
Taksin
Encyclopedia
Taksin ; (April 17, 1734 – April 7, 1782) was the only King of the Thonburi Kingdom
. He is greatly revered by the Thai people for his leadership in liberating Siam from Burmese occupation after the Second Fall of Ayutthaya
in 1767, and the subsequent unification of Siam after it fell under various warlords. He established the city Thonburi
as the new capital, as the city Ayutthaya had been almost completely destroyed by the invaders. His reign was characterized by numerous wars, fought to repel new Burmese invasions and to subjugate the northern Thai kingdom of Lanna
, the Laotian principalities, and a threatening Cambodia
. He was succeeded by the Chakri dynasty and the Rattanakosin Kingdom under his long time friend King Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke
.
Although warfare took up most of King Taksin's time, he paid a great deal of attention to politics, administration, economy, and the welfare of the country. He promoted trade and fostered relations with foreign countries including China
, Britain
, and the Netherlands
. He had roads built and canals dug. Apart from restoring and renovating temples, the king attempted to revive literature, and various branches of the arts such as drama, painting, architecture and handicrafts. He also issued regulations for the collection and arrangement of various texts to promote education and religious studies. In recognition for what he did for the Thais, he was later awarded the title of Maharaj (The Great).
. His father, Hai-Hong (Thai
:ไหฮอง; ), who worked as a tax-collector, was a Teochew
Chinese
immigrant from Chenghai County
. His mother, Lady Nok-lang (Thai:นกเอี้ยง), was Thai
(and was later awarded the feudal title of Somdet Krom Phra Phithak Thephamat). Impressed by the boy, Chao Phraya Chakri (Mhud), who was the Samuhanayok (prime minister
) in King Boromakot
's reign, adopted him and gave him the Thai name Sin (สิน,) meaning money or treasure. When he was 7, he was assigned to a monk named Tongdee to begin his education in a Buddhist monastery
called Wat Kosawat (later Wat Choeng Thar) (Thai:วัดโกษาวาส ต่อมาเปลี่ยนชื่อเป็น วัดเชิงท่า). After seven years of education he was sent by his stepfather to serve as a royal page, he studied Chinese
, Annamese, and Indian languages with diligence and soon he was able to converse in them with fluency. When Sin and his friend, Tong-Duang, were Buddhist novices they met a Chinese fortune-teller who told them that they both had lucky lines in the palms of their hands and would both become kings. Neither took it seriously, but Tong-Duang was later the successor of King Taksin, Rama I.
After taking the vows of a Buddhist monk for about 3 years, Sin joined the service of King Ekatat and was first deputy governor and later governor of the Tak
, which gained him his name Phraya Tak, the governor of Tak, which was exposed to danger from Burma, though his official noble title was "Phraya Tak".
In 1764, the Burmese army attacked the southern region of Thailand. Led by Muang Maha Noratha, the Burmese army was victorious and marched on to Phetchaburi
. Here, the Burmese were confronted by Thai soldiers led by two generals, Kosadhibodhi and Phraya Tak. The Thai army beat the Burmese back to Singkhorn Pass.
In 1765, when the Burmese attacked Ayutthaya
, Phraya Tak defended the capital, for which he was given the title "Phraya Vajiraprakarn" of Kamphaeng Phet
. But he did not have a chance to govern Kamphaeng Phet because war broke out again. He was immediately called back to Ayutthaya to protect the city. For more than a year, Thai and Burmese soldiers fought fierce battles during the siege of Ayutthaya. It was during this time that Phraya Vajiraprakarn experienced many setbacks which led him to doubt the value of his endeavours.
, on the east coast of Gulf of Thailand
. This action was never adequately explained, as the Royal compound and Ayutthaya proper was located on an island; how Taksin and his followers fought their way out of the Burmese encirclement remains a mystery.
On April 7, 1767, Ayutthaya was facing the full blast of the Burmese siege. After the destruction of Ayutthaya and the death of the Thai king, the country was split into six parts, with Sin controlling the east coast. Together with Tong-Duang, now Chao Phraya Chakri, he eventually managed to drive back the Burmese, defeat his rivals and reunify the country.
Due to his courage and skill in fighting the enemy, he was promoted to be the governor of Khampaeng Phet with the title of Phraya Vajiraprakarn (Thai:พระยาวชิรปราการ), but he was populaly referred as Phraya. He carried out the defence of Ayutthaya in its last days. Perhaps Sin saw that the situation of the kingdom was in great despair. Therefore before the end of Ayutthaya came, he decided to cut his way out from the city and travelled first to Chon Buri
, a town on the Gulf of Thailand
's eastern coast, and then to Rayong
, where he raised a small army and his supporters began to address him as Prince Tak. He planned to attack and capture Chantaburi, according to a popular version of oral history, he said "We are going to attack Chantaburi tonight, and all the food that we have left just throw it away and destroy all of the utensils that we have. As we are going to have breakfast together at Chantaburi otherwise we would rather be dead."
With his soldiers he moved to Chantaburi, and being rebuffed by the Governor of the town for his friendly overtures, he made a surprise night attack on it and captured it on June 15, 1767, only two months of after the sack of Ayutthaya. His army was rapidly increasing in numbers, as men of Chantaburi and Trat
, which had not been plundered and depopulated by the Burmese, naturally constituted a suitable base for him to make preparations for the liberation of his motherland.
Having thoroughly looted Ayutthaya, the Burmese did not seem to show serious interest in holding down the capital of Siam, since they left only a handful of troops under General Suki to control the shattered city. They turned their attention to the north of their own country which was soon threatened with Chinese invasion. On November 6, 1767, having mastered 5,000 troops and all in fine spirits, Taksin sailed up the Chao Phraya River and seized Thonburi opposite present day Bangkok
, executing the Thai governor, Thong-in, whom the Burmese had placed over it. He followed up his victory quickly by boldly attacking the main Burmese camp at Phosamton near Ayutthya. The Burmese were defeated, and Taksin won back Ayutthaya from the enemy within seven months of its destruction.
Taksin took important steps to show that he was a worthy successor to the throne. He was said to take an appropriate treatment to the remnants of the ex-Royal Family, arranged a grand cremation of the remains of King Ekatat, and tackled the problem of locating the capital. Possibly, Taksin realized that Ayutthaya city had suffered such vast destruction that to restore it to its former state would undoubtedly have strained his resources. The Burmese were quite familiar with the various routes leading to Ayutthaya, and in the event of renewal of a Burmese attack on it, the troops under the liberator would be inadequate for the effective defence of the city. With these considerations in mind, he established his capital at Thon Buri, nearer to the sea than Ayutthaya. Not only would Thon Buri be difficult to invade by land, it would also prevent an acquisition of weapons and military supplies by anyone ambitious enough to establish himself as an independent prince further up the Chao Phraya River
. As Thon Buri was a small town, Prince Tak's available forces, both soldiers and sailors, could man its fortifications, and if he found it impossible to hold it against an enemy's attack, he could embark the troops and beat a retreat to Chantaburi.
