
Synchronization model
Encyclopedia
In configuration management
(CM), one has to control (among other things) changes made to software and documentation. This is called revision control
, which manages multiple versions of the same unit of information. Although revision control is important to CM, it is not equal to it.
Synchronization Models, also known as Configuration Management Models (Feiler, 1991), describe methods to enable revision control through allowing simultaneous, concurrent changes to individual files.
from which they are checked out whenever the files are accessed, and checked in when they have changed. This repository can store multiple versions of the files. Because these files can be documentation
or source code
, but can also be a collection of files, the term Configuration item
(CI) will be used from now on. The basic mechanism used to prevent conflicts by simultaneous modifications is that of locking
.
instead of individual files. Although the complete check-out/check-in model is represented in the composition model, it enables the use of different strategies for updating through the use of improved support for the management of configurations. A configuration is defined as being built up from a system model and version selection rules. The system model determines which files are used, while the version selection rules determine which version of the files (e.g. the latest versions or of a certain development state
).
which is stored separately. Files in this configuration can be synchronized using the check-out/check-in model. When the change is completed, the complete configuration is stored back into the repository and integrated with other changes.
version.
This entry covers the check-out/check-in synchronization model, including a meta-model
(a process-data diagram). Because the check-out/check-in model is also included as a part of the other models discussed above, it is therefore further elaborated upon. Issues that are not discussed in detail are the three remaining synchronization models and the actual editing of CIs together with the methods related to this.

The process-data diagram above describes the different concepts that are applicable in the check-out/check-in synchronization model and their relation to the activities that take place. Central to the meta-data model (right side of the figure) is the Configuration Item. This is stored in one or more repositories and can for example be a source code file or a collection of other CIs. The repository can contain multiple branches and revisions of files. These in turn consist of configuration items.
The meta-process model (left side of the figure) describes the process of the check-out and check-in activities. The activities are explained in the table of activities below.
The turn-taking mechanism of locking is a real problem as well when working with many developers, as these files cannot be edited by others once it has been locked.
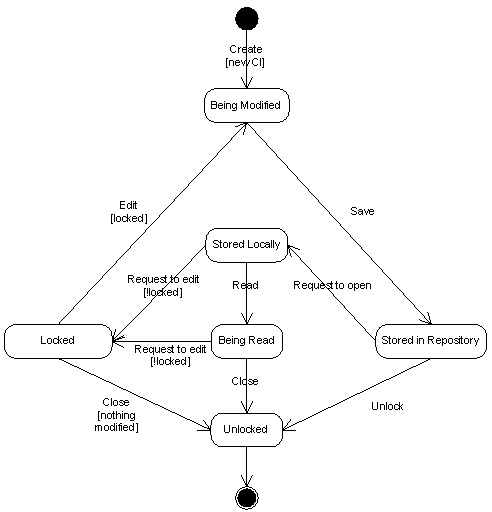
When a CI is first created, it is modified and stored in the repository. When someone requests to open the CI, it is first copied to the local machine of the developer (note: there are systems where editing occurs directly in the repository. The copy step however is the classic check-out/check-in way). When that developer also wants to edit the CI, it requests a lock. This can be done directly at the request of opening a CI, but also after some time of reading it. When the CI is not locked yet, a lock is applied and it can be modified by the developer. After modifications have been done, it is stored back in the repository and unlocked.
Now, assume that the developer that was just discussed is in the process of editing a CI that is already in the repository. You want to open a CI from the repository and so it is copied to your local drive. You start reading it and find some things you wish to change, so you request to edit it. However, the CI is already locked and you will have to wait for it to be unlocked or close the file and proceed to another one.
Configuration management
Configuration management is a field of management that focuses on establishing and maintaining consistency of a system or product's performance and its functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life.For information assurance, CM...
(CM), one has to control (among other things) changes made to software and documentation. This is called revision control
Revision control
Revision control, also known as version control and source control , is the management of changes to documents, programs, and other information stored as computer files. It is most commonly used in software development, where a team of people may change the same files...
, which manages multiple versions of the same unit of information. Although revision control is important to CM, it is not equal to it.
Synchronization Models, also known as Configuration Management Models (Feiler, 1991), describe methods to enable revision control through allowing simultaneous, concurrent changes to individual files.
Synchronization models
Feiler (1991) reports on four different synchronization models, shortly described below.Check-out/check-in
In the check-out/check-in model, files are stored individually in a repositoryRepository (publishing)
A repository in publishing, and especially in academic publishing,is a real or virtual facility for the deposit of academic publications, such as academic journal articles....
from which they are checked out whenever the files are accessed, and checked in when they have changed. This repository can store multiple versions of the files. Because these files can be documentation
Software documentation
Software documentation or source code documentation is written text that accompanies computer software. It either explains how it operates or how to use it, and may mean different things to people in different roles....
or source code
Source code
In computer science, source code is text written using the format and syntax of the programming language that it is being written in. Such a language is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source...
