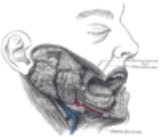
Sublingual gland
Encyclopedia
The sublingual glands are salivary gland
s in the mouth
.
They lie anterior to the submandibular gland
under the tongue
, beneath the mucous membrane
of the floor of the mouth.
They are drained by 8-20 excretory ducts called the ducts of Rivinus.
The largest ball, the sublingual duct (of Bartholin) joins the submandibular duct to drain through the sublingual caruncle
.
The sublingual gland consists mostly of Mucous acini capped with serous demilunes and is therefore categorized as a mucous gland.
Most of the remaining small sublingual ducts open separately into the mouth on an elevated crest of mucous membrane, the plica fimbriata
, formed by the gland and located on either side of the frenulum linguae
.
The chorda tympani
nerve (from the facial nerve
via the submandibular ganglion
) is secretomotor
to the sublingual glands.
Salivary gland
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands, glands with ducts, that produce saliva. They also secrete amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose...
s in the mouth
Mouth
The mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food andsaliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth....
.
They lie anterior to the submandibular gland
Submandibular gland
The paired submandibular glands are salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In humans, they account for 70% of the salivary volume and weigh about 15 grams. Unstimulated in humans, the percentage contribution to whole saliva; ~25% Parotid, Submandibular and Sublingual ~ 67% and...
under the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
, beneath the mucous membrane
Mucous membrane
The mucous membranes are linings of mostly endodermal origin, covered in epithelium, which are involved in absorption and secretion. They line cavities that are exposed to the external environment and internal organs...
of the floor of the mouth.
They are drained by 8-20 excretory ducts called the ducts of Rivinus.
The largest ball, the sublingual duct (of Bartholin) joins the submandibular duct to drain through the sublingual caruncle
Sublingual caruncle
The sublingual caruncle is a site on either side of the frenulum linguae on the sublingual surface of the tongue. There it denotes the site at which the submandibular gland empties into the oral cavity....
.
The sublingual gland consists mostly of Mucous acini capped with serous demilunes and is therefore categorized as a mucous gland.
Most of the remaining small sublingual ducts open separately into the mouth on an elevated crest of mucous membrane, the plica fimbriata
Plica fimbriata
The plica fimbriata is a slight fold of the mucous membrane on the underside of the tongue which runs laterally on either side of the lingual frenulum...
, formed by the gland and located on either side of the frenulum linguae
Frenulum linguae
The frenulum of tongue is the frenulum of the tongue, a small fold of mucous membrane extending from the floor of the mouth to the midline of the underside of the tongue.-Development:The tongue starts to develop at about 4 weeks...
.
The chorda tympani
Chorda tympani
The chorda tympani is a nerve that branches from the facial nerve inside the facial canal, just before the facial nerve exits the skull via the Stylomastoid foramen...
nerve (from the facial nerve
Facial nerve
The facial nerve is the seventh of twelve paired cranial nerves. It emerges from the brainstem between the pons and the medulla, and controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and oral cavity...
via the submandibular ganglion
Submandibular ganglion
The submandibular ganglion is part of the human autonomic nervous system. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck...
) is secretomotor
Secretomotor
Secretomotor refers to the capacity of a structure to induce a gland to secrete a substance .Secretomotor nerve endings are frequently contrasted with sensory neuron endings and motor nerve endings. An example of secretomotor activity can be seen with the lacrimal gland, which secretes the aqueous...
to the sublingual glands.
External links
- Diagram at scopevic.org.au - "Oral Cavity: Glands"
- Histology at usc.edu

