
SpinRite
Encyclopedia
SpinRite is a computer
software program for scanning magnetic data storage devices such as hard disk
s, recovering data from them and refreshing their surfaces. It is proprietary
and commercial software written by Steve Gibson of Gibson Research Corporation. The first version was released in 1988. Version 6.0, still current , was released in 2004. SpinRite may be run from a bootable floppy disk
, USB flash drive
or CD-ROM
on a PC-compatible
computer, independent of the operating system
installed on the host computer.
, and USB-interface
d hard disks, and floppy disks. It analyzes their contents and is claimed to be able to refresh the magnetic disk surfaces to allow them to operate more reliably.
SpinRite attempts to recover data from hard disks with damaged portions that may not be readable via the operating system. When the program encounters a sector with errors that cannot be corrected by the disk drive's error-correcting code, it tries to read the sector up to 2000 times, in order to determine, by comparing the successive results, the most probable value of each bit
. The data is then saved onto a new block on the same disk; it cannot be saved elsewhere. In this respect SpinRite differs from most data recovery
software, which usually provides (and recommends) an option to save the recovered data onto another disk, or onto a separate partition on the same disk.
Gibson Research Corporation claims their SpinRite software will diagnose the quality of a disk drive, and make it work as reliably as possible with future use. Its developer, Steve Gibson
, says his software was specifically designed to fix sector problems
. However, if a hard drive's circuit board, drive motors or other mechanical parts are defective, or there is systemic file system corruption, SpinRite may be of little or no help. In fact, in such circumstances no purely software-based solution would be sufficient to overcome the problem. When a hard drive has begun to develop mechanical faults, a program like SpinRite may sometimes be able to extend its usable life for long enough to carry out successful file recovery with other specialized software.
SpinRite is declared by its developer to have certain unique features, such as disabling of disk write caching, disabling of auto-relocation, compatibility with disk compression, identification of the "data-to-flux-reversal encoder-decoder" used in a drive, and separate testing of buffered and unbuffered disk read performance. Another important feature is direct hardware-level access, whereby the drive's internal controller interacts directly with the program, rather than through the operating system. This, in turn, allows dynamic head repositioning, whereby, when reading a faulty sector, the reading head is deliberately moved backwards and forwards many times, by varying amounts, in the hope that each time it returns to the sector, it may come to rest in a slightly different position. By performing statistical analysis on the succession of results thus obtained, SpinRite is, according to its maker, often able to "reconstruct" data from damaged sectors; and even in those cases in which complete reconstruction proves impossible, SpinRite is able to extract all intact bits from a partially damaged sector, and to copy them to a new block, thereby minimizing the amount of data lost.
Certain claims made by SpinRite's makers have proved controversial. The program's claimed ability to "refresh" aging drives has been met with particular skepticism, while its "recovery" of sectors marked as damaged by the file system controller is considered by some to be undesirable and ultimately counter-productive.
SpinRite is written in x86 assembly language
, and runs only on PC-compatible
computers with 32-bit Intel or AMD x86 processor, but it can operate on any attached storage device with a compatible interface. It can be run only under MS-DOS
or a compatible operating system, but the operating system installed on the machine is irrelevant, as Spinrite is distributed in bootable version with the FreeDOS
operating system. Version 6 is compatible with hard disks containing any logical volume management
or file system such as FAT16 or 32, NTFS
, Ext3
as well as other Linux File Systems, HFS+ For Mac OS X
, Tivo
and others, as it operates only on the disk itself. Drives attached to computers with other processors can be recovered by temporarily connecting the drive to a suitable computer. Version 6 includes a Microsoft Windows
utility to create a FreeDOS
boot floppy disk
or CD-ROM
for the program.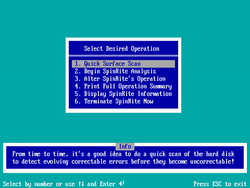 Version 6 is rather different from previous versions. It offers full access to the entire disk surface regardless of partitioning
Version 6 is rather different from previous versions. It offers full access to the entire disk surface regardless of partitioning
, Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) parameters and control of partial scanning within a specified percentage range. Version 5 was limited to AT Attachment
(PATA, IDE) hard drives; version 6 may, on suitable motherboards, work on newer Serial ATA
(SATA) and USB
hard drives, and with any other type of drive—SCSI
, 1394/Firewire—that can be made visible to MS-DOS through the addition of controller BIOS
or add-on DOS driver
s.
