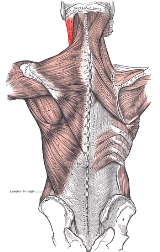
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
Encyclopedia
In human
anatomy
, the sternocleidomastoid muscle (icon), also known as sternomastoid and commonly abbreviated as SCM, is a paired muscle in the superficial
layers of the anterior portion of the neck
. It acts to flex and rotate the head.
It also acts as an accessory muscle of inspiration, along with the scalene muscles
of the neck.
of the sternum (sterno-) and the clavicle
(cleido-), and has an insertion
at the mastoid process
of the temporal bone
of the skull
.
It is thick and narrow at its central part, but broader and thinner at either end.
The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval, but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process
, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin aponeurosis
into the lateral half of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone
. The function of this muscle is to rotate the head to the opposite side or obliquely rotate the head. It also flexes the neck.
. It supplies only motor fibres. The cervical plexus supplies sensation, including proprioception
, via the dorsal primary rami of C2
and C3
.
When the clavicular origin is broad, it is occasionally subdivided into several slips, separated by narrow intervals. More rarely, the adjoining margins of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius are in contact. This would leave no posterior triangle.
The supraclavicularis muscle arises from the manubrium behind the sternocleidomastoid and passes behind the sternocleidomastoid to the upper surface of the clavicle.
). Anterior to sternocleidomastoid is the anterior triangle. Posterior to it is the posterior triangle.
Many important structures relate to the sternocleidomastoid, including the common carotid artery
, accessory nerve, and brachial plexus
.
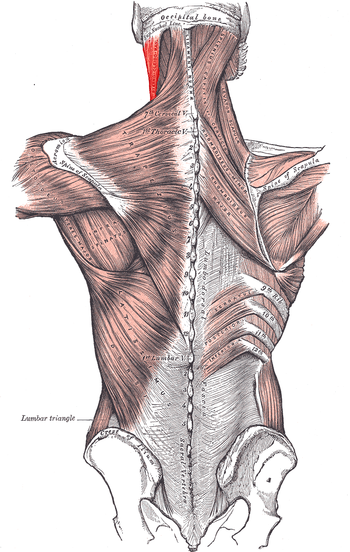
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
anatomy
Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
, the sternocleidomastoid muscle (icon), also known as sternomastoid and commonly abbreviated as SCM, is a paired muscle in the superficial
Superficial
Superficial may refer to:*Superficial , an album by Heidi Montag*"Superficial" *The Superficial, a website devoted to celebrity gossip...
layers of the anterior portion of the neck
Neck
The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney...
. It acts to flex and rotate the head.
It also acts as an accessory muscle of inspiration, along with the scalene muscles
Scalene muscles
The scalene muscles are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the scalenus anterior, scalenus medius, and scalenus posterior.They are innervated by the spinal nerves C4-C6....
of the neck.
Etymology
It is given the name sternocleidomastoid because it originates at the manubriumManubrium
The manubrium or manubrium sterni is the broad, upper part of the sternum. Located ventrally with a quadrangular shape, wider superiorly and narrower inferiorly, it articulates with the clavicles and the first two ribs.-Borders:The superior border is the thickest and presents at its center the...
of the sternum (sterno-) and the clavicle
Clavicle
In human anatomy, the clavicle or collar bone is a long bone of short length that serves as a strut between the scapula and the sternum. It is the only long bone in body that lies horizontally...
(cleido-), and has an insertion
Insertion (anatomy)
Insertion is the point at which a muscle attaches to the skin, a bone, or another muscle. The insertion attaches to the structure that will be moved by the contraction of the muscle. Insertions are usually connections of muscle via tendon to bone. The opposite end of the muscle is called the origin....
at the mastoid process
Mastoid process
The mastoid process is a conical prominence projecting from the undersurface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone. It is located just behind the external acoustic meatus, and lateral to the styloid process...
of the temporal bone
Temporal bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.The temporal bone supports that part of the face known as the temple.-Parts:The temporal bone consists of four parts:* Squama temporalis...
of the skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
.
Origin and insertion
The sternocleidomastoid passes obliquely across the side of the neck.It is thick and narrow at its central part, but broader and thinner at either end.
- The medial or sternal head is a rounded fasciculusMuscle fascicleIn anatomy, a fascicle is a bundle of skeletal muscle fibers surrounded by perimysium, a type of connective tissue.Specialized muscle fibers in the heart that transmit electrical impulses from the Atrioventricular Node to the Purkinje Fibers are fascicles, also referred to as bundle branches...
, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, which arises from the upper part of the anterior surface of the manubrium sterni, and is directed superiorly, laterally, and posteriorly.
- The lateral or clavicular head, composed of fleshy and aponeurotic fibers, arises from the superior border and anterior surface of the medial third of the clavicleClavicleIn human anatomy, the clavicle or collar bone is a long bone of short length that serves as a strut between the scapula and the sternum. It is the only long bone in body that lies horizontally...