The successes against competitors for power were due to Taksin's fighting ability as a warrior, splendid leadership, exemplary valor and effective organization of his forces. Usually he put himself in the front rank in an encounter with the enemy, thus inspiring his men to brave danger. Among the officials who threw in their fate with him during the campaigns for the recovery of national independence and for the elimination of the self-appointed local nobles were two personalities who subsequently played exceptionally important roles in Thai history. They were the sons of an official bearing the title of Pra Acksonsuntornsmiantra (Thai
:พระอักษรสุนทรเสมียนตรา), the elder of whom named Tongduang (Thai:ทองด้วง) was born in 1737 in Ayutthaya and later to be the founder of the Chakri Dynasty, while the younger one, Boonma (Thai:บุญมา), born six years later, assumed the power second to him. The two brothers joined the royal service.
Tongduang, prior to the sacking of Ayutthaya, was ennobled as Luang Yokkrabat, taking charge of royal surveillance, serving the Governor of Ratchaburi
, and Boonma had a court title conferred upon him as Nai Sudchinda. Luang Yokkrabat (Tongduang) was therefore not in Ayutthaya to witness the horrors that arose from the fall of the city, while Nai Sudchinda (Boonma) made his escape from Ayutthaya. However, while King Taksin was assembling his forces at Chantaburi, Nai Sudchinda brought his retainers to join him, thus helping to increase his fighting strength. Due to his previous acquaintance with him, the liberator was so pleased that he promoted him to be Pra Mahamontri. Just after his coronation, Taksin was fortunate to secure the service of Luang Yokkrabut on the recommendation of Pra Mahamontri (Thai:พระมหามนตรี) and as he was equally familiar with him as with his brother, he raised him to be Pra Rajwarin. Having rendered signal service to the King during his campaigns or their own expeditions against the enemies, Pra Rajwarin (Thai:พระราชวรินทร์) and Pra Mahamontri rose so quickly in the noble ranks that a few years after, the former was created Chao Phraya Chakri, the rank of the Chancellor, while the latter became Chao Phraya Surasih
.
, the new capital of Siam. He assumed the official name of Boromraja IV, but is known in Thai history as King Taksin, being a combination of his popular name, Phya Tak, and his first name, Sin, or the King of Thonburi, being the only ruler of that capital. At the time of his coronation, he was only 34 years of age. His father was Chinese or partly Chinese, and his mother Siamese. He believed that even the forces of nature were under his control when he was destined to succeeded, and this faith led him to attempt and achieve tasks which to another man would seem impossible. He never had time to build Thonburi into a great city, as he was fully occupied with suppression of internal and external enemies, as well as territorial expansion throughout his reign.
holding sway over the eastern provinces including Nakhon Ratchasima
or Khorat, while the Governor of Phitsanulok
, whose first name was Ruang (Thai:เรือง), had proclaimed himself independent, with the territory under his control extending to the province of Nakhon Sawan
. North of Phitsanulok was the town of Sawangburi (known as Fang in Uttaradit Province
), where a Buddhist monk named Ruan had made himself a prince, appointing his qualified fellow monks as army commanders. He had himself pursued Buddhist studies at Ayutthatya with such excellent results that he had been appointed the chief monk of Sawangburi by King Boromakot. In the southern provinces up to Chumphon
, a Pra Palad who was the acting Governor of Nakhon Si Thammarat
declared his independence and raised himself to the princely rank.
Having firmly established his power at Thonburi, King Taksin set out to crush his rivals so as to effect the reunification of the Kingdom. After a temporary repulse by the Governor of Phitsanulok, he concentrated on the defeat of the weakest one first. Prince Teppipit of Phimai was quelled and executed in 1768. In dealing with the Prince of Nakhon Si Thammarat, who was taken prisoner by the loyal Governor of Pattani
, the King not only pardoned him but also favoured him with a residence at Thonburi. Chao Narasuriyawongse, one of Taksin's nephews, was substituted for him as Governor. King Taksin himself led an expedition against him and took it, but the Prince disappeared and could not be found again.
of Burma never abandoned his plan to force Siam to its knees, and as soon as he had been informed of the foundation of Thonburi as King Taksin's capital, he commanded the Governor of Tavoy to subjugate him in 1767. The Burmese army advanced to the district of Bangkung in the province of Samut Songkram to the west of the new capital, but was routed by the Thai king himself.
Peace having been concluded with China
, the Burmese king sent another small army of 5,000 to attack Siam in 1774. But it was completely surrounded by the Thais at Bangkeo in Ratchaburi
, and eventually starvation compelled the Burmese to capitulate to King Taksin. It would be no exaggeration to say that he could have massacred all of them if he wished to do so, but the fact that he took them alive was to promote the morale of the Thai people. The Burmese reinforcements who had encamped themselves in the province of Kanchanaburi
were then mopped up. Undaunted by this defeat, King Hsinbyushin tried again to conquer Siam, and in October 1775 the greatest Burmese invasion in the Thonburi period began under Maha Thiha Thura
, known in Thai history as Azaewunky. He had distinguished himself as a first rate general in the wars with China and in the suppression of a recent Peguan rising.
After crossing the Thai frontier at Melamao Pass, the Burmese marched towards Phitsanulok
, capturing Phichai and Sukhothai
on the way. In his interrogation of two Phichai officials, Azaewunky referred to Chao Phraya Surasih who was the Governor of Phisanulok as "Phraya Sua" or "The Tiger", thus testifying to his boldness and decisiveness. The Burmese then besieged Phitsanulok which was defended by the brother generals, Chao Phraya Chakri and Chao Phya Surasih, and as the result of the stubborn resistance on the part of Thai soldiers, they were checked outside the city ramparts for about 4 months. Hearing about Chao Phraya Chakri's successful assaults which drove back the Burmese to their well fortified camp, Azaewunky arranged a meeting with him, in the course of which he extolled his generalship and advised him to take good care on himself. He prophesied that General Chakri would certainly become king. Was he really honest in his prediction? No definite answer has been found for it. Anyhow he was at that time seventy two years of age, while his opponent was only thirty nine. Any doubt about Azaewunky's stratagem to sow discord between King Taksin and Chao Phraya Chakri should be dismissed, since they collaborated closely in subsequent military expeditions.
In spite of King Taksin's endeavour to attack the Burmese from the rear, Chao Phraya Chakri and Chao Phraya Surasih could not hold Phitsanulok any longer, due to lack of provisions. Having collected most of the inhabitants, they successfully fought their way through enemy lines and made Phetchabun
their headquarters. Azaewunky led his army into the deserted city at the end of March 1776, but was soon confronted with the same problem of the shortage of food. At this juncture he was instructed by the new Burmese King, Singun Min or Chingkucha (1776–1782) to evacuate Thai territory. So Azaewunky's army left Siam, but the remnants of the Burmese forces continued the war until they were pushed out of the country in September of that year.
In King Taksin's opinion, so long as Chiang Mai
was ruled by the Burmese, the north of Siam would be constantly subjected to their incursions. The prerequisite for the maintenance of peace in that region would therefore be the complete expulsion of the Burmese from Chiang Mai. In 1771, the Burmese Governor of that city moved his army southwards and laid siege to Phichai
, but he was driven out. Taksin followed the Burmese with a view to studying their strength, and his army was thus not prepared for a direct assault on their city fortress. After meeting with stubborn resistance, he retired, presumably believing in an ancient prophesy to the effect that two attempts were required for the capture of Chiang Mai. King Narairaja had tried twice to seize it before it fell into his hands.