The price was US$89. Documentation may be downloaded free of charge from the SpinRite website.
Though there are many commercial and freeware file recovery programs available, besides SpinRite only the HDD Regenerator offers direct hardware-level access to the disk, while others are more suitable for recovery of deleted and corrupted files and formatted drives. Some are intended to recover only accidentally deleted files (e.g., OfficeRecovery's FreeUndelete). Others will recover files of certain types, using knowledge of the file structure (e.g., GetData's Recover My Files).
Roadkil's Unstoppable Copier runs under Windows and copies on a file, not sector, basis. It can be set to copy all undamaged files first, and then to try to copy as much as possible of damaged files (although, during extraction, it is difficult to see which file is being copied, and thus to avoid copying files not worth recovering).
Open Source Unix-based alternatives include dd_rescue and dd_rhelp, which work together, or GNU ddrescue. dd_rhelp first extracts all the readable data, and saves it to a file, inserting zeros where bytes cannot be read. Then it tries to re-read the invalid data and update this file. GNU
ddrescue can be used to copy data directly to a new disk if needed, just like Linux dd
.
dd_rhelp or GNU ddrescue will yield a complete disk image, faster but possibly with some errors. GNU ddrescue is generally much faster whereas dd_rhelp is a shell script wrapper around dd_rescue. Both dd_rhelp and GNU ddrescue aim to copy data quickly from sectors that are free of errors, then copy in smaller blocks, with retries when necessary, where errors are found. These programs are more complicated to use than SpinRite, although GNU ddrescue is fairly easy to use with default options, and can easily be downloaded and compiled on Linux-based Live CD
s such as Knoppix
. It can also be used with SystemRescueCD
.
On some disks, many files may be damaged. In practice, though, in most cases, most damaged files will be unimportant: temporary files, files which may easily be replaced by reinstalling software, and so on. Executable program files are generally not worth rescuing unless they are guaranteed 100% intact. Moreover, fully recovered program folders will often not give rise to working software, as corresponding registry entries will no longer be associated with them correctly. By contrast, some documents may be worth rescuing even if incomplete. For example, a document created by a given word-processing program may become corrupted, thus rendering it unreadable by the program normally associated with it, yet much of the text contained in the document may still be read, and perhaps extracted, by making use of a more generic text editor (although, in such a case, program-specific formatting characters will usually be dispersed throughout the text, making both reading and extraction laborious).
Any sector-based rescue system is bound to spend a lot of its time trying to read unwanted data. File-based systems, by contrast, will often allow the user to ignore files that are a waste of time, and will also often identify and list files that are not intact, so long as the file system
is not so damaged as to be unable to identify files. Such systems can, therefore, sometimes prove more practical for the purposes of useful file recovery. However, a sector-based program, which reads data in raw format, sometimes using specialized techniques to recover partially damaged information, may ultimately recover more useful data.
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
software program for scanning magnetic data storage devices such as hard disk
Hard disk
A hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the...
s, recovering data from them and refreshing their surfaces. It is proprietary
Proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
and commercial software written by Steve Gibson of Gibson Research Corporation. The first version was released in 1988. Version 6.0, still current , was released in 2004. SpinRite may be run from a bootable floppy disk
Floppy disk
A floppy disk is a disk storage medium composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular plastic carrier lined with fabric that removes dust particles...
, USB flash drive
USB flash drive
A flash drive is a data storage device that consists of flash memory with an integrated Universal Serial Bus interface. flash drives are typically removable and rewritable, and physically much smaller than a floppy disk. Most weigh less than 30 g...
or CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
on a PC-compatible
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
computer, independent of the operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
installed on the host computer.
Features
SpinRite tests the data surfaces of writeable magnetic disks, including IDE, SATASata
Sata is a traditional dish from the Malaysian state of Terengganu, consisting of spiced fish meat wrapped in banana leaves and cooked on a grill.It is a type of Malaysian fish cake, or otak-otak...