; it is directed almost vertically upward.
The two heads are separated from one another at their origins by a triangular interval, but gradually blend, below the middle of the neck, into a thick, rounded muscle which is inserted, by a strong tendon, into the lateral surface of the mastoid process
Mastoid process
The mastoid process is a conical prominence projecting from the undersurface of the mastoid portion of the temporal bone. It is located just behind the external acoustic meatus, and lateral to the styloid process...
, from its apex to its superior border, and by a thin aponeurosis
Aponeurosis
Aponeuroses are layers of flat broad tendons. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery, and peel off by sections...
into the lateral half of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone
Occipital bone
The occipital bone, a saucer-shaped membrane bone situated at the back and lower part of the cranium, is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself...
. The function of this muscle is to rotate the head to the opposite side or obliquely rotate the head. It also flexes the neck.
Innervation
The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the ipsilateral accessory nerveAccessory nerve
In anatomy, the accessory nerve is a nerve that controls specific muscles of the shoulder and neck. As part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain, it is considered a cranial nerve...
. It supplies only motor fibres. The cervical plexus supplies sensation, including proprioception
Proprioception
Proprioception , from Latin proprius, meaning "one's own" and perception, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement...
, via the dorsal primary rami of C2
Cervical spinal nerve 2
The cervical spinal nerve 2 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 2 ....
and C3
Cervical spinal nerve 3
The cervical spinal nerve 3 is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment..It originates from the spinal column from above the cervical vertebra 3 ....
.
Variations
The sternocleidomastoid varies much in the extent of its origin from the clavicle: in some cases the clavicular head may be as narrow as the sternal; in others it may be as much as 7.5 centimetres (3 in) in breadth.When the clavicular origin is broad, it is occasionally subdivided into several slips, separated by narrow intervals. More rarely, the adjoining margins of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius are in contact. This would leave no posterior triangle.
The supraclavicularis muscle arises from the manubrium behind the sternocleidomastoid and passes behind the sternocleidomastoid to the upper surface of the clavicle.
Relations
The sternocleidomastoid is within the investing fascia of the neck, along with the trapezius muscle, with which it shares its nerve supply (the accessory nerveAccessory nerve
In anatomy, the accessory nerve is a nerve that controls specific muscles of the shoulder and neck. As part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain, it is considered a cranial nerve...
). Anterior to sternocleidomastoid is the anterior triangle. Posterior to it is the posterior triangle.
Many important structures relate to the sternocleidomastoid, including the common carotid artery
Common carotid artery
In human anatomy, the common carotid artery is an artery that supplies the head and neck with oxygenated blood; it divides in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries. - Structure :...
, accessory nerve, and brachial plexus
Brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is a network of nerve fibers, running from the spine, formed by the ventral rami of the lower four cervical and first thoracic nerve roots...
.
Cultural significance
- In Tom Wolfe's novel The Bonfire of the Vanities, Larry Kramer, Bronx District Attorney and one of the novel's main protagonists, prides himself on his strong sternocleidomastoids which he "fans out" in front of women to help give themselves a more masculine, tough appearance. However in the last chapter he is publicly described by his client Maria Ruskin as "doing something weird with his neck", which deeply wounds his ego. Its use here is possibly a dramatic device signalling the lengths ambitious men might go to, looking after every ridiculous detail, in order to appear powerful.
- Creature designers often include the sternocleidomastoid muscle in models of alien characters when they want them to seem attractive and familiar to human viewers due to the muscle's uniqueness as a mammalian feature. "Even C-3POC-3POC-3PO is a robot character from the Star Wars universe who appears in both the original Star Wars films and the prequel trilogy. He is also a major character in the television show Droids, and appears frequently in the series' "Expanded Universe" of novels, comic books, and video games...
has it, in the form of little pistons on his neck. Watch Star TrekStar TrekStar Trek is an American science fiction entertainment franchise created by Gene Roddenberry. The core of Star Trek is its six television series: The Original Series, The Animated Series, The Next Generation, Deep Space Nine, Voyager, and Enterprise...
: The good guys always have them, and the bad guys don't. It's a classic alien designer trick," notes biologist and Hollywood anatomy consultant Stuart Sumida. - The famous Argentinian comedy/musical group Les LuthiersLes LuthiersLes Luthiers is an Argentine comedy-musical group, very popular also in several other Spanish-speaking countries such as Paraguay, Peru, Chile, Ecuador, Spain, Colombia, Mexico, Uruguay, Bolivia, Cuba and Venezuela. They were formed in 1967 by Gerardo Masana, during the height of a period of very...
mention the sternocleidomastoid muscle in their song "El negro quiere bailar". The main actor (Daniel Rabinovich) is asked to move his sternocleidomastoid muscle as part of a dance class, but he erroneously interprets it as a pelvic/genital body part, and nervously covers himself with his arms.
Additional images