The Burmese failure to take Phichai formed a prelude to Taksin's second-expedition to Chaing Mai. In 1773, a Burmese army which threatened Phichai was drawn into an ambush and was heavily routed. Phraya Phichai
, the Phichai Governor, engaged the Burmese in a hand to hand fight until his two long swords were broken, and thus won the name of "Broken Sword." When a Thai army under the command of Chao Phraya Chakri and Chao Phraya Surasih reached Lampang, Phraya Chaban and Phraya Kawila, the two leading officials who had deserted the Burmese joined him in laying siege to Chaing Mai and soon King Taksin arrived on the spot. The city fell to the Thai armies in January 1775, but the Burmese Governor and the commander managed to escape with their families. Before his departure for Thonburi, the King conferred honours and distinction on those who had contributed to success of his campaign. Phraya Chaban was made Governor of Chaing Mai with the title of Phraya Wichienprakarn, while Phraya Kawila and Phraya Waiwongsa governed Lampang
and Lamphun
respectively. Chao Phraya Chakri was directed to prolong his stay in order to assist them in the pacification of the north, which included the Laotian states. However, the Burmese King considered that as the Laotian states constituted his base for the maintenance of Burmese power in the territory further east, namely, Luang Prabang
and Vientiane
, Chiang Mai must be taken back, and so a Burmese army of 6,000 men was sent there to carry out its mission in 1776. The Burmese entered the city, but were forced out by a Thai army under Chao Phraya Surasih which had marched to its relief. Chaing Mai had suffered from the recent campaigns so badly that its population was greatly reduced and impoverished, and in the event of a new Burmese attack, it could not defend itself. For these reasons, King Taksin abandoned the city and its remaining inhabitants were transplanted to Lampang. Chiang Mai thus became a deserted city and remained so for fifteen years. Over the next few years, Taksin managed to gain control over Chiang Mai
, and put Cambodia under the vassalage of Siam by 1779 after repeated military campaigns.
 The annexation of Champasak Province indirectly led King Taksin to send an expedition against Vientiane. In 1777, the ruler of Champasak, which was at that time an independent principality bordering on the Thai eastern frontier, supported the Governor of Nangrong
The annexation of Champasak Province indirectly led King Taksin to send an expedition against Vientiane. In 1777, the ruler of Champasak, which was at that time an independent principality bordering on the Thai eastern frontier, supported the Governor of Nangrong
, who had rebelled against the Thai king. A Thai army under Chao Phraya Chakri was ordered to move against the rebel, who was caught and executed, and having received reinforcements under Chao Phraya Surasih, he advanced to Champasak, where the ruler, Chao O and his deputy, were captured and were summarily beheaded. Champasak was added to the Kingdom of Siam, and King Taksin was so pleased with Chao Phraya Chakri's conduct of the campaign that he promoted him to be Somdej Chao Phraya Mahakasatsuek Piluekmahima Tuknakara Ra-adet (Thai
:สมเด็จเจ้าพระยามหากษัตริย์ศึก พิลึกมหึมาทุกนคราระอาเดช) (meaning the supreme Chao Phraya, Great Warrior-King who was so remarkably powerful that every city was afraid of his might)—being the highest title of nobility that a commoner could reach. It would be equivalent to the rank of a Royal Duke
.
In Vientiane
, a Minister of State, Pra Woh, had rebelled against the ruling prince and fled to the Champasak territory, where he set himself up at Donmotdang near the present city of Ubon. He made formal submission to Siam, when he annexed Champasak, but after the withdrawal of the Thai army, he was attacked and killed by troops from Vientiane. This action was instantly regarded by King Taksin as a great insult to him, and at his command, Somdej Chao Phya Mahakasatsuek invaded Vientiane with an army of 20,000 men in 1778. It would be useful here to briefly summarise the history of Laos which had been separated into two principalities of Luang Prabang and Vientiane since the beginning of the eighteenth century. The Prince of Luang Prabang, who was in enmity with the Prince of Vientiane, submitted to Siam for his own safety, bringing his men to join Somdej Chao Phya Mahakasatsuek in besieging the city. After a siege of Vientiane which took about four months, the Thais took Vientiane and carried off the image of the Emerald Buddha
to Thonburi. The Prince of Vientiane managed to escape and went into exile. Thus Luang Prabang and Vientiane became Thai dependencies. Nothing definite is known about the origin of the celebrated Emerald Buddha. It is believed that this image was carved from green jasper by an artist or artists in northern India about two thousand years ago. It was taken to Ceylon and then to Chiang Rai
, a town in the north of Siam where it was, in 1434, found intact in a chedi which had been struck by lightning. As an object of great veneration among Thai Buddhists. it has been deposited in monasteries in Lampang
, Chiang Mai
, Luang Prabang
, Vientiane
, Thonburi
, and eventually in Bangkok
.
In 1770, King Taksin launched a war against the Nguyễn Lords over their control of Cambodia
. After some initial defeats, the joint Siamese-Cambodian army defeated the Nguyễn army in 1771 and 1772. These defeats helped provoke an internal rebellion (the Tây Sơn rebellion) which would soon sweep the Nguyễn out of power. In 1773, the Nguyễn made peace with King Taksin, giving back some land they controlled in Cambodia.
In 1769, Cambodia was in turmoil again, due to the rivalry for the throne by two royal brothers, the elder of who was King Ramraja (Non). Having suffered defeat at the hands of his brother (Ton) who was aided by Annamite troops, he sought shelter in Siam. Prince Ton proclaimed himself as King Narairaja. This struggle afforded an opportunity to King Taksin to resuscitate Thai suzerainty
over Cambodia as in the days of Ayutthaya. An army was dispatched to assist the ex-King Ramraja to regain his power, but met with no success.
In 1771, however, the Thai forces won back the Cambodia
throne for him, but Narairaja retreated to the east of the country. In the end, Ramraja and Narairaja came to a compromise, whereby the former became the first King and the latter was the second King or Maha Uparayoj
, and Prince Tam was Maha Uparat or Deputy to the first and the second King. This arrangement proved to be unsatisfactory. Prince Tam was murdered, while the second King died suddenly. Believing that King Ramraja was responsible for their deaths, many prominent officials under the leadership of Prince Talaha (Mu) revolted, caught him and drowned him in the river in 1780. Prince Talaha put Prince Ang Eng, the four year old son of the ex-King Narairaja, on the throne with himself acting as Regent
, but he soon leaned too much Annam, thus coming into conflict with King Taksin’s policy to support a pro-Thai prince on the Cambodian throne. The Thai King therefore decided on an invasion of Cambodia. A Thai army of 20,000 under Somdej Chao Phraya Mahakasatsuek moved into Cambodia, and in the event of his success in subduing the country, he was to assist in crowning Taksin’s son, Prince Intarapitak, as King of Cambodia. With the aid of an Annamite army, Prince Talana was prepared to take his stand against the Thai forces at Phnom Penh, but before any fighting started, serious disturbances which had broken out in Siam made Somdej Chao Phraya Mahakasatsuek decide on a hasty return to Thonburi, after handing the command of the army to Chao Phraya Surasih.
