
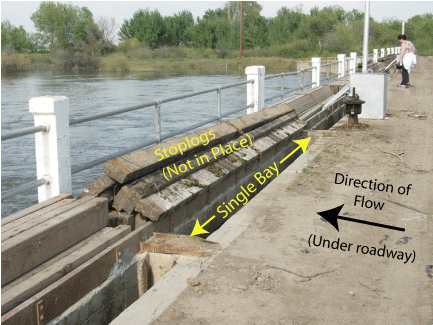
Stoplogs
Encyclopedia

Floodgate
Floodgates are adjustable gates used to control water flow in flood barriers, reservoir, river, stream, or levee systems. They may be designed to set spillway crest heights in dams, to adjust flow rates in sluices and canals, or they may be designed to stop water flow entirely as part of a levee or...
s to adjust the water level or flow rate in a river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
, canal
Canal
Canals are man-made channels for water. There are two types of canal:#Waterways: navigable transportation canals used for carrying ships and boats shipping goods and conveying people, further subdivided into two kinds:...
, or reservoir. Stoplogs are sometimes confused with flashboards, as both elements are used in bulkhead or crest gates. Stoplogs are typically long rectangular timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
beams or boards that are placed on top of each other and dropped into premade slots inside a weir
Weir
A weir is a small overflow dam used to alter the flow characteristics of a river or stream. In most cases weirs take the form of a barrier across the river that causes water to pool behind the structure , but allows water to flow over the top...
, gate
Gate (engineering)
In engineering, a gate is a rotating or sliding structure, supported by hinges or by a rotating horizontal or vertical axis, that can be located at an extreme of a large pipe or canal in order to control the flow of water or any fluid from one side to the other...
, or channel
Channel (geography)
In physical geography, a channel is the physical confine of a river, slough or ocean strait consisting of a bed and banks.A channel is also the natural or human-made deeper course through a reef, sand bar, bay, or any shallow body of water...
. Other materials, including steel and composites, can be used as stoplogs as well. Stoplogs are designed to cut off or stop flow through a conduit.
Use of Stoplogs
Stoplogs are modular in nature, giving the operator of a gated structure the ability to control the water level in a channel by adding or removing individual stoplogs. A gate may make use of one or more logs. Each log is lowered horizontally into a space or bay between two grooved piers. In larger gate structures, there will be multiple bays in which stoplogs can be placed to better control the flow rate through the structure.Stoplogs are frequently used to temporarily block flow through a spillway or canal during routine maintenance. At other times stoplogs can be used over longer periods of times, such as when a field is flooded and stoplogs are being used in smaller gates in order to control the depth of water in fields. The logs may be left in and adjusted during the entire time that the field is submerged.
In most cases, the boards used are subjected to high flow conditions. As individual stoplogs begin to age they are replaced. Typically small amounts of water will leak between individual logs.
Stoplogs are typically used in structures where the removal, installation, and replacement of the logs is expected infreqeuently. When larger flows of water are passing through a stoplog gate, it can be difficult to remove or place individuals logs. Larger logs often require multiple people to position and lift the logs.
Stoplogs vs. Flashboards
Sometimes engineers will use these two terms interchangeably by calling a stoplog a flashboard. This is done in part because unlike many other types of bulkhead gates that are one continuous unit, both stoplogs and flashboards are modular and can be easily designed to hold back different amounts of water. However, most engineering texts and design firms differentiate between the two structures. Stoplogs are specialized bulkheads that are dropped into premade slots or guides in a channel or control structure, while flashboards are bulkheadsBulkhead (barrier)
A bulkhead is a retaining wall, such as a bulkhead within a ship or a watershed retaining wall. It may also be used in mines, to contain flooding.Certain bulkheads, e.g., at the Hudson River are of historical and architectural value....
that are placed on the crest or top of a channel wall or control structure. Flashboards are sometimes designed to break away under high flow conditions and thus to provide only a temporary diversion. In contrast, stoplogs are intended to be reused, and failure of a stoplog will result in an uncontrolled flow through a gate.
Handstops
Smaller stoplogs are sometimes referred to as handstops. Handstops are used in smaller gated structures, such as irrigation delivery ditches or the gates used to control water depth in larger submerged fields (such as rice fieldsPaddy field
A paddy field is a flooded parcel of arable land used for growing rice and other semiaquatic crops. Paddy fields are a typical feature of rice farming in east, south and southeast Asia. Paddies can be built into steep hillsides as terraces and adjacent to depressed or steeply sloped features such...
). They are designed to be easily operated by a single individual.

