
Spin casting
Encyclopedia
Spin casting, also known as centrifugal rubber mold casting (CRMC), is a method of utilizing centrifugal force
to produce castings from a rubber mold. Typically, a disc-shaped mold is spun along its central axis at a set speed. The casting material, usually molten metal or liquid thermoset plastic is then poured in through an opening at the top-center of the mold. The filled mold then continues to spin as the metal solidifies or the thermoset plastic sets.
. Most spin casting is done with pewter
and zinc alloys
or thermoset plastics.
or organic rubber
as the mold-making substrate. Vulcanization
is an integral step that occurs halfway through the mold-making process. Prior to vulcanization, the mold rubber is a soft and malleable solid-like fluid, in many ways very similar to Silly Putty
. Because of the clay-like nature at this stage, the mold is easily cut or shaped to accommodate irregular models. Vulcanization serves two purposes: establishing the negative space
inside the mold as well as hardening the rubber so it will remain strong and rigid during casting.
After vulcanization, before it is usable, the mold must undergo gating and venting. This involves carving channels to ensure proper air and material flow during the casting process. Gating and venting is typically done by hand using a sharp knife or scalpel and varies in time depending upon the complexity of the mold. The final product is a cured rubber mold which can withstand anywhere from hundreds to over a thousand casting cycles before it needs replacement.
and injection molding
are similar, but not suitable for spin casting. For example, a typical zinc die-casting alloy such as zamak 3
can be used but will solidify too rapidly from a molten state when cast with centrifugal force. This typically results in incomplete filling of the mold as well as a rough, porous finish, called orange peel. Zamak 2, of a slightly different composition, was originally developed as a gravity-cast alloy with greater finished strength but was found to work well with spin-casting. Its extra copper content encourages the eutectic behaviour and gives a lower freezing point. It has become known as 'Kirksite' and has given rise to a range of dedicated spin-casting alloys, some with additional components such as magnesium, to control the surface finish.
To ensure replicable casting cycles of accurate reproductions with a high quality finish, the spin casting process requires casting materials with the following qualities, for the following reasons:
Commercial spin casting machines are available in two different types, front-loading and top-loading. Due to the weight and bulkiness of spin casting molds, front loading machines tend to offer several advantages regarding ease of use and time savings. Rubber molds can become quite heavy, especially at larger diameters and when casting metal. Because loading and unloading the caster is performed by hand, it is easiest and less fatiguing to manipulate the mold at waist level in one fluid motion as allowed by a front-loading spin caster. This is especially important when spin casting for production purposes where one is trying to maximize the number of complete casting cycles per hour.
Top loading machines tend to be cheaper and theoretically have less of a restriction on maximum mold thickness.
 As mentioned previously, vulcanization is a necessary step to prepare the uncured silicone mold for spin casting production. Under controlled heat and pressure the silicone slowly cures to a heat resistant, flexible, permanent mold. The vulcanizing press or vulcanizer uniformly compresses the mold while exposing it to high temperature over a period of several hours. The vulcanizer consists of a pair of parallel heated platens mounted on a hydraulic press
As mentioned previously, vulcanization is a necessary step to prepare the uncured silicone mold for spin casting production. Under controlled heat and pressure the silicone slowly cures to a heat resistant, flexible, permanent mold. The vulcanizing press or vulcanizer uniformly compresses the mold while exposing it to high temperature over a period of several hours. The vulcanizer consists of a pair of parallel heated platens mounted on a hydraulic press
. Smaller or home-made vulcanizers may compress the mold via screws or a heavy duty clamp instead of hydraulic pressure. Some spin casting operations choose to forgo running their own vulcanizer and instead contract out their mold production.