Chinese Court could not help but seized the chance by asking Taksin, as a 'new vassal', to be her ally in the war against the Burmese barbarians. Eventually Chinese Court approved the royal status of Taksin, as the new king of Siam.
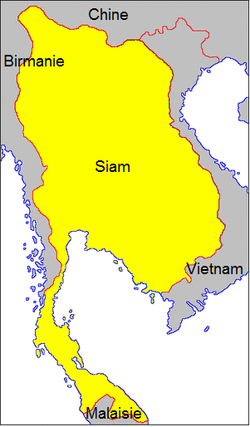 The kingdom under his rule was much bigger than it was in Ayutthaya times. It included the following provinces : Thon Buri, Ayutthaya
The kingdom under his rule was much bigger than it was in Ayutthaya times. It included the following provinces : Thon Buri, Ayutthaya
, Ang Thong
, Singburi, Lopburi
, Uthai Thani
, Nakhon Sawan
, Chachoengsao
, Prachinburi
, Nakhon Nayok, Chonburi
, Rayong
, Chantaburi, Trat
, Nakhon Chai Si
, Nakhon Pathom
, Suphanburi
, Ratchaburi
, Samut Sakhon
, Samut Songkhram
, Phetchaburi
, Kanchanaburi
, and Prachuap Khiri Khan
.
Throughout his reign, King Taksin carried out his policy of expansion.
In the north, including the whole of Lanna
. Burmese was driven out. local allies became Thonburi's subjugation.
In the south, including Syburi
(today is Kedah
) and Trengganu in Malaysia.
In the east, Cambodia
was subjugated. His forces even attacked South Vietnam
In the northeast, including Vientiane
, Phuan
, Luang Phrabang, and Hua Phan Ha Thang Hok.
In the southeast, including Phutthaimat (Hà Tiên
in Vietnam
today).
In the west, as far as Mergui
and Tenasserim in Myanmar
today leading to the Indian Ocean
.
was restored. The economy of the country gradually recovered. King Taksin sent three diplomatic envoys to China in 1767, which then was under the reign of Qianlong Emperor
. Six years later, in 1772, China recognized Taksin as the legitimate ruler of Siam.
The record dating from 1777 states: "Important goods from Thailand are amber, gold, colored rocks, good nuggets, gold dust, semi-precious stones, and hard lead." During this time the king actively encouraged the Chinese to settle in Siam, principally those from Chaozhou
, partly with the intention to revive the stagnating economy and upgrading the local workforce at that time. He had to fight almost constantly for most of his reign to maintain the independence of his country. As the economic influence of the immigrant Chinese community grew with time, many aristocrats, which he took in from the Ayutthaya nobility, began to turn against him for having allied with the Chinese merchants. According to a scholar, the opposition was led mainly by the Bunnag
s, a merchant-aristocrat family of Persian
origins, successors of Ayutthaya's minister of Port&Finance, or Phra Klang Coupled with the tax revenues that these activities provided—helped restore the kingdom's devastated economy.
Thai galleon
s travelled to Portuguese colony of Surat
, in Goa
, India. However, formal diplomatic relations were not formed. In 1776, Francis Light
sent 1,400 flintlock
s along with other goods as gifts to King Taksin. Later, Thonburi ordered some guns from England. Royal letters were exchanged and in 1777, George Stratton, the Viceroy of Madras, sent a gold scabbard
decorated with gems to King Taksin.
In 1770, natives of Terengganu
and Jakarta
presented King Taksin with 2,200 shotguns. At that time, Holland controlled the Java
Islands.
Simultaneously King Taksin was deeply engaged in restoring law and order in the Kingdom and in administering a programme of public welfare to his people. Abuses in the Buddhist establishment, and among the public, were duly rectified, and food and clothes as well as other necessities of life were hastily distributed to those who needed them, thus bringing respect and affection to him.
King Taksin was also interested in other branches of art, including dance and drama. There is evidence that when he went to suppress the Chao Nakhon Si Thammarat faction in 1769, he brought back Chao Nakhon's female dancers. Together with dancers that he had assembled from other places, they trained and set up a royal troupe in Thonburi on the Ayutthaya model. The King wrote four episodes from the Ramakian for the royal troupe to rehearse and perform.
When he went north to suppress the Phra Fang faction, he could see that monks in the north were lax and undisciplined. He invited ecclesiastical dignitaries from the capital to teach those monks and brought them back in line with the main teachings of Buddhism. Even though King Taksin had applied himself to reforming the Buddhist religion after its period of decline following the loss of Ayutthaya to Burma, gradually bringing it back to the normalcy it enjoyed during the Ayutthaya kingdom, since his reign was so brief he was not able to do very much.
The administration of the Sangha
during the Thonburi period followed the model established in Ayutthaya, and he allowed French missionaries to enter Thailand, and like a previous Thai king, helped them build a church in 1780.
Economic tension caused by war was serious. As famine spread, looting and crimes were widespread. Corrupt officials were reportedly abundant. Taksin himself executed several officials harshly. Discontent among officials could be expected.
Several historians have suggested that the tale of his 'insanity' may have been reconstructed as an excuse for his overthrow. However, the letters of a French priest who was in Thonburi at the time support the accounts of the monarch's peculiar behavior. Thus the terms 'insanity' or 'madness' possibly were the contemporary definition describing the monarch's actions. With the Burmese threat still prevalent, a strong ruler was needed on the throne. According to some sources, many oppressions and abuses made by officials were reported. King Taksin punished them harshly, torturing and executing high officials. Finally a faction led by Phraya San seized the capital and forced the king to step down.
According to the following Rattanakosin era accounts, King Taksin was described as 'insane.' The disturbance in Thonburi widely spread, with killing and looting prevalent. A coup d'état
removing Taksin from the throne consequently took place, although Taksin requested to be allowed to join the monkhood. When the coup occurred, General Chao Phraya Chakri
was away fighting in Cambodia
, but he quickly returned to the Thai capital following being informed of the coup. Upon having arrived at the capital, the General extinguished the coup through arrests, investigations and punishments. Peace was then restored in the capital.
According to the Royal Thai Chronicles, General Chao Phraya Chakri decided to put the deposed Taksin to death. The Chronicles stated that, while being taken to the executing venue, Taksin asked for an audience with General Chao Phraya Chakri but was turned down by the General. Taksin was beheaded in front of Wichai Prasit fortress on Wednesday, April 10, 1782, and his body was buried at Wat Bang Yi Ruea Tai. General Chao Phraya Chakri then seized control of the capital and declared himself king together with establishing the House of Chakri.
The Official Annamese Chronicles states that Taksin was ordered to be executed by General Chao Phraya Chakri at Wat Chaeng by being sealed in a velvet sack and was beaten to death with a scented sandalwood club. There was an account claiming that Taksin was secretly sent to a palace located in the remote mountains of Nakhon Si Thammarat
where he lived until 1825, and that a substitute was beaten to death in his place. King Taksin ashes and that of his wife are located at Wat Intharam (located in Thonburi). They have been placed in two lotus bud shaped stupas which stand before the old hall.
