
T-stage
Encyclopedia
T-stages are the small compressor stages, featured on some turbofan
engines, that are mounted on the low pressure (LP) shaft directly behind the fan.
Although T-stages usually only supercharge
the core stream, some engines do feature a deliberately oversized intermediate pressure (IP) compressor, which compresses both the core flow and a proportion of the bypass flow. This enhances the stability of the T-stages during throttling. Where necessary, the alternative is to employ blow-off valves.
T-stages are used to increase overall pressure ratio and, for a given core size, the core mass flow. This is demonstrated by the following relationship:
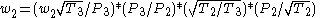
T-stages are a popular method for uprating the thrust of an engine (see, for example the Pratt & Whitney Canada PW500
).
The alternative is to place a zero-stage
, mounted on the HP shaft, at the front of the HP compressor. This approach requires a significant change in the HP turbine, whereas a T-stage can, if necessary, be accommodated by simply adding an additional stage to the rear of the LP turbine.
Turbofan
The turbofan is a type of airbreathing jet engine that is widely used for aircraft propulsion. A turbofan combines two types of engines, the turbo portion which is a conventional gas turbine engine, and the fan, a propeller-like ducted fan...
engines, that are mounted on the low pressure (LP) shaft directly behind the fan.
Although T-stages usually only supercharge
Supercharger
A supercharger is an air compressor used for forced induction of an internal combustion engine.The greater mass flow-rate provides more oxygen to support combustion than would be available in a naturally aspirated engine, which allows more fuel to be burned and more work to be done per cycle,...
the core stream, some engines do feature a deliberately oversized intermediate pressure (IP) compressor, which compresses both the core flow and a proportion of the bypass flow. This enhances the stability of the T-stages during throttling. Where necessary, the alternative is to employ blow-off valves.
T-stages are used to increase overall pressure ratio and, for a given core size, the core mass flow. This is demonstrated by the following relationship:
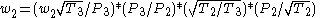
- where:
- core mass flow =

- core size =
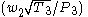
- core total head pressure ratio =
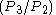
- inverse of core total head temperature ratio =
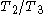 i.e. f(
i.e. f(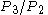 )
)
- core entry total pressure =
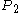
- core entry total temperature =
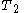
- Note:
- in this case, the core refers to the whole of the gas generator compression, not just that of the high pressure (HP) compressor.
T-stages are a popular method for uprating the thrust of an engine (see, for example the Pratt & Whitney Canada PW500
Pratt & Whitney Canada PW500
-External links:*...
).
The alternative is to place a zero-stage
Zero-stage
Jet engines are often uprated by adding a zero-stage to the front of a compressor. At a given core size, adding a stage to the front of the compressor not only increases the cycle overall pressure ratio, but increases the core mass flow....
, mounted on the HP shaft, at the front of the HP compressor. This approach requires a significant change in the HP turbine, whereas a T-stage can, if necessary, be accommodated by simply adding an additional stage to the rear of the LP turbine.