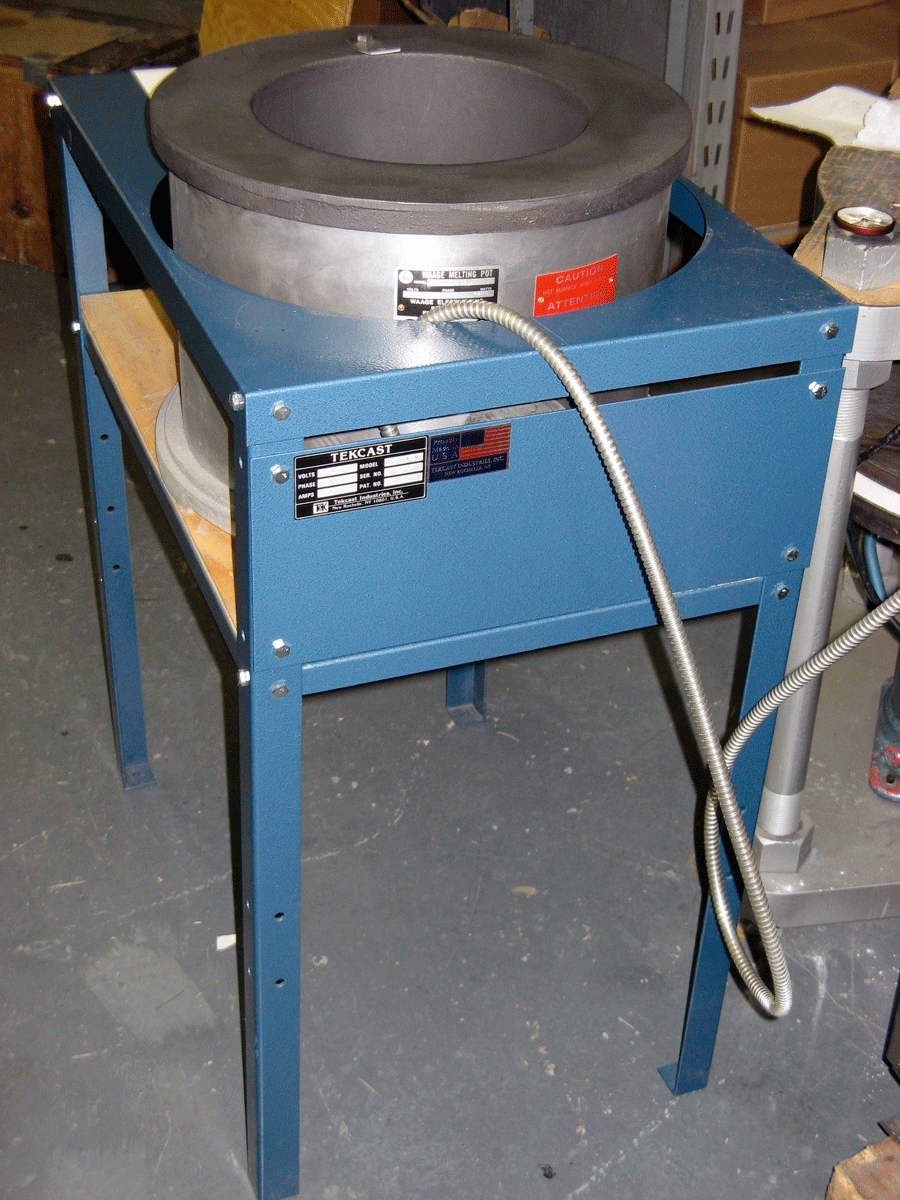 A melting furnace is necessary only when spin casting with metal. Understandably the metal must be in a molten state prior to introduction into the mold. However, it is necessary for a spin casting furnace to have a temperature controller as there is an approximate range that works best for each metal. For example a particular zinc alloy is typically cast between 775-800 °F, whereas it actually melts much lower around 500 °F. If the metal is introduced to the mold at a higher temperature (in this case, above 800 °F), it will start to wear the silicone down prematurely, greatly shortening the mold life. If the metal is introduced at significantly lower temperatures (below 775 °F), its solidification time will similarly be shortened resulting in incomplete or low quality castings. Therefore, spin casting with metal requires not only a furnace with fine temperature control, but knowledge of at what range to cast.
A melting furnace is necessary only when spin casting with metal. Understandably the metal must be in a molten state prior to introduction into the mold. However, it is necessary for a spin casting furnace to have a temperature controller as there is an approximate range that works best for each metal. For example a particular zinc alloy is typically cast between 775-800 °F, whereas it actually melts much lower around 500 °F. If the metal is introduced to the mold at a higher temperature (in this case, above 800 °F), it will start to wear the silicone down prematurely, greatly shortening the mold life. If the metal is introduced at significantly lower temperatures (below 775 °F), its solidification time will similarly be shortened resulting in incomplete or low quality castings. Therefore, spin casting with metal requires not only a furnace with fine temperature control, but knowledge of at what range to cast.