, but can also be a collection of files, the term Configuration item
Configuration item
The term configuration item or CI refers to the fundamental structural unit of a configuration management system. Examples of CIs include individual requirements documents, software, models, plans, and people...
(CI) will be used from now on. The basic mechanism used to prevent conflicts by simultaneous modifications is that of locking
Lock (computer science)
In computer science, a lock is a synchronization mechanism for enforcing limits on access to a resource in an environment where there are many threads of execution. Locks are one way of enforcing concurrency control policies.-Types:...
.
Composition
The composition model is an extension on the check-out/check-in model. This model allows developers to think in configurationsComputer configuration
In communications or computer systems, a configuration is an arrangement of functional units according to their nature, number, and chief characteristics. Often, configuration pertains to the choice of hardware, software, firmware, and documentation...
instead of individual files. Although the complete check-out/check-in model is represented in the composition model, it enables the use of different strategies for updating through the use of improved support for the management of configurations. A configuration is defined as being built up from a system model and version selection rules. The system model determines which files are used, while the version selection rules determine which version of the files (e.g. the latest versions or of a certain development state
Development stage
A software release life cycle refers to the phases of development and maturity for a piece of computer software—ranging from its initial development, to its eventual release, and updated versions of the released version to help improve software or fix bugs still present in the software.- Pre-alpha...
).
Long transactions
The long transactions model takes a broader approach by assuming that a system is built up out of logical changes. Its focus is on the coordination and integration of these changes. Basically, it uses versions of configurations and versions of files. A configuration is created based on a change requestChange request
A change request is a document containing a call for an adjustment of a system; it is of great importance in the change management process. A change request is not raised for a wording change in a letter....
which is stored separately. Files in this configuration can be synchronized using the check-out/check-in model. When the change is completed, the complete configuration is stored back into the repository and integrated with other changes.
Change set
The change set model also works based on change requests and has a lot in common with the long transactions model. However, it starts with a certain configuration as the basis for changes. This is then changed according to the independent change requests that come in. New configurations of the product are then created by applying sets of the independently stored changes on the baselineBaseline (configuration management)
Configuration management is the process of managing change in hardware, software, firmware, documentation, measurements, etc. As change requires an initial state and next state, the marking of significant states within a series of several changes becomes important...
version.
This entry covers the check-out/check-in synchronization model, including a meta-model
Meta model
A meta-model typically defines the language and processes from which to form a model. It has many uses:-Computing:*Metamodeling a modeling methodology used in software engineering*MODAF Meta-Model...
(a process-data diagram). Because the check-out/check-in model is also included as a part of the other models discussed above, it is therefore further elaborated upon. Issues that are not discussed in detail are the three remaining synchronization models and the actual editing of CIs together with the methods related to this.
Vocabulary
| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Version | A version is a state of an object or concept that varies from its previous state or condition. |
| Configuration item Configuration item The term configuration item or CI refers to the fundamental structural unit of a configuration management system. Examples of CIs include individual requirements documents, software, models, plans, and people... |
An element of software or a document placed under version control. A group of CIs can also be defined as a CI (Crnkovic et al., 2003). |
| Configuration item history | A concept to facilitate version stamping. Splits version specific attributes from attributes common to all versions (Van de Weerd, 2005) |
| Document | Many types of documentation are part of software engineering. Consider documents that describe the software architecture, technical documentation, user manuals, etc. |
| Source code Source code In computer science, source code is text written using the format and syntax of the programming language that it is being written in. Such a language is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source... file |
A source code file contains any series of statements written in some human-readable computer programming language. A computer program's source code is the collection of files that can be converted from human-readable form to an equivalent computer-executable form. |
| Repository Information repository An information repository is an easy way to deploy a secondary tier of data storage that can comprise multiple, networked data storage technologies running on diverse operating systems, where data that no longer needs to be in primary storage is protected, classified according to captured metadata,... |
A repository is also called a vault. A repository contains only one complete version of a configuration item. Differences between versions are usually stored using a delta algorithm (Crnkovic, Asklund & Persson-Dahlqvist, 2003). |
| Versioning organization | Versions of a CI may be organized in a number of different ways. This is the parent for the concepts that describe the organization of versions (Crnkovic et al., 2003). |
| Branch Branch A branch or tree branch is a woody structural member connected to but not part of the central trunk of a tree... |
Versions organized as parallel development lines (Crnkovic et al., 2003). |
| Revision Revision Revision is the process of revising.More specifically, it may refer to:* Update, a modification of software or a database* Revision control, the management of changes to sets of computer files* Belief revision... |
Versions organized in a sequence (Crnkovic et al., 2003). |
| Development state Development stage A software release life cycle refers to the phases of development and maturity for a piece of computer software—ranging from its initial development, to its eventual release, and updated versions of the released version to help improve software or fix bugs still present in the software.- Pre-alpha... |
Expresses how the development of a piece of software has progressed and how much further development it may require. Each major version of a product usually goes through a stage when new features are added (alpha stage / state), then a stage when it is actively debugged (beta stage / state), and finally a stage when all important bugs have been removed (stable stage / state). |
Elaboration on check-out/check-in model
This section contains an elaboration on the check-out/check-in synchronization model.Process-data diagram

The process-data diagram above describes the different concepts that are applicable in the check-out/check-in synchronization model and their relation to the activities that take place. Central to the meta-data model (right side of the figure) is the Configuration Item. This is stored in one or more repositories and can for example be a source code file or a collection of other CIs. The repository can contain multiple branches and revisions of files. These in turn consist of configuration items.