, and USB-interface
Interface
-Academic journals:* Interface: a journal for and about social movements* Interfaces * Journal of the Royal Society Interface* The Technology Interface Journal-Science:* Biointerface* Interface , boundary surface...
d hard disks, and floppy disks. It analyzes their contents and is claimed to be able to refresh the magnetic disk surfaces to allow them to operate more reliably.
SpinRite attempts to recover data from hard disks with damaged portions that may not be readable via the operating system. When the program encounters a sector with errors that cannot be corrected by the disk drive's error-correcting code, it tries to read the sector up to 2000 times, in order to determine, by comparing the successive results, the most probable value of each bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
. The data is then saved onto a new block on the same disk; it cannot be saved elsewhere. In this respect SpinRite differs from most data recovery
Data recovery
Data recovery is the process of salvaging data from damaged, failed, corrupted, or inaccessible secondary storage media when it cannot be accessed normally. Often the data are being salvaged from storage media such as internal or external hard disk drives, solid-state drives , USB flash drive,...
software, which usually provides (and recommends) an option to save the recovered data onto another disk, or onto a separate partition on the same disk.
Gibson Research Corporation claims their SpinRite software will diagnose the quality of a disk drive, and make it work as reliably as possible with future use. Its developer, Steve Gibson
Steve Gibson
Steve Gibson is a computer enthusiast, software engineer and security researcher who studied Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the University of California, Berkeley. Gibson currently lives in Laguna Hills, California...
, says his software was specifically designed to fix sector problems
Bad Sector
Bad Sector is an ambient/noise project formed in 1992 in Tuscany, Italy by Massimo Magrini. While working at the Computer Art Lab of ISTI in Pisa , he developed original gesture interfaces that he uses in live performances: 'Aerial Painting Hand' , 'UV-Stick' Bad Sector is an ambient/noise...
. However, if a hard drive's circuit board, drive motors or other mechanical parts are defective, or there is systemic file system corruption, SpinRite may be of little or no help. In fact, in such circumstances no purely software-based solution would be sufficient to overcome the problem. When a hard drive has begun to develop mechanical faults, a program like SpinRite may sometimes be able to extend its usable life for long enough to carry out successful file recovery with other specialized software.
SpinRite is declared by its developer to have certain unique features, such as disabling of disk write caching, disabling of auto-relocation, compatibility with disk compression, identification of the "data-to-flux-reversal encoder-decoder" used in a drive, and separate testing of buffered and unbuffered disk read performance. Another important feature is direct hardware-level access, whereby the drive's internal controller interacts directly with the program, rather than through the operating system. This, in turn, allows dynamic head repositioning, whereby, when reading a faulty sector, the reading head is deliberately moved backwards and forwards many times, by varying amounts, in the hope that each time it returns to the sector, it may come to rest in a slightly different position. By performing statistical analysis on the succession of results thus obtained, SpinRite is, according to its maker, often able to "reconstruct" data from damaged sectors; and even in those cases in which complete reconstruction proves impossible, SpinRite is able to extract all intact bits from a partially damaged sector, and to copy them to a new block, thereby minimizing the amount of data lost.
Certain claims made by SpinRite's makers have proved controversial. The program's claimed ability to "refresh" aging drives has been met with particular skepticism, while its "recovery" of sectors marked as damaged by the file system controller is considered by some to be undesirable and ultimately counter-productive.
SpinRite is written in x86 assembly language
Assembly language
An assembly language is a low-level programming language for computers, microprocessors, microcontrollers, and other programmable devices. It implements a symbolic representation of the machine codes and other constants needed to program a given CPU architecture...
, and runs only on PC-compatible
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
computers with 32-bit Intel or AMD x86 processor, but it can operate on any attached storage device with a compatible interface. It can be run only under MS-DOS
MS-DOS
MS-DOS is an operating system for x86-based personal computers. It was the most commonly used member of the DOS family of operating systems, and was the main operating system for IBM PC compatible personal computers during the 1980s to the mid 1990s, until it was gradually superseded by operating...
or a compatible operating system, but the operating system installed on the machine is irrelevant, as Spinrite is distributed in bootable version with the FreeDOS
FreeDOS
FreeDOS is an operating system for IBM PC compatible computers. FreeDOS is made up of many different, separate programs that act as "packages" to the overall FreeDOS Project...
operating system. Version 6 is compatible with hard disks containing any logical volume management
Logical volume management
In computer storage, logical volume management or LVM provides a method of allocating space on mass-storage devices that is more flexible than conventional partitioning schemes...
or file system such as FAT16 or 32, NTFS
NTFS
NTFS is the standard file system of Windows NT, including its later versions Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, and Windows 7....