,a prominent Thai historian, writer, and political commentator, Taksin could be seen as the originator, new style of leader, promoting the 'decentralized' kingdom and new generation of the nobles, of Chinese merchants-origin, his major helpers in the wars. On the other hand, Phraya Chakri and his supporters were of 'old' generation of the Ayutthaya nobles, discontent with the previously said changes.
However, this overlooks the fact that Chao Phraya Chakri was himself of partly Chinese origin as well as he himself being married to one of Taksin's daughters. No previous conflicts between them were mentioned in histories. Reports on the conflicts between the king and the Chinese merchants were seen caused by the control of the rice price in the time of famine. However, prior to returning to Thonburi, Chao Phraya Chakri had Taksin's son summoned to Cambodia
and executed. All in all, Phraya Chakri was, in fact, the highest noble in the kingdom, charging the state affairs as the Chancellor. Therefore he was of the greatest potential to be the new leader.
Another view of the events is that Thailand owed China for millions of baht. In order to cancel the agreement between China and Thailand, King Taksin decided to ordain and pretend to die in an execution.
King Taksin was, said, not as highly honoured as other Siamese Kings because the leaders in the Chakri Dynasty were still concerned about their own political legitimacy. After 1932, when the absolute monarchy gave way to the democratic period, King Taksin become more honoured than ever before. Instead, King Taksin became one of the national heroes. This was because the leaders of that time such as Plaek Pibulsonggram
and even later military junta, on the other hand, wanted to glorify and publicise the stories of certain historical figures in the past in order to support their own policy of nationalism
, expansionism
and patriotism
.
King Taksin statue was unveiled in the middle of Wongwian Yai
(the Big Traffic Circle) in Thonburi, at the intersection of Prajadhipok/Inthara Phithak/Lat Ya/Somdet Phra Chao Taksin Roads. The king is portrayed with his right hand holding a sword, measuring approximately 9 metres in height from his horse's feet to the spire of his hat, rests on a reinforced concrete pedestal of 8.90 x 1.80 x 3.90 metres. There are four frames of stucco relief on the two sides of the pedestal. The opening ceremony of this monument was held on April 17, 1954 and the royal homage-paying fair takes place annually on 28 December. The king today officially comes to pay respect to king Taksin statue.
The monument featuring King Taksin riding on a horseback surrounded by his four trusted soldiers; Pra Chiang-ngen (later Phraya Sukhothai), Luang Pichai-asa (later Phraya Phichai
), Luang Prom-sena, Luang Raj-saneha. It is placed on the groung of Toong na-chey public park on Leab muang road, just opposite the City Hall, Chantaburi.
In 1981 the Thai cabinet passed a resolution to bestow on King Taksin the honorary title of the Great. The date of his coronation, December 28, is the official day of homage to King Taksin, although it is not designated as a public holiday. The Maw Sukha Association on January 31, 1999 cast the King Taksin Savior of the Nation Amulet, which sought to honour the contributions of King Taksin to Siam during his reign.
The Na Nagara (also spelled Na Nakorn) family is descended in the direct male line from King Taksin.
A tomb containing King Taksin's clothes and a family shrine were found at Chenghai district in Guangdong province in China in 1921. It is believed that a descendant of King Taksin the Great must have sent his clothes to be buried there to conform to Chinese practice. This supports the claim that the place was his father's hometown.
King Taksin the Great Shrine is located on Tha Luang Road in front of Camp Taksin. It is an important place of Chantaburi in order to demonstrate binding of People in Chanthaburi to King Taksin. It is a nine-sided building. The roof is a pointed helmet. Inside of this place enshrined the statue of King Taksin.
Thonburi Kingdom
Thon Buri was the capital of Siam for a short time during the reign of King Taksin the Great, after the ruin of capital Ayutthaya by the Burmese. King Rama I removed the capital to Bangkok on the other side of the Chao Phraya River in 1782...
. He is greatly revered by the Thai people for his leadership in liberating Siam from Burmese occupation after the Second Fall of Ayutthaya
Ayutthaya kingdom
Ayutthaya was a Siamese kingdom that existed from 1350 to 1767. Ayutthaya was friendly towards foreign traders, including the Chinese, Vietnamese , Indians, Japanese and Persians, and later the Portuguese, Spanish, Dutch and French, permitting them to set up villages outside the walls of the...
in 1767, and the subsequent unification of Siam after it fell under various warlords. He established the city Thonburi
Thonburi
Thon Buri is an area of modern Bangkok. It was capital of Thailand from 1767 to 1782, during the reign of King Taksin, after the previous capital Ayutthaya was sacked by the Burmese. It is located on the opposite bank of Chao Phraya River to Bangkok...
as the new capital, as the city Ayutthaya had been almost completely destroyed by the invaders. His reign was characterized by numerous wars, fought to repel new Burmese invasions and to subjugate the northern Thai kingdom of Lanna
Lanna
The Kingdom of Lanna was a kingdom centered in present-day northern Thailand from the 13th to 18th centuries. The cultural development of the people of Lanna, the Tai Yuan people, had begun long before as successive Tai Yuan kingdoms preceded Lanna...
, the Laotian principalities, and a threatening Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
. He was succeeded by the Chakri dynasty and the Rattanakosin Kingdom under his long time friend King Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke
Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke
Phra Bat Somdet Phra Poramintharamaha Chakri Borommanat Phra Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke , posthumously titled "the Great", or Rama I , was the founder and the first monarch of the reigning House of Chakri of Siam . He ascended the throne in 1782, after defeating a rebellion which had deposed King...
.
Although warfare took up most of King Taksin's time, he paid a great deal of attention to politics, administration, economy, and the welfare of the country. He promoted trade and fostered relations with foreign countries including China
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
, Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
, and the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
. He had roads built and canals dug. Apart from restoring and renovating temples, the king attempted to revive literature, and various branches of the arts such as drama, painting, architecture and handicrafts. He also issued regulations for the collection and arrangement of various texts to promote education and religious studies. In recognition for what he did for the Thais, he was later awarded the title of Maharaj (The Great).
Early life and career
The future ruler was born on April 17, 1734 in AyutthayaAyutthaya (city)
Ayutthaya city is the capital of Ayutthaya province in Thailand. Located in the valley of the Chao Phraya River. The city was founded in 1350 by King U Thong, who went there to escape a smallpox outbreak in Lop Buri and proclaimed it the capital of his kingdom, often referred to as the Ayutthaya...
. His father, Hai-Hong (Thai
Thai language
Thai , also known as Central Thai and Siamese, is the national and official language of Thailand and the native language of the Thai people, Thailand's dominant ethnic group. Thai is a member of the Tai group of the Tai–Kadai language family. Historical linguists have been unable to definitively...
:ไหฮอง; ), who worked as a tax-collector, was a Teochew
Chaozhou
Chaozhou is a city in eastern Guangdong province of the People's Republic of China. It borders Shantou to the south, Jieyang to the southwest, Meizhou to the northwest, the province of Fujian to the east, and the South China Sea to the southeast...
