
Supercapacitor
Encyclopedia

Double layer (interfacial)
A double layer is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object...
capacitor, or ultracapacitor, is an electrochemical capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
with relatively high energy density
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
. Their energy density
Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
is typically hundreds of times greater than conventional electrolytic capacitor
Electrolytic capacitor
An electrolytic capacitor is a type of capacitor that uses an electrolyte, an ionic conducting liquid, as one of its plates, to achieve a larger capacitance per unit volume than other types. They are often referred to in electronics usage simply as "electrolytics"...
s. They also have a much higher power density
Power density
Power density is the amount of power per unit volume....
than batteries or fuel cells.
A typical D-cell
D battery
A D battery is a size of dry cell. A D cell is cylindrical with electrical contacts at each end; the positive end having a nub or bump...
-sized electrolytic capacitor may have capacitance
Capacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
of up to tens of millifarads. The same size EDLC might reach several farad
Farad
The farad is the SI unit of capacitance. The unit is named after the English physicist Michael Faraday.- Definition :A farad is the charge in coulombs which a capacitor will accept for the potential across it to change 1 volt. A coulomb is 1 ampere second...
s, an improvement of two orders of magnitude. EDLCs had a maximum working voltage of a few volts (standard electrolytics can work at hundreds of volts) and capacities of up to 5,000 farads. In 2010 the highest available EDLC specific energy was 30 Wh/kg (0.1 MJ/kg
MJ/kg
MJ/kg may refer to:* megajoules per kilogram* Specific kinetic energy* Heat of fusion* Heat of combustion...
).
The amount of energy stored per unit of mass is called specific energy
Specific energy
Specific energy is defined as the energy per unit mass. Common metric units are J/kg. It is an intensive property. Contrast this with energy, which is an extensive property. There are two main types of specific energy: potential energy and specific kinetic energy. Others are the gray and sievert,...
, which is often measured in Watt-hour per kilogram
Watt-hour per kilogram
The watt-hour per kilogram is a unit of specific energy commonly used to measure the density of energy in batteries and other capacitors. One watt-hour per kilogram is equal to 3600 joules per kilogram....
(Wh/kg) or MegaJoules per kilogram (MJ/kg). Up to 85 Wh/kg has been achieved at room temperature in the lab, lower than rapid-charging lithium-titanate batteries
Lithium-titanate battery
The lithium–titanate battery is a type of rechargeable battery, which has the advantage of being faster to charge than other lithium-ion batteries. Some analysts speculate that lithium–titanate batteries will power electric cars of the future....
.
Much research is being carried out to improve performance; for example an order of magnitude energy density improvement was achieved in the laboratory in mid-2011. Prices are dropping: a 3 kF capacitor that was US$5,000 ten years before was $50 in 2011.
EDLCs are used for energy storage rather than as general-purpose circuit components.
They have a variety of commercial applications, notably in "energy smoothing" and momentary-load devices. They have applications as energy-storage and KERS
Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems
Kinetic Energy Recovery Systems are automotive systems whereby the kinetic energy of a moving vehicle is recovered under braking and stored in a reservoir for later use under acceleration....
devices used in vehicle
Vehicle
A vehicle is a device that is designed or used to transport people or cargo. Most often vehicles are manufactured, such as bicycles, cars, motorcycles, trains, ships, boats, and aircraft....
s, and for smaller applications like home solar energy systems where extremely fast charging is a valuable feature.
Concept
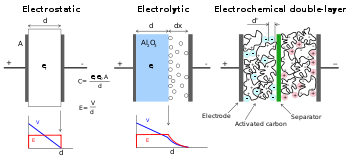
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
, energy is stored by the removal of charge carrier
Charge carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
s, typically electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s, from one metal plate and depositing them on another. This charge separation creates a potential
Electric potential
In classical electromagnetism, the electric potential at a point within a defined space is equal to the electric potential energy at that location divided by the charge there...
between the two plates, which can be harnessed in an external circuit. The total energy stored in this fashion increases with both the amount of charge stored and the potential between the plates. The amount of charge stored per unit voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
is essentially a function of the size, the distance, and the material properties of the plates and the material in between the plates (the dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
), while the potential between the plates is limited by the breakdown field strength of the dielectric. The dielectric controls the capacitor's voltage. Optimizing the material leads to higher energy density for a given size of capacitor.
