
Surasena
Encyclopedia
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n region corresponding to the present-day Braj
Braj
Braj is a region mainly in Uttar Pradesh of India, around Mathura-Vrindavan. Braj, though never a clearly defined political region in India but is very well demarcated culturally, is considered to be the land of Krishna and is derived from the Sanskrit word vraja...
region in Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
. According to the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya
Anguttara Nikaya
The Anguttara Nikaya is a Buddhist scripture, the fourth of the five nikayas, or collections, in the Sutta Pitaka, which is one of the "three baskets" that comprise the Pali Tipitaka of Theravada Buddhism...
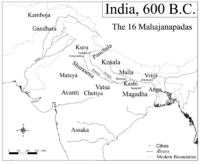
, Surasena was one of the solasa (sixteen) Mahajanapadas
Mahajanapadas
Mahājanapadas , literally "great realms", were ancient Indian kingdoms or countries...
(powerful realms) in 6th century BCE The ancient Greek writers refer the region as Sourasenoi and mention its capital as Methora.
Etymology
There are several traditions regarding the etymology of its name. According to one tradition, it was derived from a famed YadavaYadu
Yadu is one of the five Indo-Aryan tribes mentioned in the Rig Veda . The Mahabharata, the Harivamsha and the Puranas mention Yadu as the eldest son of king Yayati and his queen Devayani. The prince of King Yayati, Yadu was a self-respecting and a very established ruler...
king Surasena, while others see it as an extension of Surabhir (Abhira). According to Megasthenes
Megasthenes
Megasthenes was a Greek ethnographer in the Hellenistic period, author of the work Indica.He was born in Asia Minor and became an ambassador of Seleucus I of Syria possibly to Chandragupta Maurya in Pataliputra, India. However the exact date of his embassy is uncertain...
, people of this place worshipped the shepherd God Herakles, which according to many scholars was due to a misconception while others see in it connotations of Scythic origin of Yadu
Yadu
Yadu is one of the five Indo-Aryan tribes mentioned in the Rig Veda . The Mahabharata, the Harivamsha and the Puranas mention Yadu as the eldest son of king Yayati and his queen Devayani. The prince of King Yayati, Yadu was a self-respecting and a very established ruler...
s. It was the sacred land of Lord Krishna
Krishna
Krishna is a central figure of Hinduism and is traditionally attributed the authorship of the Bhagavad Gita. He is the supreme Being and considered in some monotheistic traditions as an Avatar of Vishnu...
in which he was born, raised, and ruled. It was an ancient Janapada
Janapadas
The Janapadas were the major realms or kingdoms of Vedic India which, by the 6th century BC, evolved into the sixteen classical Mahajanapadas.-Etymology:...
. It has been well mentioned in Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
.
History
The Mahabharata and the PuranasPuranas
The Puranas are a genre of important Hindu, Jain and Buddhist religious texts, notably consisting of narratives of the history of the universe from creation to destruction, genealogies of kings, heroes, sages, and demigods, and descriptions of Hindu cosmology, philosophy, and geography.Puranas...
refer the rulers of the Mathura region as the Yadus or Yadava
Yadava
The Yadavas were an ancient Indian people who believed themselves to be descended from Yadu, a mythical king. The community was probably formed of four clans, being the Abhira, Andhaka, Vrishni, and Satvatas, who all worshipped Lord Krishna. They are listed in ancient Indian literature as the...
s, divided in to a number of septs, which include the Vrishni
Vrishni
The Vrishnis were an ancient Indian clan who were believed as the descendants of Vrishni, a descendent of Yadu. It is believed that Vrishni was son of Satvata, a descendant of Yadu, the son of Yayati. He had two wives, Gandhari and Madri. He has a son named Devamidhusha by his wife Madri....
s. The Buddhist texts refer to Avantiputta, the king of the Surasenas in the time of Maha Kachchana
Katyayana (Buddhist)
Katyayana was a disciple of Gautama Buddha.Katyayana, also known as Kaccana , Mahakatyayana, Mahakaccana and in Japanese as Kasennen, is one of the "Ten Disciples of the Buddha". [ Mahakashyapa, 2) Ananda, 3) Shariputra, 4) Subhuti, 5) Purna, 6) Mahamaudgalyayana, 7) Maha Katyayana, 8) Aniruddha,...
, one of the chief disciples of Gautama Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
, who spread Buddhism in the Mathura region.
Its capital, Mathura, was situated on the bank of the river Yamuna
Yamuna
The Yamuna is the largest tributary river of the Ganges in northern India...
, presently a sacred place for the Hindus
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
. The ancient Greek writers mention about another city named Cleisobora in this region.

