
Step recovery diode
Encyclopedia
In electronics
, a step recovery diode (SRD) is a semiconductor junction diode having the ability to generate extremely short pulses. It is also called snap-off diode or charge-storage diode or memory varactor, and has a variety of uses in microwave
electronics as pulse generator
or parametric amplifier.
When diodes switch from forward conduction to reverse cut-off, a reverse current flows briefly as stored charge is removed. It is the abruptness with which this reverse current ceases which characterises the step recovery diode.
pulses". They also refer that they first observed this phenomenon in February, 1959.
during forward conduction, which is present in all semiconductor junction diodes and is due to finite lifetime of minority carriers in semiconductor
s. Assume that the SRD is forward biased and in steady state
i.e. the anode
bias current does not change with time
: since charge
transport in a junction diode is mainly due to diffusion
, i.e. to a non constant spatial charge
carrier density
caused by bias voltage, a charge
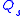 is stored in the device. This stored charge depends on
is stored in the device. This stored charge depends on
Quantitatively, if the steady state
of forward conduction lasts for a time much greater than , the stored charge
, the stored charge
has the following approximate expression
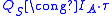
Now suppose that the voltage bias abruptly changes, switching from its stationary positive value to a higher magnitude
constant negative value: then, since a certain amount of charge has been stored during forward conduction, diode resistance
is still low (i.e. the anode-to-cathode voltage has nearly the same forward conduction value). Anode current
has nearly the same forward conduction value). Anode current
does not cease but reverses its polarity (i.e. the direction of its flow) and stored charge
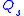 starts to flow out of the device at an almost constant rate
starts to flow out of the device at an almost constant rate 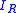 . All the stored charge is thus removed in a certain amount of time: this time is the storage time
. All the stored charge is thus removed in a certain amount of time: this time is the storage time 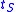 and its approximate expression is
and its approximate expression is

When all stored charge has been removed, diode
resistance
suddenly changes, rising to its cut-off
value at reverse bias within a time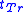 , the transition time. This can be exploited to produce a pulse with a rise time of
, the transition time. This can be exploited to produce a pulse with a rise time of 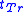 .
.
SRD.. It is a PhD thesis in which an SRD is a key element. Chapter 5 is particularly relevant.
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, a step recovery diode (SRD) is a semiconductor junction diode having the ability to generate extremely short pulses. It is also called snap-off diode or charge-storage diode or memory varactor, and has a variety of uses in microwave
Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
electronics as pulse generator
Pulse generator
A pulse generator is either an electronic circuit or a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. This article describes the test equipment.-Bench pulse generators:...
or parametric amplifier.
When diodes switch from forward conduction to reverse cut-off, a reverse current flows briefly as stored charge is removed. It is the abruptness with which this reverse current ceases which characterises the step recovery diode.
Historical note
The first published paper on the SRD is : the authors start the brief survey stating that "the recovery characteristics of certain types of pn-junction diodes exhibit a discontinuity which may be used to advantage for the generation of harmonics or for the production of millimicrosecondNanosecond
A nanosecond is one billionth of a second . One nanosecond is to one second as one second is to 31.7 years.The word nanosecond is formed by the prefix nano and the unit second. Its symbol is ns....
pulses". They also refer that they first observed this phenomenon in February, 1959.
Physical principles
The main phenomenon used in SRDs is the storage of electric chargeElectric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
during forward conduction, which is present in all semiconductor junction diodes and is due to finite lifetime of minority carriers in semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
s. Assume that the SRD is forward biased and in steady state
Steady state
A system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
i.e. the anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
bias current does not change with time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
: since charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
transport in a junction diode is mainly due to diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
, i.e. to a non constant spatial charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
carrier density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
caused by bias voltage, a charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
 is stored in the device. This stored charge depends on
is stored in the device. This stored charge depends on- Intensity of the forward anodeAnodeAn anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
currentElectric currentElectric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
 flowing in the device during its steady stateSteady stateA system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
flowing in the device during its steady stateSteady stateA system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
. - Minority carrier lifetime
 , i.e. the mean time a free charge carrierCharge carrierIn physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
, i.e. the mean time a free charge carrierCharge carrierIn physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
moves inside a semiconductorSemiconductorA semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
region before recombiningCarrier generation and recombinationIn the solid state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as...
.
Quantitatively, if the steady state
Steady state
A system in a steady state has numerous properties that are unchanging in time. This implies that for any property p of the system, the partial derivative with respect to time is zero:...
of forward conduction lasts for a time much greater than
 , the stored charge
, the stored chargeElectric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
has the following approximate expression
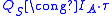
Now suppose that the voltage bias abruptly changes, switching from its stationary positive value to a higher magnitude
Magnitude (mathematics)
The magnitude of an object in mathematics is its size: a property by which it can be compared as larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind; in technical terms, an ordering of the class of objects to which it belongs....
constant negative value: then, since a certain amount of charge has been stored during forward conduction, diode resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
is still low (i.e. the anode-to-cathode voltage
 has nearly the same forward conduction value). Anode current
has nearly the same forward conduction value). Anode currentElectric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
does not cease but reverses its polarity (i.e. the direction of its flow) and stored charge
Electric charge
Electric charge is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, called positive and negative. Two positively charged substances, or objects, experience a mutual repulsive force, as do two...
 starts to flow out of the device at an almost constant rate
starts to flow out of the device at an almost constant rate 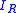 . All the stored charge is thus removed in a certain amount of time: this time is the storage time
. All the stored charge is thus removed in a certain amount of time: this time is the storage time 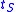 and its approximate expression is
and its approximate expression is
When all stored charge has been removed, diode
Diode
In electronics, a diode is a type of two-terminal electronic component with a nonlinear current–voltage characteristic. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material connected to two electrical terminals...
resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
suddenly changes, rising to its cut-off
Cut-off (electronics)
In electronics, the term Cut-off identifies a state of negligible electrical conduction which is proper of several types of electronic components when a control parameter , is lowered or increased past a value called conduction threshold or simply...
value at reverse bias within a time
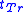 , the transition time. This can be exploited to produce a pulse with a rise time of
, the transition time. This can be exploited to produce a pulse with a rise time of 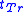 .
.See also
- Minority carrier.
- P-n junctionP-n junctionA p–n junction is formed at the boundary between a P-type and N-type semiconductor created in a single crystal of semiconductor by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy .If two separate pieces of material were used, this would...
. - Pulse generatorPulse generatorA pulse generator is either an electronic circuit or a piece of electronic test equipment used to generate rectangular pulses. This article describes the test equipment.-Bench pulse generators:...
- Semiconductor diode.
External links
. An interesting paper describing the construction and reporting the measured performance of an extremely fast heterojunctionHeterojunction
A heterojunction is the interface that occurs between two layers or regions of dissimilar crystalline semiconductors. These semiconducting materials have unequal band gaps as opposed to a homojunction...
SRD.. It is a PhD thesis in which an SRD is a key element. Chapter 5 is particularly relevant.