EDLCs do not have a conventional dielectric. Rather than two separate plates separated by an intervening insulator, these capacitors use virtual plates that are in fact two layers of the same substrate. Their electrochemical properties, the so-called "electrical double layer
Double layer (interfacial)
A double layer is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object...
", result in the effective separation of charge despite the vanishingly thin (on the order of nanometers) physical separation of the layers. The lack of need for a bulky layer of dielectric, and the porosity
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
of the material used, permits the packing of plates with much larger surface area into a given volume, resulting in high capacitances in practical-sized packages.
In an electrical double layer, each layer by itself is quite conductive, but the physics at the interface where the layers are effectively in contact means that no significant current can flow between the layers. However, the double layer can withstand only a low voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
, which means that electric double-layer capacitors rated for higher voltages must be made of matched series-connected
Series and parallel circuits
Components of an electrical circuit or electronic circuit can be connected in many different ways. The two simplest of these are called series and parallel and occur very frequently. Components connected in series are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through all of the...
individual EDLCs, much like series-connected cells in higher-voltage batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
.
EDLCs have much higher power density
Power density
Power density is the amount of power per unit volume....
than batteries. Power density combines the energy density with the speed that the energy can be delivered to the load. Batteries, which are based on the movement of charge carriers in a liquid electrolyte, have relatively slow charge and discharge times. Capacitors, on the other hand, can be charged or discharged at a rate that is typically limited by current heating of the electrodes.
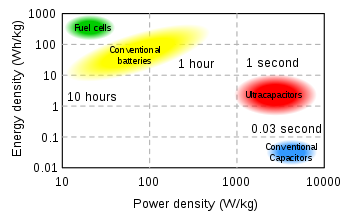
So while existing EDLCs have energy densities that are perhaps 1/10 that of a conventional battery, their power density is generally 10 to 100 times as great. This makes them most suited to an intermediary role between electrochemical batteries and electrostatic capacitors, where neither sustained energy release nor immediate power demands dominate one another.
History
General ElectricGeneral Electric
General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States...
engineers experimenting with devices using porous carbon electrodes first observed the EDLC effect in 1957. They believed that the energy was stored in the carbon pores and the device exhibited "exceptionally high capacitance", although the mechanism was unknown at that time.
General Electric did not immediately follow up on this work. In 1966 researchers at Standard Oil of Ohio
Standard Oil of Ohio
Standard Oil of Ohio or Sohio was an American oil company that was acquired by British Petroleum, now called BP.It was one of the successor companies to Standard Oil after the antitrust breakup in 1911. Standard Oil of Ohio was the original Standard Oil company founded by John D. Rockefeller. It...
developed the modern version of the devices, after they accidentally re-discovered the effect while working on experimental fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
designs. Their cell design used two layers of activated charcoal
Activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
separated by a thin porous insulator, and this basic mechanical design remains the basis of most electric double-layer capacitors.
Standard Oil did not commercialize their invention, licensing the technology to NEC
NEC
, a Japanese multinational IT company, has its headquarters in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. NEC, part of the Sumitomo Group, provides information technology and network solutions to business enterprises, communications services providers and government....
, who finally marketed the results as “supercapacitors” in 1978, to provide backup power for maintaining computer memory. The market expanded slowly for a time, but starting around the mid-1990s various advances in materials science
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
and refinement of the existing systems led to rapidly improving performance and an equally rapid reduction in cost.
The first trials of supercapacitors in industrial applications were carried out for supporting the energy supply to robots.
In 2005 aerospace systems and controls company Diehl Luftfahrt Elektronik
Diehl Aerospace
Diehl Aerospace GmbH is a Joint venture between Diehl BGT Defence and Thales Group operating in the field of Avionics. The headquarters of the company are in Überlingen, Germany....