The meta-process model (left side of the figure) describes the process of the check-out and check-in activities. The activities are explained in the table of activities below.
| Activity | Sub-activity | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Check-Out | Files are not read or changed directly from the repository. Checking out describes these activities. | |
| Copy CI | A particular version of a CI is copied from the repository. | |
| Lock CI | If write access is required and if the CI is not already locked by someone else, the CI is locked. Otherwise the CI cannot be written back to the repository (read-only access). | |
| Modify CI | The person editing the CI makes changes to it. This is out of the scope of the current meta-model regarding version management. | |
| Check-In | The CI needs to be placed back into the repository. Checking in describes these activities. | |
| Select versioning strategy | The new CI has to be placed back in the repository using a versioning strategy. This describes the selection of the strategy used to place the CI back into the repository. | |
| Create branch | The CI is selected to be the start of a new branch. | |
| Create revision | The CI is selected to be a revision of another CI. | |
| Select development state | The CI is determined to be of a certain development state. | |
| Write CI | The CI is stored in the repository. | |
| Unlock CI | The CI is unlocked. |
Evaluation
Feiler (1991) evaluated the check-out/check-in synchronization model. It has the clear advantage that it’s easy to use and understand. However, this simplicity results in a lack of management of configurations, such as product version tracking and checking version history across multiple logically connected files.The turn-taking mechanism of locking is a real problem as well when working with many developers, as these files cannot be edited by others once it has been locked.
Example
To illustrate the check-out/check-in synchronization model, this section contains an example of how this process works. The figure below contains a state transition diagram of a CI.
When a CI is first created, it is modified and stored in the repository. When someone requests to open the CI, it is first copied to the local machine of the developer (note: there are systems where editing occurs directly in the repository. The copy step however is the classic check-out/check-in way). When that developer also wants to edit the CI, it requests a lock. This can be done directly at the request of opening a CI, but also after some time of reading it. When the CI is not locked yet, a lock is applied and it can be modified by the developer. After modifications have been done, it is stored back in the repository and unlocked.
Now, assume that the developer that was just discussed is in the process of editing a CI that is already in the repository. You want to open a CI from the repository and so it is copied to your local drive. You start reading it and find some things you wish to change, so you request to edit it. However, the CI is already locked and you will have to wait for it to be unlocked or close the file and proceed to another one.
See also
- Configuration managementConfiguration managementConfiguration management is a field of management that focuses on establishing and maintaining consistency of a system or product's performance and its functional and physical attributes with its requirements, design, and operational information throughout its life.For information assurance, CM...
- Revision controlRevision controlRevision control, also known as version control and source control , is the management of changes to documents, programs, and other information stored as computer files. It is most commonly used in software development, where a team of people may change the same files...
- Change management processChange management processThe change management process in systems engineering is the process of requesting, determining attainability, planning, implementing, and evaluating of changes to a system...
- Release managementRelease managementThe release management process is a relatively new but rapidly growing discipline within software engineering of managing software releases....
- Product structure modelingProduct Structure ModelingProduct structure is a hierarchical decomposition of a product, typically known as the bill of materials .As business becomes more responsive to unique consumer tastes and derivative products grow to meet the unique configurations, BOM management can become unmanageable.Advanced modeling techniques...
- Product family engineeringProduct Family EngineeringProduct family engineering , also known as product line engineering, is a synonym for "domain engineering" created by the Software Engineering Institute, a term coined by James Neighbors in his 1980 dissertation at University of California, Irvine...
- Product life-cycle management
- List of revision control software

