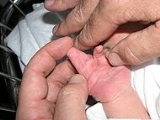
Syndactyly
Encyclopedia
Syndactyly is a condition wherein two or more digits are fused together. It occurs normally in some mammal
s, such as the siamang
and kangaroo
, but is an unusual condition in humans.
Syndactyly can be complete or incomplete.
Complex syndactyly occurs as part of a syndrome (such as Apert syndrome
) and typically involves more digits and with complex syndactyly.
Fenestrated syndactyly means the skin is joined for most of the digit but in a proximal area there is gap in the syndactyly with normal skin. This type of syndactyly is found in amniotic band syndrome
.
Simple syndactyly can be full or partial, and is present at birth (congenital). In early human fetal development, webbing (syndactyly) of the toes and fingers is normal. At about 16 weeks of gestation, apoptosis
takes place and an enzyme dissolves the tissue between the fingers and toes, and the webbing disappears. In some fetuses, this process does not occur completely between all fingers or toes and some residual webbing remains.
associated with these types and their common phenotypical
expression are as follows:
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s, such as the siamang
Siamang
The siamang is a tailless, arboreal, black-furred gibbon native to the forests of Malaysia, Thailand, and Sumatra. The largest of the lesser apes, the siamang can be twice the size of other gibbons, reaching 1 m in height, and weighing up to 14 kg...
and kangaroo
Kangaroo
A kangaroo is a marsupial from the family Macropodidae . In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, especially those of the genus Macropus, Red Kangaroo, Antilopine Kangaroo, Eastern Grey Kangaroo and Western Grey Kangaroo. Kangaroos are endemic to the country...
, but is an unusual condition in humans.
Classification
Syndactyly can be simple or complex.- In simple syndactyly, adjacent fingers or toes are joined by soft tissue.
- In complex syndactyly, the bones of adjacent digits are fused. The kangarooKangarooA kangaroo is a marsupial from the family Macropodidae . In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, especially those of the genus Macropus, Red Kangaroo, Antilopine Kangaroo, Eastern Grey Kangaroo and Western Grey Kangaroo. Kangaroos are endemic to the country...
exhibits complex syndactyly.
Syndactyly can be complete or incomplete.
- In complete syndactyly, the skin is joined all the way to the tip of the finger
- In incomplete syndactyly, the skin is only joined part of the distance to the fingertip.
Complex syndactyly occurs as part of a syndrome (such as Apert syndrome
Apert syndrome
Apert syndrome is a form of acrocephalosyndactyly, a congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial arch, the precursor of the maxilla and mandible...
) and typically involves more digits and with complex syndactyly.
Fenestrated syndactyly means the skin is joined for most of the digit but in a proximal area there is gap in the syndactyly with normal skin. This type of syndactyly is found in amniotic band syndrome
Amniotic band syndrome
Amniotic band syndrome is a congenital disorder caused by entrapment of fetal parts in fibrous amniotic bands while in utero.-Epidemiology:Amniotic banding affects approximately 1 in 1,200 live births...
.
Simple syndactyly can be full or partial, and is present at birth (congenital). In early human fetal development, webbing (syndactyly) of the toes and fingers is normal. At about 16 weeks of gestation, apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
takes place and an enzyme dissolves the tissue between the fingers and toes, and the webbing disappears. In some fetuses, this process does not occur completely between all fingers or toes and some residual webbing remains.
Genetics
Five types of syndactyly have been identified in humans. The corresponding lociLocus (genetics)
In the fields of genetics and genetic computation, a locus is the specific location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome. A variant of the DNA sequence at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a genetic map...
associated with these types and their common phenotypical
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
expression are as follows:
- type I: 2q34-q36; webbing occurs between middle and ring fingers and/or second and third toes.
- type II: 2q31; also involves long and ring fingers, but has a sixth finger merged in between.
- type III: 6q21-q23; small finger is merged into the ring finger.
- type IV: 7q36; involves all fingers and/or toes
- type V: 2q31-q32; similar to type I, but the metacarpals and metatarsalsMetatarsusThe metatarsus or metatarsal bones are a group of five long bones in the foot located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side : the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth...
may also be fused.
Treatment


