypha
A hypha is a long, branching filamentous structure of a fungus, and also of unrelated Actinobacteria. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium; yeasts are unicellular fungi that do not grow as hyphae.-Structure:A hypha consists of one or...
e approach, each contain a single nucleus. The cell wall between these organs is dissolved at the time of fertilization and the male and female nuclei unite and a fresh wall is laid down between the two organs.

Ascus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
. The the cell in which the egg nucleus develops and is fertilized (the carpogonium) elongates, divides and a curved row of 5 or 6 cells is formed. The penultimate cell of this row contains two large nuclei, while the other cells of the row have one nucleus each. The young ascus develops from this penultimate cell in which the two nuclei fuse following a rapid increase in the size of the ascus, which presses against the inner wall cells of the perithecium and absorbs them. The nucleus of the ascus finally divides three times, producing the nuclei of the eight ascospores, which subsequently are formed by free cell formation. From the half-grown perithecium there arise hyphae which grow out as the appendages. These appendages serve to attach the perithecia to plants.
Spore discharge
Spore discharge in S. castagnei involves the rupture of the cleistothecium, and the escape of the spores from the ascusAscus
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. On average, asci normally contain eight ascospores, produced by a meiotic cell division followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can number one , two, four, or multiples...
. This is accomplished by the appearance of a vertical slit in the perithecium from which the ascus protrudes, swelling to several times the diameter of the perithecium. The walls of the ascus become rigid, the ascospores collect at the apex, eventually being discharged forcibly through the slit. Sometimes an ascus slips out of the perithecium, bursting open to discharge the spores.