GmbH chose supercapacitors to power emergency actuation systems for doors and evacuation slide
Evacuation slide
An evacuation slide is an inflatable slide used to evacuate an aircraft quickly. An escape slide is required on all commercial aircraft where the door sill height is such that, in the event of an evacuation, passengers would be unable to "step down" from the door uninjured An evacuation slide is...
s in airliner
Airliner
An airliner is a large fixed-wing aircraft for transporting passengers and cargo. Such aircraft are operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an aircraft intended for carrying multiple passengers in commercial...
s, including the new Airbus 380 jumbo jet. In 2005, the ultracapacitor market was between US $272 million and $400 million, depending on the source.
As of 2007 all solid state
Solid state
Solid state may refer to:In science:* Solid-state chemistry* Solid-state physics* Solid-state laser* Solid matterIn electronics:* Solid state , circuits built of solid materials* Solid-state fan...
micrometer-scale electric double-layer capacitors based on advanced superionic conductors had been for low-voltage electronics such as deep-sub-voltage nanoelectronics
Deep-sub-voltage nanoelectronics
Deep-sub-voltage nanoelectronics are integrated circuits operating near theoretical limits of energy consumption per unit of processing. These devices are intended to address the needs of applications such as wireless sensor networks which have dramatically different requirements from traditional...
and related technologies (the 22 nm technological node of CMOS and beyond).
Comparisons
Supercapacitors have several disadvantages and advantages relative to batteries, as described below.Disadvantages
- The amount of energy stored per unit weight is generally lower than that of an electrochemical battery (3–5 W·h/kg for a standard ultracapacitor, although 85 W.h/kg has been achieved in the lab compared to 30–40 W·h/kg for a lead acid battery), 100-250 W·h/kg for a lithium-ion battery and about 1/1,000th the volumetric energy density of gasoline.
- Has the highest dielectric absorptionDielectric absorptionDielectric absorption is the name given to the effect by which a capacitor that has been charged for a long time discharges only incompletely when briefly discharged. Although an ideal capacitor would remain at zero volts after being discharged, real capacitors will develop a small voltage, a...
of any type of capacitor. - High self-dischargeSelf-dischargeSelf-discharge is a phenomenon in batteries in which internal chemical reactions reduce the stored charge of the battery without any connection between the electrodes...
– the rate is considerably higher than that of an electrochemical battery. - Low maximum voltage – serial connections are needed to obtain higher voltages, and voltage balancing is required.
- Unlike practical batteries, the voltage across any capacitor, including EDLCs, drops significantly as it discharges. Effective storage and recovery of energy requires complex electronic control and switching equipment, with consequent energy loss. A detailed paper on a multi-voltage 5.3 W EDLC power supply for medical equipment discusses design principles in detail. It uses a total of 55 F of capacitance, charges in about 150 seconds, and runs for about 60 seconds. The circuit uses switch-mode voltage regulators followed by linear regulators for clean and stable power, reducing efficiency to about 70%. The authors discuss the types of switching regulator available, buck, boost, and buck-boost, and conclude that for the widely varying voltage across an EDLC buck-boost is best, boost second-best, and buck unsuitable.
- Very low internal resistance allows extremely rapid discharge when shorted, resulting in a spark hazard similar to any other capacitor of similar voltage and capacitance (generally much higher than electrochemical cells).
Advantages
- Long life, with little degradation over hundreds of thousands of charge cycleCharge cycleA charge cycle is the process of charging a rechargeable battery and discharging it as required into a load. The term is typically used to specify a battery's expected life, as the number of charge cycles affects life more than the mere passage of time...
s. Due to the capacitor's high number of charge-discharge cycles (millions or more compared to 200 to 1000 for most commercially available rechargeable batteries) it will last for the entire lifetime of most devices, which makes the device environmentally friendly. Rechargeable batteries wear out typically over a few years, and their highly reactive chemical electrolytes present a disposal and safety hazard. Battery lifetime can be optimised by charging only under favorable conditions, at an ideal rate and, for some chemistries, as infrequently as possible. EDLCs can help in conjunction with batteries by acting as a charge conditioner, storing energy from other sources for load balancing purposes and then using any excess energy to charge the batteries at a suitable time. - Low cost per cycle
- Good reversibility
- Very high rates of charge and discharge.
- Extremely low internal resistance (ESREquivalent series resistancePractical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated to a very good approximation as ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a resistance; this resistance is defined to be the equivalent...