, plaster mold casting
or investment casting
. However these three techniques (sand, plaster and lost wax) are not directly comparable as each utilizes a one-time use or expendable mold
The remarkable disparity in tooling cost and lead time is a result of the expensive and time consuming machining required to produce the precision metal molds (dies) used with die-casting and plastic injection molding. However, the precision tooling and resilient nature of the machined metal die translates to an extremely longer-lasting mold (die) and slight improvements to casting tolerances. Furthermore thermoplastics and die casting metal alloys are in wider use than their specialized spin casting analogs, and as a result are typically cheaper.
Furthermore, because of the low start up costs, and ease of use, spin casting is available to ranks of individuals and businesses who are unable to make the deep investments required by die casting, injection molding or other similar processes. These users include smaller business and design houses that would normally contract their work to production “job” shops, as well as hobbyists interested in producing their own unique items for personal enjoyment. In this way, spin casting is accessible to an arguably broader range of applications than competing technologies.
Centrifugal force
Centrifugal force can generally be any force directed outward relative to some origin. More particularly, in classical mechanics, the centrifugal force is an outward force which arises when describing the motion of objects in a rotating reference frame...
to produce castings from a rubber mold. Typically, a disc-shaped mold is spun along its central axis at a set speed. The casting material, usually molten metal or liquid thermoset plastic is then poured in through an opening at the top-center of the mold. The filled mold then continues to spin as the metal solidifies or the thermoset plastic sets.
General description
The two defining characteristics of spin casting are semi-permanent (non-expendable) rubber molds and the use of centrifugal force. These make the process relatively unique compared to machined die-based and expendable mold casting methods. These qualities also encourage operators to use casting materials specially formulated for low melting points and viscositiesViscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
. Most spin casting is done with pewter
Pewter
Pewter is a malleable metal alloy, traditionally 85–99% tin, with the remainder consisting of copper, antimony, bismuth and lead. Copper and antimony act as hardeners while lead is common in the lower grades of pewter, which have a bluish tint. It has a low melting point, around 170–230 °C ,...
and zinc alloys
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
or thermoset plastics.
Silicone molds
The spin casting process typically uses vulcanized siliconeSilicone
Silicones are inert, synthetic compounds with a variety of forms and uses. Typically heat-resistant and rubber-like, they are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medical applications , cookware, and insulation....
or organic rubber
Rubber
Natural rubber, also called India rubber or caoutchouc, is an elastomer that was originally derived from latex, a milky colloid produced by some plants. The plants would be ‘tapped’, that is, an incision made into the bark of the tree and the sticky, milk colored latex sap collected and refined...
as the mold-making substrate. Vulcanization
Vulcanization
Vulcanization or vulcanisation is a chemical process for converting rubber or related polymers into more durable materials via the addition of sulfur or other equivalent "curatives." These additives modify the polymer by forming crosslinks between individual polymer chains. Vulcanized material is...
is an integral step that occurs halfway through the mold-making process. Prior to vulcanization, the mold rubber is a soft and malleable solid-like fluid, in many ways very similar to Silly Putty
Silly Putty
Silly Putty , is the Crayola-owned trademark name for a class of silicone polymers. It is marketed today as a toy for children, but was originally created by accident during research into potential rubber substitutes for use by the United States in World War II...
. Because of the clay-like nature at this stage, the mold is easily cut or shaped to accommodate irregular models. Vulcanization serves two purposes: establishing the negative space
Negative space
Negative space, in art, is the space around and between the subject of an image. Negative space may be most evident when the space around a subject, and not the subject itself, forms an interesting or artistically relevant shape, and such space is occasionally used to artistic effect as the "real"...
inside the mold as well as hardening the rubber so it will remain strong and rigid during casting.
After vulcanization, before it is usable, the mold must undergo gating and venting. This involves carving channels to ensure proper air and material flow during the casting process. Gating and venting is typically done by hand using a sharp knife or scalpel and varies in time depending upon the complexity of the mold. The final product is a cured rubber mold which can withstand anywhere from hundreds to over a thousand casting cycles before it needs replacement.
