T cell
Overview
White blood cell
White blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
s known as lymphocytes, and play a central role in cell-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity
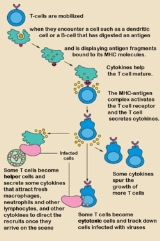
Cell-mediated immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies but rather involves the activation of macrophages, natural killer cells , antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in response to an antigen...
. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cell
B cell
B cells are lymphocytes that play a large role in the humoral immune response . The principal functions of B cells are to make antibodies against antigens, perform the role of antigen-presenting cells and eventually develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction...
s and natural killer cell
Natural killer cell
Natural killer cells are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte that constitute a major component of the innate immune system. NK cells play a major role in the rejection of tumors and cells infected by viruses...
s (NK cells), by the presence of a T cell receptor
T cell receptor
The T cell receptor or TCR is a molecule found on the surface of T lymphocytes that is responsible for recognizing antigens bound to major histocompatibility complex molecules...
(TCR) on the cell surface. They are called T cells because they mature in the thymus
Thymus
The thymus is a specialized organ of the immune system. The thymus produces and "educates" T-lymphocytes , which are critical cells of the adaptive immune system....
. There are several subsets of T cells, each with a distinct function.
T helper cell
T helper cell
T helper cells are a sub-group of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, that play an important role in the immune system, particularly in the adaptive immune system. These cells have no cytotoxic or phagocytic activity; they cannot kill infected host cells or pathogens. Rather, they help other...
(TH cells) assist other white blood cells in immunologic processes, including maturation of B cell
B cell
B cells are lymphocytes that play a large role in the humoral immune response . The principal functions of B cells are to make antibodies against antigens, perform the role of antigen-presenting cells and eventually develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction...
s into plasma cell
Plasma cell
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells, plasmocytes, and effector B cells, are white blood cells which produce large volumes of antibodies. They are transported by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system...
s and memory B cell
Memory B cell
Memory B cells are a B cell sub-type that are formed following primary infection.-Primary response, paratopes, and epitopes:In wake of first infection involving a particular antigen, the responding naïve cells proliferate to produce a colony of cells, most of which differentiate into the plasma...
s, and activation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophage
Macrophage
Macrophages are cells produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. Human macrophages are about in diameter. Monocytes and macrophages are phagocytes. Macrophages function in both non-specific defense as well as help initiate specific defense mechanisms of vertebrate animals...
s.