, Ext3
Ext3
The ext3 or third extended filesystem is a journaled file system that is commonly used by the Linux kernel. It is the default file system for many popular Linux distributions, including Debian...
as well as other Linux File Systems, HFS+ For Mac OS X
HFS Plus
HFS Plus or HFS+ is a file system developed by Apple Inc. to replace their Hierarchical File System as the primary file system used in Macintosh computers . It is also one of the formats used by the iPod digital music player...
, Tivo
TiVo
TiVo is a digital video recorder developed and marketed by TiVo, Inc. and introduced in 1999. TiVo provides an on-screen guide of scheduled broadcast programming television programs, whose features include "Season Pass" schedules which record every new episode of a series, and "WishList"...
and others, as it operates only on the disk itself. Drives attached to computers with other processors can be recovered by temporarily connecting the drive to a suitable computer. Version 6 includes a Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
utility to create a FreeDOS
FreeDOS
FreeDOS is an operating system for IBM PC compatible computers. FreeDOS is made up of many different, separate programs that act as "packages" to the overall FreeDOS Project...
boot floppy disk
Floppy disk
A floppy disk is a disk storage medium composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular plastic carrier lined with fabric that removes dust particles...
or CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
for the program.

Disk partitioning
Disk partitioning is the act of dividing a hard disk drive into multiple logical storage units referred to as partitions, to treat one physical disk drive as if it were multiple disks. Partitions are also termed "slices" for operating systems based on BSD, Solaris or GNU Hurd...
, Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.) parameters and control of partial scanning within a specified percentage range. Version 5 was limited to AT Attachment
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA , originally ATA, is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disks, solid-state drives, floppy drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by X3/INCITS committee...
(PATA, IDE) hard drives; version 6 may, on suitable motherboards, work on newer Serial ATA
Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
(SATA) and USB
USB mass storage device class
The USB mass storage device class, otherwise known as USB MSC or UMS, is a protocol that allows a Universal Serial Bus device to become accessible to a host computing device, to enable file transfers between the two...
hard drives, and with any other type of drive—SCSI
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, and electrical and optical interfaces. SCSI is most commonly used for hard disks and tape drives, but it...
, 1394/Firewire—that can be made visible to MS-DOS through the addition of controller BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
or add-on DOS driver
Device driver
In computing, a device driver or software driver is a computer program allowing higher-level computer programs to interact with a hardware device....
s.
The price was US$89. Documentation may be downloaded free of charge from the SpinRite website.
Issue with Serial ATA drives
While SATA drives are supported, SATA controllers that include a processor and diagnostic software can limit SpinRite's ability to obtain and display SMART data ("thin controller" SATA controllers do not have this limitation). This data monitor does not affect SpinRite's recovery and diagnostics ability; SMART data when available helps long-term disk maintenance and failure prediction. GRC said in 2006 that this issue would be resolved in version 6.1, a free-of-charge upgrade for SpinRite 6.0 users.Alternatives
SpinRite works entirely on the drive under investigation, attempting to recover partially damaged data by rewriting it to an undamaged part of the disk. This approach can cause irreversible data loss and may be unsuitable if there are many errors, as the task may take an unreasonably long time to complete (literally years for a large, badly damaged disc, attempting to read each sector 2000 times). The program may also be unsuitable for disks that are badly damaged and possibly worsening with use, as the data, even if successfully read, cannot be re-written securely on the disk. Also, if little free space remains on a faulty disk, there may be insufficient room to transfer all of the recovered data. In these cases, software that can recover as much data as possible and copy it to another drive will generally be a more suitable alternative. However, standard disk imaging and cloning software is not ideally suited for data recovery, even if some such software may be configured to copy only good sectors, ignoring sectors that are not easily readable.Though there are many commercial and freeware file recovery programs available, besides SpinRite only the HDD Regenerator offers direct hardware-level access to the disk, while others are more suitable for recovery of deleted and corrupted files and formatted drives. Some are intended to recover only accidentally deleted files (e.g., OfficeRecovery's FreeUndelete). Others will recover files of certain types, using knowledge of the file structure (e.g., GetData's Recover My Files).