Metal
Generally, the casting materials used for competing processes like metal die castingDie casting
Die casting is a metal casting process that is characterized by forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity. The mold cavity is created using two hardened tool steel dies which have been machined into shape and work similarly to an injection mold during the process...
and injection molding
Injection molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts from both thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic materials. Material is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity...
are similar, but not suitable for spin casting. For example, a typical zinc die-casting alloy such as zamak 3
ZAMAK
Zamak is a family of alloys with a base metal of zinc and alloying elements of aluminium, magnesium and copper. Zamak alloys are part of the zinc aluminium alloy family; they are distinguished from the other ZA alloys because of their constant 4% aluminium composition...
can be used but will solidify too rapidly from a molten state when cast with centrifugal force. This typically results in incomplete filling of the mold as well as a rough, porous finish, called orange peel. Zamak 2, of a slightly different composition, was originally developed as a gravity-cast alloy with greater finished strength but was found to work well with spin-casting. Its extra copper content encourages the eutectic behaviour and gives a lower freezing point. It has become known as 'Kirksite' and has given rise to a range of dedicated spin-casting alloys, some with additional components such as magnesium, to control the surface finish.
To ensure replicable casting cycles of accurate reproductions with a high quality finish, the spin casting process requires casting materials with the following qualities, for the following reasons:
- Low temperature operation - Spin casting is a low temperature process, as overexposure to high temperatures causes the rubber mold to degrade. Depending on the actual compound, the mold may become overly soft or hard while forming cracks and chips.
- Slow solidification and low viscosity - Uniform and unrestricted flow of the casting material has a substantial effect on the quality and finish of the final items.
Plastic
Aside from the aforementioned metal alloys, thermoset resins and plastics work well with spin casting as they can be introduced as liquids and will set or solidify while the mold spins. In general, spin casting encourages the use of casting materials that are liquid upon introduction to the mold and solidify at a slow, uniform rate during the spin cycle.Spin caster
During the casting process, the finished mold spins along its central axis for anywhere from 30 seconds to several minutes depending upon the chosen casting material. Internally a spin casting machine or spin caster consists of a motor and pressure clamping system which holds and positions the mold properly while it spins at a steady rate. These components are placed inside of a machine body which shields against flashing of molten metal or liquid plastic that is inadvertently ejected from the mold during the spinning process. Without the proper containment, hot melted flashing can be a serious hazard to the machine operator and anyone else nearby.Commercial spin casting machines are available in two different types, front-loading and top-loading. Due to the weight and bulkiness of spin casting molds, front loading machines tend to offer several advantages regarding ease of use and time savings. Rubber molds can become quite heavy, especially at larger diameters and when casting metal. Because loading and unloading the caster is performed by hand, it is easiest and less fatiguing to manipulate the mold at waist level in one fluid motion as allowed by a front-loading spin caster. This is especially important when spin casting for production purposes where one is trying to maximize the number of complete casting cycles per hour.
Top loading machines tend to be cheaper and theoretically have less of a restriction on maximum mold thickness.
Vulcanizer

Hydraulic press
A hydraulic is a machine using a hydraulic cylinder to generate a compressive force. It uses the hydraulic equivalenta mechanical lever, and was also known as a Bramah press after the inventor, Joseph Bramah, of England. He invented and was issued a patent on this press in 1795...
. Smaller or home-made vulcanizers may compress the mold via screws or a heavy duty clamp instead of hydraulic pressure. Some spin casting operations choose to forgo running their own vulcanizer and instead contract out their mold production.
Melting furnace

Similar processes
Spin casting is a favored method for anyone fabricating items in the specified materials – low temperature metals and thermoset plastics. Compared to the two main competing processes – injection molding and (zinc) die-casting; spin casting has significant advantages in terms of startup costs and ease of use. In some cases, spin casting can also be an alternative to sand castingSand casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mold material.It is relatively cheap and sufficiently refractory even for steel foundry use. A suitable bonding agent is mixed or occurs with the sand...
, plaster mold casting
Plaster mold casting
Plaster mold casting is a metalworking casting process similar to sand casting except the molding material is plaster of paris instead of sand. Like sand casting, plaster mold casting is an expendable mold processes, however it can only be used with non-ferrous materials. It is used for castings as...
or investment casting
Investment casting
Investment casting is an industrial process based on and also called lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. From 5,000 years ago, when beeswax formed the pattern, to today’s high-technology waxes, refractory materials and specialist alloys, the castings allow the...