) and consequent high cycle efficiency (95% or more) and extremely low heating levels - High output power
- High specific power. According to ITS (Institute of Transportation Studies, Davis, California) test results, the specific powerSpecific powerIn physics and engineering, surface power density or sometimes simply specific power is power per unit area.-Applications:* The intensity of electromagnetic radiation can be expressed in W/m2...
of electric double-layer capacitors can exceed 6 kW/kg at 95% efficiency - Improved safety, no corrosive electrolyte and low toxicity of materials.
- Simple charge methods—no full-charge detection is needed; no danger of overchargingOverchargingOvercharging can refer to:*Overcharging , a prosecutorial practice*Charging a battery too much*Charging a customer too much...
. - When used in conjunction with rechargeable batteries, in some applications the EDLC can supply energy for a short time, reducing battery cycling duty and extending life
Materials
In general, EDLCs improve storage density through the use of a nanoporousNanopore
A nanopore is a small hole. It may, for example, be created by a pore-forming protein or as a hole in synthetic materials such as silicon or graphene....
material, typically activated charcoal
Activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
, in place of the conventional insulating barrier. Activated charcoal is an extremely porous, "spongy" form of carbon with an extraordinarily high specific surface area
Specific surface area
Specific surface area is a material property of solids which measures the total surface area per unit of mass, solid or bulk volume, or cross-sectional area...
— a common approximation is that 1 gram (a pencil-eraser-sized amount) has a surface area of roughly 250 m2 — about the size of a tennis court. It is typically a powder made up of extremely fine but very "rough" particles, which, in bulk, form a low-density heap with many holes. As the surface area of even a thin layer of such a material is many times greater than a traditional material like aluminum, many more charge carriers (ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s or radicals
Radical (chemistry)
Radicals are atoms, molecules, or ions with unpaired electrons on an open shell configuration. Free radicals may have positive, negative, or zero charge...
from the electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
) can be stored in a given volume. As carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
is not a good insulator (vs. the excellent insulators used in conventional devices), in general EDLCs are limited to low potentials on the order of 2–3 V, and thus must be "stacked" (connected in series), just as conventional battery cells must be, to supply higher voltages.
Activated charcoal is not the "perfect" material for this application. The charge carriers are actually (in effect) quite large—especially when surrounded by molecules
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
—and are often larger than the holes left in the charcoal, which are too small to accept them, limiting the storage.
virtually all commercial supercapacitors use powdered activated carbon
Activated carbon
Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
made from coconut
Coconut
The coconut palm, Cocos nucifera, is a member of the family Arecaceae . It is the only accepted species in the genus Cocos. The term coconut can refer to the entire coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which is not a botanical nut. The spelling cocoanut is an old-fashioned form of the word...
shells. Higher performance devices are available, at a significant cost increase, based on synthetic carbon precursors that are activated with potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, commonly called caustic potash.Along with sodium hydroxide , this colorless solid is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications. Most applications exploit its reactivity toward acids and its corrosive...
(KOH).
Research in EDLCs focuses on improved materials that offer higher usable surface areas.
- GrapheneGrapheneGraphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
has excellent surface area per unit of gravimetric or volumetric densities, is highly conductive and can now be produced in various labs, but is not available in production quantities. Specific energy density of 85.6 Wh/kg at room temperature and 136 Wh/kg at 80 °C (all based on the total electrode weight), measured at a current density of 1 A/g have been observed. These energy density values are comparable to that of the Nickel metal hydride batteryNickel metal hydride batteryA nickel–metal hydride cell, abbreviated NiMH, is a type of rechargeable battery similar to the nickel–cadmium cell. The NiMH battery uses a hydrogen-absorbing alloy for the negative electrode instead of cadmium. As in NiCd cells, the positive electrode is nickel oxyhydroxide...
. The device makes full utilization of the highest intrinsic surface capacitance and specific surface area of single-layer graphene by preparing curved graphene sheets that do not restack face-to-face. The curved shape enables the formation of mesopores accessible to and wettable by environmentally benign ionic liquids capable of operating at a voltage >4 V. - Carbon nanotubes have excellent nanoporosity properties, allowing tiny spaces for the polymer to sit in the tube and act as a dielectric. Carbon nanotubeCarbon nanotubeCarbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical nanostructure. Nanotubes have been constructed with length-to-diameter ratio of up to 132,000,000:1, significantly larger than for any other material...
s can store about the same charge as charcoal (which is almost pure carbon) per unit surface area but nanotubes can be arranged in a more regular pattern that exposes greater suitable surface area. The addition of carbon nanotubes in capacitors can greatly improve and enhance the performance of electric double-layer capacitors. Due to the high surface area and high conductivity of single-wall carbon nanotubes, the addition of these nanotubes allows optimization for these capacitors. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes have a presence of mesopores that allow for easy access of ions at the electrode/electrolyte interface. The thin walls of a carbon nanotube allow for high capacitance in an electric double-layer capacitor. By adding multi-walled nanotubes to these capacitors, the resistance of the electrodes can be decreased. The capacitor cells with multi-walled nanotube fibers had higher electron and electrolyte-ion conductivities as compared to cells that did not have these nanotubes. These nanotubes also improved the power capabilities of the capacitors.
- Some polymers (e.g. polyacenes and conducting polymers) have a redoxRedoxRedox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
(reduction-oxidation) storage mechanism along with a high surface area.
- Carbon aerogelAerogelAerogel is a synthetic porous material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component of the gel has been replaced with a gas. The result is a solid with extremely low density and thermal conductivity...
provides extremely high surface area gravimetric densities of about 400–1000 m²/g. The electrodes of aerogel supercapacitors are a composite materialComposite materialComposite materials, often shortened to composites or called composition materials, are engineered or naturally occurring materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties which remain separate and distinct at the macroscopic or...
usually made of non-wovenWovenA woven is a cloth formed by weaving. It only stretches in the bias directions , unless the threads are elastic. Woven cloth usually frays at the edges, unless measures are taken to counter this, such as the use of pinking shears or hemming.Woven fabrics are worked on a loom and made of many...
paper made from carbon fiberCarbon fiberCarbon fiber, alternatively graphite fiber, carbon graphite or CF, is a material consisting of fibers about 5–10 μm in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the long axis of the fiber...
s and coated with organic aerogel, which then undergoes pyrolysisPyrolysisPyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures without the participation of oxygen. It involves the simultaneous change of chemical composition and physical phase, and is irreversible...
. The carbon fibers provide structural integrity and the aerogel provides the required large surface area. Small aerogel supercapacitors are being used as backup electricity storage in microelectronics. Aerogel capacitors can only work at a few volts; higher voltages ionize the carbon and damage the capacitor. Carbon aerogel capacitors have achieved 325 J/g (90 W·h/kg) energy density and 20 W/g power density.
- Solid activated carbonActivated carbonActivated carbon, also called activated charcoal, activated coal or carbo activatus, is a form of carbon that has been processed to make it extremely porous and thus to have a very large surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions.The word activated in the name is sometimes replaced...
, also termed consolidated amorphous carbonAmorphous carbonAmorphous carbon or free, reactive carbon, is an allotrope of carbon that does not have any crystalline structure. As with all glassy materials, some short-range order can be observed...
(CAC). It can have a surface area exceeding 2800 m2/g and may be cheaper to produce than aerogel carbon.
- Tunable nanoporous carbonTunable nanoporous carbonUltracapacitors may have the potential to become key components for energy storage in the industrial market with the rising push for environmental technology. There are several different approaches to creating ultracapacitors, as detailed here, and tunable nanoporous carbon is a relatively new...
exhibits systematic pore size control. adsorptionAdsorptionAdsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
treatment can be used to increase the energy density by as much as 75% over what was commercially available .
- Mineral-based carbon is a nonactivated carbon, synthesised from metal or metalloid carbideCarbideIn chemistry, a carbide is a compound composed of carbon and a less electronegative element. Carbides can be generally classified by chemical bonding type as follows: salt-like, covalent compounds, interstitial compounds, and "intermediate" transition metal carbides...
s, e.g. SiC, TiC, . The synthesised nanostructured porous carbon, often called Carbide Derived Carbon (CDC), has a surface area of about 400 m²/g to 2000 m²/g with a specific capacitance of up to 100 F/mL (in organic electrolyte). this material was used in a supercapacitor with a volume of 135 mL and 200 g weight having 1.6 kF capacitance. The energy density is more than 47 kJ/L at 2.85 V and power density of over 20 W/g.
- In August 2007 researchers combined a biodegradable paper batteryBattery (electricity)An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
with aligned carbon nanotubes, designed to function as both a lithium-ion battery and a supercapacitor (called bacitor). The device employed an ionic liquidIonic liquidAn ionic liquid is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below some arbitrary temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of electrically neutral molecules, ILs are largely made...
, essentially a liquid salt, as the electrolyteElectrolyteIn chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
. The paper sheets can be rolled, twisted, folded, or cut with no loss of integrity or efficiency, or stacked, like ordinary paper (or a voltaic pileVoltaic pileA voltaic pile is a set of individual Galvanic cells placed in series. The voltaic pile, invented by Alessandro Volta in 1800, was the first electric battery...
), to boost total output. They can be made in a variety of sizes, from postage stampPostage stampA postage stamp is a small piece of paper that is purchased and displayed on an item of mail as evidence of payment of postage. Typically, stamps are made from special paper, with a national designation and denomination on the face, and a gum adhesive on the reverse side...
to broadsheetBroadsheetBroadsheet is the largest of the various newspaper formats and is characterized by long vertical pages . The term derives from types of popular prints usually just of a single sheet, sold on the streets and containing various types of material, from ballads to political satire. The first broadsheet...
. Their light weight and low cost make them attractive for portable electronics, aircraftAircraftAn aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
, automobileAutomobileAn automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
s, and toys (such as model aircraftModel aircraftModel aircraft are flying or non-flying models of existing or imaginary aircraft using a variety of materials including plastic, diecast metal, polystyrene, balsa wood, foam and fibreglass...
), while their ability to use electrolytes in blood make them potentially useful for medical devices such as pacemakers.
- Other teams are experimenting with custom materials made of activated polypyrrolePolypyrrolePolypyrrole is a chemical compound formed from a number of connected pyrrole ring structures. For example a tetrapyrrole is a compound with four pyrrole rings connected. Methine-bridged cyclic tetrapyrroles are called porphyrins. Polypyrroles are conducting polymers of the rigid-rod polymer host...
, and nanotube-impregnated papers.
Capacitance
The capacitanceCapacitance
In electromagnetism and electronics, capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store energy in an electric field. Capacitance is also a measure of the amount of electric potential energy stored for a given electric potential. A common form of energy storage device is a parallel-plate capacitor...
of EDLCs was up to several thousands of farads .
Voltage
EDLCs rated up to a maximum working voltage of about 5 V were available.Specific energy
The specific energySpecific energy
Specific energy is defined as the energy per unit mass. Common metric units are J/kg. It is an intensive property. Contrast this with energy, which is an extensive property. There are two main types of specific energy: potential energy and specific kinetic energy. Others are the gray and sievert,...
of existing commercial EDLCs ranges from around 0.5 to 30 W·h/kg including lithium ion capacitor
Lithium ion capacitor
A lithium-ion capacitor is a hybrid type of capacitor. Activated carbon is used as cathode. The anode of the LIC consists of carbon material which is pre-doped with lithium ion...
s, known also as a "hybrid capacitor". Experimental electric double-layer capacitors have demonstrated specific energies of 30 W·h/kg and have been shown to be scalable to at least 136 W·h/kg. For comparison, a conventional lead-acid battery
Lead-acid battery
Lead–acid batteries, invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté, are the oldest type of rechargeable battery. Despite having a very low energy-to-weight ratio and a low energy-to-volume ratio, their ability to supply high surge currents means that the cells maintain a relatively large...
stores typically 30 to 40 W·h/kg and modern lithium-ion batteries about 160 W·h/kg. Gasoline
Gasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
has a net calorific value (NCV) of around 12,000 W·h/kg; automobile applications operate at about 20% tank-to-wheel efficiency, giving an effective specific energy of 2,400 W·h/kg (effective specific energy of ultracapacitors is not known since data is not available for electrical-output-to-wheel efficiency for ultracapacitor driven vehicles).