Chinese
Thai Chinese
The Thai Chinese are an overseas Chinese community who live in Thailand. Thailand is home to the largest, oldest, most prominent, and most integrated overseas Chinese community in the world with a population of approximately 9.5 million people...
immigrant from Chenghai County
Chenghai District
Chenghai or Tenghai is a district of the city of Shantou, Guangdong Province, People's Republic of China.It is the birthplace of Qin Mu, and Hai-Hong, the father of Taksin who was a Thai king....
. His mother, Lady Nok-lang (Thai:นกเอี้ยง), was Thai
Thai people
The Thai people, or Siamese, are the main ethnic group of Thailand and are part of the larger Tai ethnolinguistic peoples found in Thailand and adjacent countries in Southeast Asia as well as southern China. Their language is the Thai language, which is classified as part of the Kradai family of...
(and was later awarded the feudal title of Somdet Krom Phra Phithak Thephamat). Impressed by the boy, Chao Phraya Chakri (Mhud), who was the Samuhanayok (prime minister
Prime minister
A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime...
) in King Boromakot
Boromakot
Somdet Phra Chaoyuhua Boromakot or Somdet Phra Boromaracha Dhiraj III was the king of Ayutthaya from 1732 to 1758. His reign was the last blooming period of Ayutthaya as the kingdom would fall nine years after his death....
's reign, adopted him and gave him the Thai name Sin (สิน,) meaning money or treasure. When he was 7, he was assigned to a monk named Tongdee to begin his education in a Buddhist monastery
Wat
A wat is a monastery temple in Cambodia, Thailand, or Laos. The word "wat" means "school".- Introduction :...
called Wat Kosawat (later Wat Choeng Thar) (Thai:วัดโกษาวาส ต่อมาเปลี่ยนชื่อเป็น วัดเชิงท่า). After seven years of education he was sent by his stepfather to serve as a royal page, he studied Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
, Annamese, and Indian languages with diligence and soon he was able to converse in them with fluency. When Sin and his friend, Tong-Duang, were Buddhist novices they met a Chinese fortune-teller who told them that they both had lucky lines in the palms of their hands and would both become kings. Neither took it seriously, but Tong-Duang was later the successor of King Taksin, Rama I.
After taking the vows of a Buddhist monk for about 3 years, Sin joined the service of King Ekatat and was first deputy governor and later governor of the Tak
Tak Province
Tak is one of the northern provinces of Thailand. Neighboring provinces are Mae Hong Son, Chiang Mai, Lamphun, Lampang, Sukhothai, Kamphaeng Phet, Nakhon Sawan, Uthai Thani and Kanchanaburi...
, which gained him his name Phraya Tak, the governor of Tak, which was exposed to danger from Burma, though his official noble title was "Phraya Tak".
In 1764, the Burmese army attacked the southern region of Thailand. Led by Muang Maha Noratha, the Burmese army was victorious and marched on to Phetchaburi
Phetchaburi
Phetchaburi , also known as Phetburi, is a town in central Thailand, capital of the Phetchaburi Province. In Thai, Phetchaburi means city of diamonds . It is approximately 160km south of Bangkok, at the northern end of the Thai Peninsula...
. Here, the Burmese were confronted by Thai soldiers led by two generals, Kosadhibodhi and Phraya Tak. The Thai army beat the Burmese back to Singkhorn Pass.
In 1765, when the Burmese attacked Ayutthaya
Ayutthaya (city)
Ayutthaya city is the capital of Ayutthaya province in Thailand. Located in the valley of the Chao Phraya River. The city was founded in 1350 by King U Thong, who went there to escape a smallpox outbreak in Lop Buri and proclaimed it the capital of his kingdom, often referred to as the Ayutthaya...
, Phraya Tak defended the capital, for which he was given the title "Phraya Vajiraprakarn" of Kamphaeng Phet
Kamphaeng Phet
Kamphaeng Phet is a town in northern Thailand, capital of the Kamphaeng Phet Province. It covers the complete tambon Nai Mueang of the Mueang Kamphaeng Phet district. As of 2005 it has a population of 30,114.-External links:...
. But he did not have a chance to govern Kamphaeng Phet because war broke out again. He was immediately called back to Ayutthaya to protect the city. For more than a year, Thai and Burmese soldiers fought fierce battles during the siege of Ayutthaya. It was during this time that Phraya Vajiraprakarn experienced many setbacks which led him to doubt the value of his endeavours.
Resistance and independence
On January 3, 1766, shortly before Ayutthaya fell in 1767, he cut his way out of the city at the head of 500 followers to RayongRayong
Rayong is a city located on the shore of the Gulf of Thailand, in the east coast region of Thailand. It is the capital of Rayong Province, and covers the tambon Tha Pradu and Pak Nam and parts of tambon Choeng Noen and Noen Phra, all within Mueang Rayong district...
, on the east coast of Gulf of Thailand
Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand , also known in to Malays as Teluk Siam literally meant Gulf of Siam, is a shallow arm of the South China Sea.-Geography:...
. This action was never adequately explained, as the Royal compound and Ayutthaya proper was located on an island; how Taksin and his followers fought their way out of the Burmese encirclement remains a mystery.
On April 7, 1767, Ayutthaya was facing the full blast of the Burmese siege. After the destruction of Ayutthaya and the death of the Thai king, the country was split into six parts, with Sin controlling the east coast. Together with Tong-Duang, now Chao Phraya Chakri, he eventually managed to drive back the Burmese, defeat his rivals and reunify the country.
Due to his courage and skill in fighting the enemy, he was promoted to be the governor of Khampaeng Phet with the title of Phraya Vajiraprakarn (Thai:พระยาวชิรปราการ), but he was populaly referred as Phraya. He carried out the defence of Ayutthaya in its last days. Perhaps Sin saw that the situation of the kingdom was in great despair. Therefore before the end of Ayutthaya came, he decided to cut his way out from the city and travelled first to Chon Buri
Chonburi (city)
Chonburi is the capital of Chonburi Province in Thailand. It is located about 100km east of Bangkok, on the coast to the Gulf of Thailand. The name means city of water.Chonburi has had town status since 1935.-External links:...
, a town on the Gulf of Thailand
Gulf of Thailand
The Gulf of Thailand , also known in to Malays as Teluk Siam literally meant Gulf of Siam, is a shallow arm of the South China Sea.-Geography:...
's eastern coast, and then to Rayong
Rayong
Rayong is a city located on the shore of the Gulf of Thailand, in the east coast region of Thailand. It is the capital of Rayong Province, and covers the tambon Tha Pradu and Pak Nam and parts of tambon Choeng Noen and Noen Phra, all within Mueang Rayong district...
, where he raised a small army and his supporters began to address him as Prince Tak. He planned to attack and capture Chantaburi, according to a popular version of oral history, he said "We are going to attack Chantaburi tonight, and all the food that we have left just throw it away and destroy all of the utensils that we have. As we are going to have breakfast together at Chantaburi otherwise we would rather be dead."
