
Suessiones
Encyclopedia
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
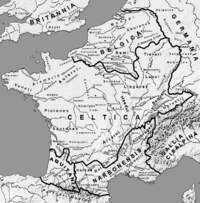
in the 1st century BC, inhabiting the region between the Oise
Oise River
The River Oise is a right tributary of the River Seine, flowing for 302 km in Belgium and France. Its source is in the Belgian province Hainaut, south of the town Chimay. It crosses the border with France after about 20 km. It flows into the Seine in Conflans-Sainte-Honorine, near Paris...
and the Marne
Marne River
The Marne is a river in France, a right tributary of the Seine in the area east and southeast of Paris. It is long. The river gave its name to the départements of Haute-Marne, Marne, Seine-et-Marne, and Val-de-Marne....
, based around the present-day city of Soissons
Soissons
Soissons is a commune in the Aisne department in Picardy in northern France, located on the Aisne River, about northeast of Paris. It is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital of the Suessiones...
. They were conquered in 57 BC
57 BC
Year 57 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Metellus...
by Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
.
They may have been known to the Romans as Suaeuconi.
Caesar recounts in his Gallic Wars
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were a series of military campaigns waged by the Roman proconsul Julius Caesar against several Gallic tribes. They lasted from 58 BC to 51 BC. The Gallic Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the...
that in 57 BC
57 BC
Year 57 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Metellus...
the Suessiones were ruled by Galba
Galba (Suessiones)
Galba was a king of the Suessiones, a Celtic polity of Belgic Gaul, during the Gallic Wars. When Julius Caesar entered the part of Gaul that was still independent of Roman rule in 58 BC, a number of Belgic polities formed a defensive alliance and universally acclaimed Galba commander-in-chief...
, and that in living memory of that time their king Diviciacus
Diviciacus (Suessiones)
Diviciacus or Divitiacus was a king of the Belgic nation of the Suessiones in the early 1st century BC. Julius Caesar, writing in the mid-1st century BC, says that he had within living memory been the most powerful king in Gaul, ruling a large portion not only of Gallia Belgica, but also of...
had exercised sovereignty over most of the Belgians and even parts of Britain
Prehistoric Britain
For the purposes of this article, Prehistoric Britain is that period of time between the first arrival of humans on the land mass now known as Great Britain and the start of recorded British history...
.
Coinage minted by Belgic Gauls first appeared in Britain in the mid-2nd century bc with the coinage now categorized as the "Gallo-Belgic A" type. Coins associated with King Diviciacus of the Suessiones, issued near or between 90 and 60 bc, have been categorized as "Gallo-Belgic C." Finds of this issue of coin extend from Sussex to the Wash, with a concentration of finds near Kent. A later issue of coin, "Gallo-Belgic F" (c. 60-50 bc), has concentrated finds near Paris, throughout the lands of the Suessiones, and the southern, coastal areas of Britain. These finds lead scholars to suggest that the Suessiones had significant trade and migration into Britain during the 2nd and 1st centuries prior to Roman conquest.
Caesar describes the Belgae as going to Britain looking for booty: "The inland part of Britain is inhabited by tribes declared in their own tradition to be indigenous to the island, the maritime part by tribes that migrated at an earlier time from Belgium to seek booty by invasion. ..."
The town mentioned by Caesar as their capital, Noviodunum ("New hill-fort"), established the present city of Soissons
Soissons
Soissons is a commune in the Aisne department in Picardy in northern France, located on the Aisne River, about northeast of Paris. It is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital of the Suessiones...
. The city of Soissons has remained the regional capital of the contemporary provence of Aisne
Aisne
Aisne is a department in the northern part of France named after the Aisne River.- History :Aisne is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790. It was created from parts of the former provinces of Île-de-France, Picardie, and Champagne.Most of the old...
, north of the region of Champagne
Champagne, France
Champagne is a historic province in the northeast of France, now best known for the sparkling white wine that bears its name.Formerly ruled by the counts of Champagne, its western edge is about 100 miles east of Paris. The cities of Troyes, Reims, and Épernay are the commercial centers of the area...
. It was the capital city of the Merovingian Kingdom of Soissons, 511-613. Soissons was the birthplace of the Frankish
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
Prince
Prince
Prince is a general term for a ruler, monarch or member of a monarch's or former monarch's family, and is a hereditary title in the nobility of some European states. The feminine equivalent is a princess...
Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
, in the year 747, son of King Pippin the Short and Bertrada of Laon
Bertrada of Laon
Bertrada of Laon, also called Bertha Broadfoot , was a Frankish queen.- Biography :...
.
The region is still commonly referred to as the "Soissonnais" and people of the region are the "Soissonaire."