Power density
EDLCs have energy densities perhaps one tenth that of a rechargeable battery, but power densities typically 10 to 100 times greater.Self-discharge
An EDLC which is charged and stored loses its charge (self-discharge) much faster than a typical electrolytic capacitor, and somewhat faster than a rechargeable battery.Price
Research and development bring rapid improvements in price as well as physical properties.Costs have fallen quickly, with cost per kilojoule dropping faster than cost per farad. By 2006 the cost of supercapacitors was 1 cent per farad and $2.85 per kilojoule and dropping. A 3 kF capacitor that was US$5,000 ten years before was $50 in 2011.
Heavy and public transport
Some of the earliest uses were motor startup capacitors for large engines in tankTank
A tank is a tracked, armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat which combines operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defensive capabilities...
s and submarine
Submarine
A submarine is a watercraft capable of independent operation below the surface of the water. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability...
s, and as the cost has fallen they have started to appear on diesel
Diesel engine
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber...
trucks and railroad locomotives. In the 2000s they attracted attention in the green energy world, where their ability to charge much faster than batteries makes them particularly suitable for regenerative braking applications. New technology could potentially make EDLCs with high enough energy density to be an attractive replacement for batteries in all-electric cars
Battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle, or BEV, is a type of electric vehicle that uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of, or in addition to, internal combustion engines for propulsion.A battery-only electric vehicle or...
and plug-in hybrids, as EDLCs charge quickly and are stable with respect to temperature.
China is experimenting with a new form of electric bus
Electric bus
An electric bus is a bus powered by electricity.There are two main electric bus categories:* Non-autonomous electric buses:**The trolleybus is a type of electric bus powered by two overhead electric wires, with electricity being drawn from one wire and returned via the other wire, using two...
(capabus) that runs without powerlines using large onboard EDLCs, which quickly recharge whenever the bus is at any bus stop
Bus stop
A bus stop is a designated place where buses stop for passengers to board or leave a bus. These are normally positioned on the highway and are distinct from off-highway facilities such as bus stations. The construction of bus stops tends to reflect the level of usage...
(under so-called electric umbrellas), and fully charge in the terminus
Bus terminus
A bus terminus is a designated place where a bus or coach starts or ends its scheduled route. The terminus is the designated place that a timetable is timed from. Termini can be located at bus stations, interchanges, bus garages or simple bus stops. Termini can both start and stop at the same...
. A few prototypes were being tested in Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
in early 2005. In 2006, two commercial bus routes began to use electric double-layer capacitor buses; one of them is route 11 in Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
.
In 2001 and 2002 VAG, the public transport operator in Nuremberg
Nuremberg
Nuremberg[p] is a city in the German state of Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Situated on the Pegnitz river and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it is located about north of Munich and is Franconia's largest city. The population is 505,664...
, Germany tested an hybrid bus
Hybrid electric bus
A hybrid electric bus combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. These type of buses normally use a diesel-electric powertrain and are also known as hybrid diesel-electric buses....
that uses a diesel-electric battery drive system with electric double-layer capacitors. Since 2003 Mannheim Stadtbahn in Mannheim, Germany has operated a light-rail vehicle (LRV) that uses EDLCs to store braking energy.
Other public transport manufacturers are developing EDLC technology, including mobile storage and a stationary trackside power supply.
A triple hybrid forklift truck uses fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
s and batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
as primary energy storage and EDLCs to supplement this energy storage solution.
Automotive
Ultracapacitors are used in some concept prototype vehicles, in order to keep batteries within resistive heating limits and extend battery life. The ultrabattery combines a supercapacitor and a battery in one unit, creating an electric vehicle battery that lasts longer, costs less and is more powerful than current plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).Motor racing
The FIA, the governing body for many motor racing events, proposed in the Power-Train Regulation Framework for Formula 1 version 1.3 of 23 May 2007 that a new set of power train regulations be issued that includes a hybrid drive of up to 200 kW input and output power using "superbatteries" made with both batteries and supercapacitors.Complementing batteries
When used in conjunction with rechargeable batteries in uninterruptible power supplies and similar applications, the EDLC can handle short interruptions, requiring the batteries to be used only during long interruptions, reducing the cycling duty and extending their lifeLow-power applications
EDLCs can be used to operate low-power equipment such as PC CardPC Card
In computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
s, photographic flash
Flash (photography)
A flash is a device used in photography producing a flash of artificial light at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light...
