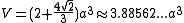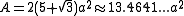Square gyrobicupola
Encyclopedia
In geometry
, the square gyrobicupola is one of the Johnson solid
s (J29). Like the square orthobicupola
(J28), it can be obtained by joining two square cupola
e (J4) along their bases. The difference is that in this solid, the two halves are rotated 45 degrees with respect to one another.
The square gyrobicupola is the second in an infinite set of gyrobicupolae
.
The 92 Johnson solids were named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.
e for volume
and surface area
can be used if all faces
are regular
, with edge length a:
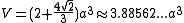
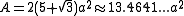
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, the square gyrobicupola is one of the Johnson solid
Johnson solid
In geometry, a Johnson solid is a strictly convex polyhedron, each face of which is a regular polygon, but which is not uniform, i.e., not a Platonic solid, Archimedean solid, prism or antiprism. There is no requirement that each face must be the same polygon, or that the same polygons join around...
s (J29). Like the square orthobicupola
Square orthobicupola
In geometry, the square orthobicupola is one of the Johnson solids . As the name suggests, it can be constructed by joining two square cupolae along their octagonal bases, matching like faces...
(J28), it can be obtained by joining two square cupola
Square cupola
In geometry, the square cupola, sometimes called lesser dome, is one of the Johnson solids . It can be obtained as a slice of the rhombicuboctahedron...
e (J4) along their bases. The difference is that in this solid, the two halves are rotated 45 degrees with respect to one another.
The square gyrobicupola is the second in an infinite set of gyrobicupolae
Bicupola (geometry)
In geometry, a bicupola is a solid formed by connecting two cupolae on their bases.There are two classes of bicupola because each cupola half is bordered by alternating triangles and squares...
.
The 92 Johnson solids were named and described by Norman Johnson in 1966.
Formulae
The following formulaFormula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
e for volume
Volume
Volume is the quantity of three-dimensional space enclosed by some closed boundary, for example, the space that a substance or shape occupies or contains....
and surface area
Surface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
can be used if all faces
Face (geometry)
In geometry, a face of a polyhedron is any of the polygons that make up its boundaries. For example, any of the squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube...
are regular
Regular polygon
A regular polygon is a polygon that is equiangular and equilateral . Regular polygons may be convex or star.-General properties:...
, with edge length a: