State
Overview
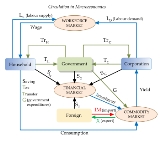
Government
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
. States may be sovereign
Sovereign
A sovereign is the supreme lawmaking authority within its jurisdiction.Sovereign may also refer to:*Monarch, the sovereign of a monarchy*Sovereign Bank, banking institution in the United States*Sovereign...
and may enjoy a monopoly on the legal initiation of force and are not dependent on, or subject to any other power or state. Many states are federated states which participate in a federal union
Federal union
In politics, a federal union is any organization of states or other entities that unite under a federalist system. Usually a federal union will action jointly in matters of defense and foreign relations, with individual states having independence in local matters. Examples of federal unions include...
. Some states are subject to external sovereignty or hegemony where ultimate sovereignty lies in another state.
The state can also be used to refer to the secular branches of government within a state, often as a manner of contrasting them with churches and civilian institutions (civil society).
The word state and its cognates in other European languages (stato in Italian, état in French, Staat in German) ultimately derive from the Latin status, meaning "condition" or "status."
With the revival of the Roman law
Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, and the legal developments which occurred before the 7th century AD — when the Roman–Byzantine state adopted Greek as the language of government. The development of Roman law comprises more than a thousand years of jurisprudence — from the Twelve...
in the 14th century in Europe, this Latin term was used to refer to the legal standing of persons (such as the various "estates of the realm
Estates of the realm
The Estates of the realm were the broad social orders of the hierarchically conceived society, recognized in the Middle Ages and Early Modern period in Christian Europe; they are sometimes distinguished as the three estates: the clergy, the nobility, and commoners, and are often referred to by...
" - noble, common, and clerical), and in particular the special status of the king.