, flashlights
Self-powered equipment
Human-powered equipment describes electrical appliances which can be powered by electricity generated by human muscle power as an alternative to conventional sources of electricity such as primary batteries and the power grid....
, portable media player
Portable media player
A portable media player or digital audio player, is a consumer electronics device that is capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, video, documents, etc. the data is typically stored on a hard drive, microdrive, or flash memory. In contrast, analog portable audio...
s, and automated meter reading equipment. They are advantageous when extremely fast charging is required. In professional medical applications, EDLCs have been used to power a handheld, laser-based breast cancer detector (55 F to provide 5.3 W at multiple voltages; charges in 150 seconds, runs for 60 seconds).
In 2007 a cordless electric screwdriver that uses an EDLC for energy storage was produced. It charges in 90 seconds, retains 85% of the charge after 3 months, and holds enough charge for about half the screws (22) a comparable screwdriver with a rechargeable battery will handle (37). Two LED flashlights using EDLCs were released in 2009. They charge in 90 seconds.
Alternative energy
The idea of replacing batteries with capacitors in conjunction with novel energy sources became a conceptual umbrella of the Green Electricity (GEL) Initiative. One successful GEL Initiative concept was a muscle-driven autonomous solution that employs a multi-farad EDLC as energy storage to power a variety of portable electrical and electronic devices such as MP3 players, AM/FM radios, flashlights, cell phones, and emergency kits.Market
According to Innovative Research and Products (iRAP), ultracapacitor market growth will continue during 2009 to 2014. Worldwide business, over US$275 million in 2009, will continue to grow at an AAGR of 21.4% through 2014.See also
- Electric vehicle batteryElectric vehicle batteryAn electric vehicle battery or traction battery is a rechargeable battery used for propulsion of battery electric vehicles...
- Types of capacitors
- NanoflowerNanoflowerA nanoflower, in chemistry, refers to a compound of certain elements that results in formations which in microscopic view resemble flowers or, in some cases, trees that are called nanobouquets or nanotrees...
- Rechargeable electricity storage system
- Flywheel energy storageFlywheel energy storageFlywheel energy storage works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy...
- List of emerging technologies
- Lithium ion capacitorLithium ion capacitorA lithium-ion capacitor is a hybrid type of capacitor. Activated carbon is used as cathode. The anode of the LIC consists of carbon material which is pre-doped with lithium ion...
- Self-powered equipmentSelf-powered equipmentHuman-powered equipment describes electrical appliances which can be powered by electricity generated by human muscle power as an alternative to conventional sources of electricity such as primary batteries and the power grid....
- Mechanically powered flashlight
External links
- Super Capacitor Seminar
- Article on ultracapacitors at electronicdesign.com
- Article on ultracapacitors at batteryuniversity.com
- A new version of an old idea is threatening the battery industry (The EconomistThe EconomistThe Economist is an English-language weekly news and international affairs publication owned by The Economist Newspaper Ltd. and edited in offices in the City of Westminster, London, England. Continuous publication began under founder James Wilson in September 1843...
). - An Encyclopedia Article From the Yeager center at CWRU.
- Ultracapacitors & Supercapacitors Forum
- Special Issue of Interface magazine on electrochemical capacitors
- Nanoflowers Improve Ultracapacitors: A novel design could boost energy storage (Technology ReviewTechnology ReviewTechnology Review is a magazine published by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was founded in 1899 as "The Technology Review", and was re-launched without the "The" in its name on April 23, 1998 under then publisher R. Bruce Journey...
) and Can nanoscopic meadows drive electric cars forward? (New ScientistNew ScientistNew Scientist is a weekly non-peer-reviewed English-language international science magazine, which since 1996 has also run a website, covering recent developments in science and technology for a general audience. Founded in 1956, it is published by Reed Business Information Ltd, a subsidiary of...
) - If the cap fits... How supercapacitors can help to solve power problems in portable products.
- A web that describes the development of solid-state and hybrid supercapacitors from CNR-ITAE (Messina) Italy