With his soldiers he moved to Chantaburi, and being rebuffed by the Governor of the town for his friendly overtures, he made a surprise night attack on it and captured it on June 15, 1767, only two months of after the sack of Ayutthaya. His army was rapidly increasing in numbers, as men of Chantaburi and Trat
Trat
Trat is a town in Thailand, capital of Trat Province and the Mueang Trat district. The town is located in the east of Thailand, at the mouth of the Trat River, near the border with Cambodia.-Travel and Accommodation:...
, which had not been plundered and depopulated by the Burmese, naturally constituted a suitable base for him to make preparations for the liberation of his motherland.
Having thoroughly looted Ayutthaya, the Burmese did not seem to show serious interest in holding down the capital of Siam, since they left only a handful of troops under General Suki to control the shattered city. They turned their attention to the north of their own country which was soon threatened with Chinese invasion. On November 6, 1767, having mastered 5,000 troops and all in fine spirits, Taksin sailed up the Chao Phraya River and seized Thonburi opposite present day Bangkok
Bangkok
Bangkok is the capital and largest urban area city in Thailand. It is known in Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon or simply Krung Thep , meaning "city of angels." The full name of Bangkok is Krung Thep Mahanakhon Amon Rattanakosin Mahintharayutthaya Mahadilok Phop Noppharat Ratchathani Burirom...
, executing the Thai governor, Thong-in, whom the Burmese had placed over it. He followed up his victory quickly by boldly attacking the main Burmese camp at Phosamton near Ayutthya. The Burmese were defeated, and Taksin won back Ayutthaya from the enemy within seven months of its destruction.
Taksin took important steps to show that he was a worthy successor to the throne. He was said to take an appropriate treatment to the remnants of the ex-Royal Family, arranged a grand cremation of the remains of King Ekatat, and tackled the problem of locating the capital. Possibly, Taksin realized that Ayutthaya city had suffered such vast destruction that to restore it to its former state would undoubtedly have strained his resources. The Burmese were quite familiar with the various routes leading to Ayutthaya, and in the event of renewal of a Burmese attack on it, the troops under the liberator would be inadequate for the effective defence of the city. With these considerations in mind, he established his capital at Thon Buri, nearer to the sea than Ayutthaya. Not only would Thon Buri be difficult to invade by land, it would also prevent an acquisition of weapons and military supplies by anyone ambitious enough to establish himself as an independent prince further up the Chao Phraya River
Chao Phraya River
The Chao Phraya is a major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It runs through Bangkok, the capital city, and then empties into the Gulf of Thailand.-Etymology:...
. As Thon Buri was a small town, Prince Tak's available forces, both soldiers and sailors, could man its fortifications, and if he found it impossible to hold it against an enemy's attack, he could embark the troops and beat a retreat to Chantaburi.
The successes against competitors for power were due to Taksin's fighting ability as a warrior, splendid leadership, exemplary valor and effective organization of his forces. Usually he put himself in the front rank in an encounter with the enemy, thus inspiring his men to brave danger. Among the officials who threw in their fate with him during the campaigns for the recovery of national independence and for the elimination of the self-appointed local nobles were two personalities who subsequently played exceptionally important roles in Thai history. They were the sons of an official bearing the title of Pra Acksonsuntornsmiantra (Thai
Thai language
Thai , also known as Central Thai and Siamese, is the national and official language of Thailand and the native language of the Thai people, Thailand's dominant ethnic group. Thai is a member of the Tai group of the Tai–Kadai language family. Historical linguists have been unable to definitively...
:พระอักษรสุนทรเสมียนตรา), the elder of whom named Tongduang (Thai:ทองด้วง) was born in 1737 in Ayutthaya and later to be the founder of the Chakri Dynasty, while the younger one, Boonma (Thai:บุญมา), born six years later, assumed the power second to him. The two brothers joined the royal service.
Tongduang, prior to the sacking of Ayutthaya, was ennobled as Luang Yokkrabat, taking charge of royal surveillance, serving the Governor of Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi ) is a town in western Thailand, capital of the Ratchaburi Province. It covers the whole tambon Nai Mueang of Mueang Ratchaburi district. As of 2006 it has a population of 38,208.-External links:*...
, and Boonma had a court title conferred upon him as Nai Sudchinda. Luang Yokkrabat (Tongduang) was therefore not in Ayutthaya to witness the horrors that arose from the fall of the city, while Nai Sudchinda (Boonma) made his escape from Ayutthaya. However, while King Taksin was assembling his forces at Chantaburi, Nai Sudchinda brought his retainers to join him, thus helping to increase his fighting strength. Due to his previous acquaintance with him, the liberator was so pleased that he promoted him to be Pra Mahamontri. Just after his coronation, Taksin was fortunate to secure the service of Luang Yokkrabut on the recommendation of Pra Mahamontri (Thai:พระมหามนตรี) and as he was equally familiar with him as with his brother, he raised him to be Pra Rajwarin. Having rendered signal service to the King during his campaigns or their own expeditions against the enemies, Pra Rajwarin (Thai:พระราชวรินทร์) and Pra Mahamontri rose so quickly in the noble ranks that a few years after, the former was created Chao Phraya Chakri, the rank of the Chancellor, while the latter became Chao Phraya Surasih
Maha Sura Singhanat
Somdet Phra Bawornrajchao Maha Sura Singhanat was the younger brother of Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke, the first monarch of the Chakri dynasty of Siam. As an Ayutthayan general, he fought alongside his brother in various campaigns against Burmese invaders and the local warlords...
.
Ascension to the throne
On December 28, 1768, he was crowned king of Siam at Wang Derm Palace in ThonburiThonburi
Thon Buri is an area of modern Bangkok. It was capital of Thailand from 1767 to 1782, during the reign of King Taksin, after the previous capital Ayutthaya was sacked by the Burmese. It is located on the opposite bank of Chao Phraya River to Bangkok...
, the new capital of Siam. He assumed the official name of Boromraja IV, but is known in Thai history as King Taksin, being a combination of his popular name, Phya Tak, and his first name, Sin, or the King of Thonburi, being the only ruler of that capital. At the time of his coronation, he was only 34 years of age. His father was Chinese or partly Chinese, and his mother Siamese. He believed that even the forces of nature were under his control when he was destined to succeeded, and this faith led him to attempt and achieve tasks which to another man would seem impossible. He never had time to build Thonburi into a great city, as he was fully occupied with suppression of internal and external enemies, as well as territorial expansion throughout his reign.
Five separate states
After the sacking of Ayutthaya, the country had fallen apart, due to the disappearance of the central authority. Besides King Taksin, who had organized his force in the south-eastern provinces, Prince Teppipit, King Boromakot's son, who had been unsuccessful in a diversionary action against the Burmese in 1766, had set himself up as the ruler of PhimaiPhimai
Phimai is a township in the Nakhon Ratchasima Province in the northeast of Thailand. The town is located at . As of 2005 the town has a population of 9,768...
holding sway over the eastern provinces including Nakhon Ratchasima
Nakhon Ratchasima
Nakhon Ratchasima or is a city in the north-east of Thailand and gateway to Isan. It is the capital of the Nakhon Ratchasima Province and Nakhon Ratchasima district...
or Khorat, while the Governor of Phitsanulok
Phitsanulok
Phitsanulok is an important and historic city in lower northern Thailand and is the capital of Phitsanulok Province, which stretches all the way to the Laotian border. Phitsanulok is one of the oldest cities in Thailand, founded over 600 years ago...
