
Stationary subspace analysis
Encyclopedia
Stationary Subspace Analysis (SSA) is a blind source separation algorithm
which factorizes a multivariate time series
into stationary
and non-stationary components.
analysis, the electrodes on the scalp record the activity of a large number of sources located inside the brain. These sources can be stationary or non-stationary, but they are not discernible in the electrode signals, which are a mixture of these sources. SSA allows the separation of the stationary from the non-stationary sources in an observed time series.
According to the SSA model, the observed multivariate time series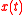 is assumed to be generated as a linear superposition of stationary sources
is assumed to be generated as a linear superposition of stationary sources 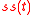 and non-stationary sources
and non-stationary sources 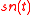 ,
,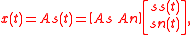
where is an unknown but time-constant mixing matrix;
is an unknown but time-constant mixing matrix; 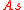 and
and 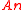 are the basis of the stationary and non-stationary subspace respectively.
are the basis of the stationary and non-stationary subspace respectively.
Given samples from the time series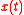 , the aim of Stationary Subspace Analysis is to estimate the inverse mixing matrix
, the aim of Stationary Subspace Analysis is to estimate the inverse mixing matrix 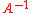 separating the stationary from non-stationary sources in the mixture
separating the stationary from non-stationary sources in the mixture 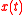 .
.
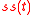 are identifiable (up to a linear transformation) and the true non-stationary subspace
are identifiable (up to a linear transformation) and the true non-stationary subspace 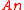 is identifiable. The true non-stationary sources
is identifiable. The true non-stationary sources 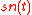 and the true stationary subspace
and the true stationary subspace 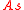 cannot be identified, because arbitrary contributions from the stationary sources do not change the non-stationary nature of a non-stationary source
cannot be identified, because arbitrary contributions from the stationary sources do not change the non-stationary nature of a non-stationary source
, Computer Vision
and Temporal Segmentation. There are variants of the SSA problem that can be solved analytically in closed form, without numerical optimization.
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
which factorizes a multivariate time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
into stationary
Stationary
Stationary can mean:* In statistics and probability: a stationary process.* In mathematics: a stationary point.* In mathematics: a stationary set.* In physics: a time-invariant quantity, such as a constant position or temperature....
and non-stationary components.
Introduction
In many settings, the measured time series contains contributions from various underlying sources that cannot be measured directly. For instance, in EEGEEG
EEG commonly refers to electroencephalography, a measurement of the electrical activity of the brain.EEG may also refer to:* Emperor Entertainment Group, a Hong Kong-based entertainment company...
analysis, the electrodes on the scalp record the activity of a large number of sources located inside the brain. These sources can be stationary or non-stationary, but they are not discernible in the electrode signals, which are a mixture of these sources. SSA allows the separation of the stationary from the non-stationary sources in an observed time series.
According to the SSA model, the observed multivariate time series
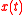 is assumed to be generated as a linear superposition of stationary sources
is assumed to be generated as a linear superposition of stationary sources 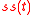 and non-stationary sources
and non-stationary sources 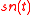 ,
,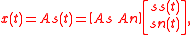
where
 is an unknown but time-constant mixing matrix;
is an unknown but time-constant mixing matrix; 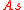 and
and 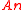 are the basis of the stationary and non-stationary subspace respectively.
are the basis of the stationary and non-stationary subspace respectively.Given samples from the time series
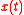 , the aim of Stationary Subspace Analysis is to estimate the inverse mixing matrix
, the aim of Stationary Subspace Analysis is to estimate the inverse mixing matrix  separating the stationary from non-stationary sources in the mixture
separating the stationary from non-stationary sources in the mixture 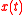 .
.Identifiability of the solution
The true stationary sources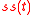 are identifiable (up to a linear transformation) and the true non-stationary subspace
are identifiable (up to a linear transformation) and the true non-stationary subspace 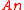 is identifiable. The true non-stationary sources
is identifiable. The true non-stationary sources 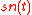 and the true stationary subspace
and the true stationary subspace 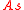 cannot be identified, because arbitrary contributions from the stationary sources do not change the non-stationary nature of a non-stationary source
cannot be identified, because arbitrary contributions from the stationary sources do not change the non-stationary nature of a non-stationary sourceApplications and Extensions
Stationary Subspace Analysis has been successfully applied to Brain Computer InterfacingBrain-computer interface
A brain–computer interface , sometimes called a direct neural interface or a brain–machine interface , is a direct communication pathway between the brain and an external device...
, Computer Vision
Computer vision
Computer vision is a field that includes methods for acquiring, processing, analysing, and understanding images and, in general, high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g., in the forms of decisions...
and Temporal Segmentation. There are variants of the SSA problem that can be solved analytically in closed form, without numerical optimization.
See also
- Blind signal separation (BSS)Blind signal separationBlind signal separation, also known as blind source separation, is the separation of a set of signals from a set of mixed signals, without the aid of information about the source signals or the mixing process....
- Factor analysisFactor analysisFactor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved, uncorrelated variables called factors. In other words, it is possible, for example, that variations in three or four observed variables...
- Independent component analysisIndependent component analysisIndependent component analysis is a computational method for separating a multivariate signal into additive subcomponents supposing the mutual statistical independence of the non-Gaussian source signals...
- CointegrationCointegrationCointegration is a statistical property of time series variables. Two or more time series are cointegrated if they share a common stochastic drift.-Introduction:...

