TCP-Illinois
Encyclopedia
TCP-Illinois is a variant of TCP
congestion control protocol, developed at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
. It is especially targeted at high-speed, long-distance networks. A sender side modification to the standard TCP congestion control algorithm, it achieves a higher average throughput than the standard TCP, allocates the network resource fairly as the standard TCP, is compatible with the standard TCP, and provides incentives for TCP users to switch.
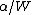 for each acknowledgment, and decreases
for each acknowledgment, and decreases 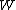 by
by 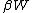 for each loss event. Unlike the standard TCP,
for each loss event. Unlike the standard TCP,  and
and 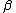 are not constants. Instead, they are functions of average queuing delay
are not constants. Instead, they are functions of average queuing delay 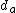 :
: 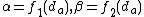 , where
, where 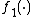 is decreasing and
is decreasing and 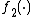 is increasing.
is increasing.
There are numerous choices of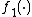 and
and 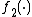 . One such class is:
. One such class is:
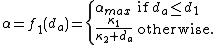
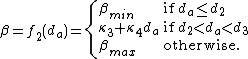
We let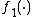 and
and 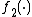 be continuous functions and thus
be continuous functions and thus 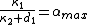 ,
, 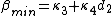 and
and 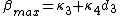 . Suppose
. Suppose 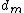 is the maximum average queuing delay and we denote
is the maximum average queuing delay and we denote 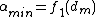 , then we also have
, then we also have 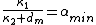 . From these conditions, we have
. From these conditions, we have
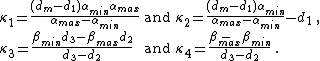
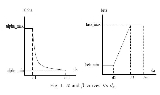
This specific choice is demonstrated in Figure 1.
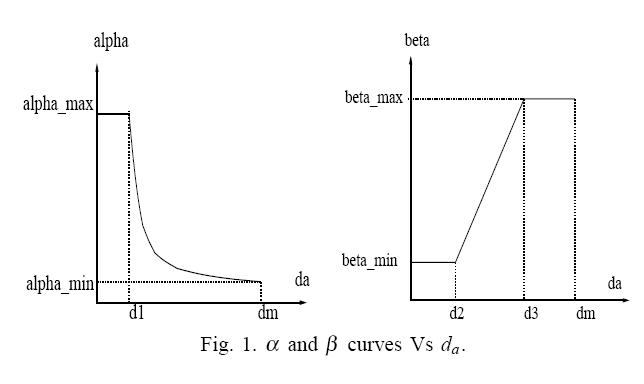
It also has many other desirable features, like fairness, compatibility with the standard TCP, providing incentive for TCP users to switch, robust against inaccurate delay measurement.
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
congestion control protocol, developed at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
The University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign is a large public research-intensive university in the state of Illinois, United States. It is the flagship campus of the University of Illinois system...
. It is especially targeted at high-speed, long-distance networks. A sender side modification to the standard TCP congestion control algorithm, it achieves a higher average throughput than the standard TCP, allocates the network resource fairly as the standard TCP, is compatible with the standard TCP, and provides incentives for TCP users to switch.
Principles of operation
TCP-Illinois is a loss-delay based algorithm, which uses packet loss as the primary congestion signal to determine the direction of window size change, and uses queuing delay as the secondary congestion signal to adjust the pace of window size change. Similarly to the standard TCP, TCP-Illinois increases the window size W by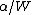 for each acknowledgment, and decreases
for each acknowledgment, and decreases 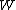 by
by 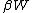 for each loss event. Unlike the standard TCP,
for each loss event. Unlike the standard TCP,  and
and 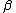 are not constants. Instead, they are functions of average queuing delay
are not constants. Instead, they are functions of average queuing delay 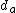 :
: 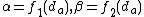 , where
, where 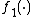 is decreasing and
is decreasing and 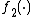 is increasing.
is increasing.There are numerous choices of
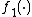 and
and 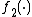 . One such class is:
. One such class is: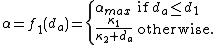
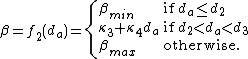
We let
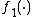 and
and 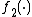 be continuous functions and thus
be continuous functions and thus 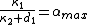 ,
, 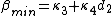 and
and 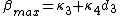 . Suppose
. Suppose 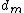 is the maximum average queuing delay and we denote
is the maximum average queuing delay and we denote 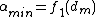 , then we also have
, then we also have 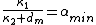 . From these conditions, we have
. From these conditions, we have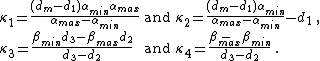
This specific choice is demonstrated in Figure 1.

Properties and Performance
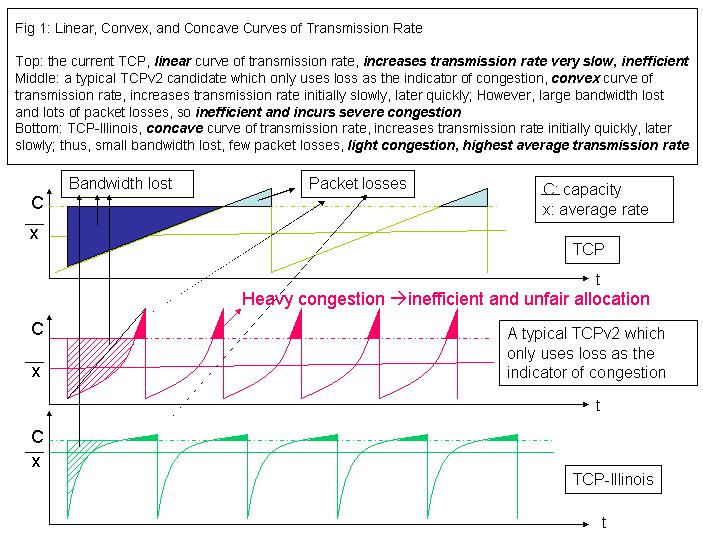
TCP-Illinois increases the throughput much more quickly than TCP when congestion is far and increases the throughput very slowly when congestion is imminent. As a result, the window curve is concave and the average throughput achieved is much larger than the standard TCP, see Figure 2.
It also has many other desirable features, like fairness, compatibility with the standard TCP, providing incentive for TCP users to switch, robust against inaccurate delay measurement.
See also
- H-TCPH-TCPH-TCP is another implementation of TCP with an optimized congestion control algorithm for high speed networks with high latency...
- BIC TCPBIC TCPBIC TCP is an implementation of TCP with an optimized congestion control algorithm for high speed networks with high latency: so-called "long fat networks".BIC has a unique congestion window algorithm...
- HSTCPHSTCPHighSpeed TCP is a new congestion control algorithm protocol defined in RFC 3649 for TCP. Standard TCP performs poorly in networks with a large bandwidth delay product. It is unable to fully utilize available bandwidth...
- TCPTransmission Control ProtocolThe Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
- FAST TCPFAST TCPFAST TCP is a TCP congestion avoidance algorithm especially targeted at long-distance, high latency links, developed at the , California Institute of Technology and now being commercialized by...
External links
- Paper on experimental evaluation of TCP Illinois Hamilton Institute and Caltech, March 2008.