Roadkil's Unstoppable Copier runs under Windows and copies on a file, not sector, basis. It can be set to copy all undamaged files first, and then to try to copy as much as possible of damaged files (although, during extraction, it is difficult to see which file is being copied, and thus to avoid copying files not worth recovering).
Open Source Unix-based alternatives include dd_rescue and dd_rhelp, which work together, or GNU ddrescue. dd_rhelp first extracts all the readable data, and saves it to a file, inserting zeros where bytes cannot be read. Then it tries to re-read the invalid data and update this file. GNU
GNU
GNU is a Unix-like computer operating system developed by the GNU project, ultimately aiming to be a "complete Unix-compatible software system"...
ddrescue can be used to copy data directly to a new disk if needed, just like Linux dd
Dd (Unix)
In computing, dd is a common Unix program whose primary purpose is the low-level copying and conversion of raw data. According to the manual page for Version 7 Unix, it will "convert and copy a file". It is used to copy a specified number of bytes or blocks, performing on-the-fly byte order...
.
dd_rhelp or GNU ddrescue will yield a complete disk image, faster but possibly with some errors. GNU ddrescue is generally much faster whereas dd_rhelp is a shell script wrapper around dd_rescue. Both dd_rhelp and GNU ddrescue aim to copy data quickly from sectors that are free of errors, then copy in smaller blocks, with retries when necessary, where errors are found. These programs are more complicated to use than SpinRite, although GNU ddrescue is fairly easy to use with default options, and can easily be downloaded and compiled on Linux-based Live CD
Live CD
A live CD, live DVD, or live disc is a CD or DVD containing a bootable computer operating system. Live CDs are unique in that they have the ability to run a complete, modern operating system on a computer lacking mutable secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive...
s such as Knoppix
Knoppix
Knoppix, or KNOPPIX , is an operating system based on Debian designed to be run directly from a CD / DVD or a USB key , one of the first of its kind for any operating system. Knoppix was developed by Linux consultant Klaus Knopper. When starting a program, it is loaded from the removable medium...
. It can also be used with SystemRescueCD
SystemRescueCD
SystemRescueCd is an operating system for the x86 computer platform, though the primary purpose of SystemRescueCD is to repair unbootable or otherwise damaged computer systems after a system crash. SystemRescueCD is not intended to be used as a permanent operating system. It runs from a Live CD or...
.
On some disks, many files may be damaged. In practice, though, in most cases, most damaged files will be unimportant: temporary files, files which may easily be replaced by reinstalling software, and so on. Executable program files are generally not worth rescuing unless they are guaranteed 100% intact. Moreover, fully recovered program folders will often not give rise to working software, as corresponding registry entries will no longer be associated with them correctly. By contrast, some documents may be worth rescuing even if incomplete. For example, a document created by a given word-processing program may become corrupted, thus rendering it unreadable by the program normally associated with it, yet much of the text contained in the document may still be read, and perhaps extracted, by making use of a more generic text editor (although, in such a case, program-specific formatting characters will usually be dispersed throughout the text, making both reading and extraction laborious).
Any sector-based rescue system is bound to spend a lot of its time trying to read unwanted data. File-based systems, by contrast, will often allow the user to ignore files that are a waste of time, and will also often identify and list files that are not intact, so long as the file system
File system
A file system is a means to organize data expected to be retained after a program terminates by providing procedures to store, retrieve and update data, as well as manage the available space on the device which contain it. A file system organizes data in an efficient manner and is tuned to the...
is not so damaged as to be unable to identify files. Such systems can, therefore, sometimes prove more practical for the purposes of useful file recovery. However, a sector-based program, which reads data in raw format, sometimes using specialized techniques to recover partially damaged information, may ultimately recover more useful data.

