
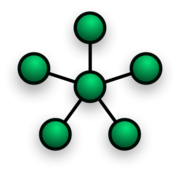
Star network
Encyclopedia
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
topologies
Network topology
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements of a computer or biological network....
. In its simplest form, a star network consists of one central switch
Network switch
A network switch or switching hub is a computer networking device that connects network segments.The term commonly refers to a multi-port network bridge that processes and routes data at the data link layer of the OSI model...
, hub or computer, which acts as a conduit to transmit messages. This consists of a central node, to which all other nodes are connected; this central node provides a common connection point for all nodes through a hub.
Thus, the hub and leaf nodes, and the transmission lines between them, form a graph with the topology of a star
Star (graph theory)
In graph theory, a star Sk is the complete bipartite graph K1,k: a tree with one internal node and k leaves...
. If the central node is passive, the originating node must be able to tolerate the reception of an echo of its own transmission, delayed by the two-way transmission time (i.e. to and from the central node) plus any delay generated in the central node. An active star network has an active central node that usually has the means to prevent echo-related problems.
The star topology reduces the chance of network failure by connecting all of the systems to a central node. When applied to a bus-based network, this central hub rebroadcasts all transmissions received from any peripheral node to all peripheral nodes on the network, sometimes including the originating node. All peripheral nodes may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the central node only. The failure of a transmission line linking any peripheral node to the central node will result in the isolation of that peripheral node from all others, but the rest of the systems will be unaffected.
It is also designed with each node (file servers, workstations, and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub, switch, or concentrator
Concentrator
In telecommunication, the term concentrator has the following meanings:# In data transmission, a functional unit that permits a common path to handle more data sources than there are channels currently available within the path...
.
Data on a star network passes through the hub, switch, or concentrator before continuing to its destination. The hub, switch, or concentrator manages and controls all functions of the network. It is also acts as a repeater for the data flow. This configuration is common with twisted pair cable. However, it can also be used with coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
or optical fibre cable.
Advantages
- Better performance: star topology prevents the passing of data packets through an excessive number of nodes. At most, 3 devices and 2 links are involved in any communication between any two devices. Although this topology places a huge overhead on the central hub, with adequate capacity, the hub can handle very high utilization by one device without affecting others.
- Isolation of devices: Each device is inherently isolated by the link that connects it to the hub. This makes the isolation of individual devices straightforward and amounts to disconnecting each device from the others. This isolation also prevents any non-centralized failure from affecting the network.
- Benefits from centralization: As the central hub is the bottleneck, increasing its capacity, or connecting additional devices to it, increases the size of the network very easily. Centralization also allows the inspection of traffic through the network. This facilitates analysis of the traffic and detection of suspicious behavior.
- Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
- No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices.
Disadvantages
- High dependence of the system on the functioning of the central hub
- Failure of the central hub renders the network inoperable
See also
- Bus networkBus networkA bus network topology is a network architecture in which a set of clients are connected via a shared communications line, called a bus. There are several common instances of the bus architecture, including one in the motherboard of most computers, and those in some versions of Ethernet...
- Ring networkRing networkA ring network is a network topology in which each node connects to exactly two other nodes, forming a single continuous pathway for signals through each node - a ring...
- Mesh networkingMesh networkingMesh networking is a type of networking where each node must not only capture and disseminate its own data, but also serve as a relay for other nodes, that is, it must collaborate to propagate the data in the network....
- Token ring
- Token busToken busToken bus is a network implementing the token ring protocol over a "virtual ring" on a coaxial cable. A token is passed around the network nodes and only the node possessing the token may transmit. If a node doesn't have anything to send, the token is passed on to the next node on the virtual ring...
- Tree and hypertree networks