. However these three techniques (sand, plaster and lost wax) are not directly comparable as each utilizes a one-time use or expendable mold
| Spin casting | Die casting | Injection molding | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mold material | Vulcanized rubber | Machined tool steel | Machined aluminum, brass or tool steel |
| Casting material | Zinc, tin, lead, pewter, thermoset plastics, pattern wax | Zinc, aluminum, magnesium | Most thermoplastic Thermoplastic Thermoplastic, also known as a thermosoftening plastic, is a polymer that turns to a liquid when heated and freezes to a very glassy state when cooled sufficiently... s |
| Average cost of tooling (USD) | $35–250 | $10,000–250,000 | $5,000–150,000 |
| Ability to make design changes | Easiest | Very difficult | Very difficult |
| Typical initial lead time | 4 hours to 2 days | 12 to 24 weeks | 12 to 24 weeks |
| Casting tolerances | Very close | Closest | Closest |
| Piece price | Very low | Lowest | Lowest |
| Size range | 0.5–12 in (12.7–304.8 mm) | 0.5–24 in (12.7–609.6 mm) | 0.5–24 in (12.7–609.6 mm) |
The remarkable disparity in tooling cost and lead time is a result of the expensive and time consuming machining required to produce the precision metal molds (dies) used with die-casting and plastic injection molding. However, the precision tooling and resilient nature of the machined metal die translates to an extremely longer-lasting mold (die) and slight improvements to casting tolerances. Furthermore thermoplastics and die casting metal alloys are in wider use than their specialized spin casting analogs, and as a result are typically cheaper.
Applications
Spin casting is very commonly used for the manufacture of the following types of items:- Gaming miniatures and figurinesFigurinesFigurines is an indie rock band from Denmark, formed in the mid-1990s. The band released their first EP, The Detour, in 2001 and their first full-length album, Shake a Mountain, in 2004. The band began to receive national attention in Denmark around the time of the full-length release, and began...
– in both metal and plastics. - Fishing lureFishing lureA fishing lure is an object attached to the end of a fishing line which is designed to resemble and move like the prey of a fish. The purpose of the lure is to use movement, vibration, and colour to catch the fish's attention so it bites the hook...
s and fishing tackle components including jig headsJig (fishing)Jigging is the practice of fishing with a jig, a type of fishing lure. A jig consists of a lead sinker with a hook molded into it and usually covered by a soft body to attract fish. Jigs are intended to create a jerky, vertical motion, as opposed to spinnerbaits which move through the water...
and lead weights. - Decorative and novelty type itemsNoveltiesA novelty item is a small manufactured adornment, especially a personal adornment.- Novelty item :This term covers a range of small manufactured goods, such as*antiques*collectables*chocolates*esoterica*executive toys*gadgets*tools and implements...
– belt buckles, pins, emblems, medallions, trophies, assorted souvenirs etc. - Industrial manufacturing and replacement part production.
- Rapid prototypingRapid prototypingRapid prototyping is the automatic construction of physical objects using additive manufacturing technology. The first techniques for rapid prototyping became available in the late 1980s and were used to produce models and prototype parts. Today, they are used for a much wider range of applications...
/ rapid manufacturing – spin casting is an excellent adjunct process as it allows the quick and efficient production of fully functional copies from fragile rapid prototype models.
Furthermore, because of the low start up costs, and ease of use, spin casting is available to ranks of individuals and businesses who are unable to make the deep investments required by die casting, injection molding or other similar processes. These users include smaller business and design houses that would normally contract their work to production “job” shops, as well as hobbyists interested in producing their own unique items for personal enjoyment. In this way, spin casting is accessible to an arguably broader range of applications than competing technologies.
See also
- Centrifugal casting (industrial)Centrifugal casting (industrial)Centrifugal casting or rotocasting is a casting technique that is typically used to cast thin-walled cylinders. It is noted for the high quality of the results attainable, particularly for precise control of their metallurgy and crystal structure...
, on an industrial scale - Centrifugal casting (silversmithing), for a smaller scale