, whose first name was Ruang (Thai:เรือง), had proclaimed himself independent, with the territory under his control extending to the province of Nakhon Sawan
Nakhon Sawan
Nakhon Sawan is a city in Thailand, the name literally means "Heavenly City". The city is the capital of Nakhon Sawan Province, and covers the complete subdistrict Pak Nam Pho and parts of Khwae Yai, Nakhon Sawan Tok, Nakhon Sawan Ok and Wat Sai, all of Mueang Nakhon Sawan district...
. North of Phitsanulok was the town of Sawangburi (known as Fang in Uttaradit Province
Uttaradit Province
Uttaradit is one of the northern provinces of Thailand. Neighboring provinces are Phitsanulok, Sukhothai, Phrae and Nan...
), where a Buddhist monk named Ruan had made himself a prince, appointing his qualified fellow monks as army commanders. He had himself pursued Buddhist studies at Ayutthatya with such excellent results that he had been appointed the chief monk of Sawangburi by King Boromakot. In the southern provinces up to Chumphon
Chumphon
Chumphon is a town in southern Thailand, capital of the Chumphon Province and the Mueang Chumphon district. The city is located about 463 kilometers away from Bangkok...
, a Pra Palad who was the acting Governor of Nakhon Si Thammarat
Nakhon Si Thammarat
Nakhon Si Thammarat is a town in southern Thailand, capital of the Nakhon Si Thammarat Province and the Nakhon Si Thammarat district. It is about south of Bangkok, on the east coast of the Malay Peninsula. The city was the administrative center of southern Thailand during most of its history. ...
declared his independence and raised himself to the princely rank.
Having firmly established his power at Thonburi, King Taksin set out to crush his rivals so as to effect the reunification of the Kingdom. After a temporary repulse by the Governor of Phitsanulok, he concentrated on the defeat of the weakest one first. Prince Teppipit of Phimai was quelled and executed in 1768. In dealing with the Prince of Nakhon Si Thammarat, who was taken prisoner by the loyal Governor of Pattani
Pattani
Pattani may refer to* Pattani Province, in southern Thailand* Pattani , in southern Thailand* Pattani , which includes the above province** Pattani Kingdom, a former semi-independent kingdom...
, the King not only pardoned him but also favoured him with a residence at Thonburi. Chao Narasuriyawongse, one of Taksin's nephews, was substituted for him as Governor. King Taksin himself led an expedition against him and took it, but the Prince disappeared and could not be found again.
Wars and rebellions
Needless to say, HsinbyushinHsinbyushin
Hsinbyushin was king of the Konbaung dynasty of Burma from 1763 to 1776. The second son of the dynasty founder Alaungpaya is best known for his wars with China and Siam, and is considered the most militaristic king of the dynasty. His successful defense against four Chinese invasions preserved...
of Burma never abandoned his plan to force Siam to its knees, and as soon as he had been informed of the foundation of Thonburi as King Taksin's capital, he commanded the Governor of Tavoy to subjugate him in 1767. The Burmese army advanced to the district of Bangkung in the province of Samut Songkram to the west of the new capital, but was routed by the Thai king himself.
Peace having been concluded with China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, the Burmese king sent another small army of 5,000 to attack Siam in 1774. But it was completely surrounded by the Thais at Bangkeo in Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi ) is a town in western Thailand, capital of the Ratchaburi Province. It covers the whole tambon Nai Mueang of Mueang Ratchaburi district. As of 2006 it has a population of 38,208.-External links:*...
, and eventually starvation compelled the Burmese to capitulate to King Taksin. It would be no exaggeration to say that he could have massacred all of them if he wished to do so, but the fact that he took them alive was to promote the morale of the Thai people. The Burmese reinforcements who had encamped themselves in the province of Kanchanaburi
Kanchanaburi
Kanchanaburi ) is a town in the west of Thailand and the capital of Kanchanaburi province. In 2006 it had a population of 31,327...
were then mopped up. Undaunted by this defeat, King Hsinbyushin tried again to conquer Siam, and in October 1775 the greatest Burmese invasion in the Thonburi period began under Maha Thiha Thura
Maha Thiha Thura
Maha Thiha Thura was commander-in-chief of the Burmese military from 1768 to 1776. Regarded as a brilliant military strategist, the general is best known in Burmese history for defeating the Chinese invasions of Burma...
, known in Thai history as Azaewunky. He had distinguished himself as a first rate general in the wars with China and in the suppression of a recent Peguan rising.
After crossing the Thai frontier at Melamao Pass, the Burmese marched towards Phitsanulok
Phitsanulok
Phitsanulok is an important and historic city in lower northern Thailand and is the capital of Phitsanulok Province, which stretches all the way to the Laotian border. Phitsanulok is one of the oldest cities in Thailand, founded over 600 years ago...
, capturing Phichai and Sukhothai
Sukhothai (city)
Sukhothai ) was the capital of the Sukhothai Kingdom.Sukhothai is 12 km from the modern city of New Sukhothai.Sukhothai, which literally means "Dawn of Happiness" with an area of 6,596 km2., is about 427 km north of Bangkok and was founded in 1238. Sukhothai was the capital of the...
on the way. In his interrogation of two Phichai officials, Azaewunky referred to Chao Phraya Surasih who was the Governor of Phisanulok as "Phraya Sua" or "The Tiger", thus testifying to his boldness and decisiveness. The Burmese then besieged Phitsanulok which was defended by the brother generals, Chao Phraya Chakri and Chao Phya Surasih, and as the result of the stubborn resistance on the part of Thai soldiers, they were checked outside the city ramparts for about 4 months. Hearing about Chao Phraya Chakri's successful assaults which drove back the Burmese to their well fortified camp, Azaewunky arranged a meeting with him, in the course of which he extolled his generalship and advised him to take good care on himself. He prophesied that General Chakri would certainly become king. Was he really honest in his prediction? No definite answer has been found for it. Anyhow he was at that time seventy two years of age, while his opponent was only thirty nine. Any doubt about Azaewunky's stratagem to sow discord between King Taksin and Chao Phraya Chakri should be dismissed, since they collaborated closely in subsequent military expeditions.
In spite of King Taksin's endeavour to attack the Burmese from the rear, Chao Phraya Chakri and Chao Phraya Surasih could not hold Phitsanulok any longer, due to lack of provisions. Having collected most of the inhabitants, they successfully fought their way through enemy lines and made Phetchabun
Phetchabun
Phetchabun is a town in Thailand, capital of the Phetchabun Province. It covers the tambon Nai Mueang of the Phetchabun district, along the Pa Sak River...
their headquarters. Azaewunky led his army into the deserted city at the end of March 1776, but was soon confronted with the same problem of the shortage of food. At this juncture he was instructed by the new Burmese King, Singun Min or Chingkucha (1776–1782) to evacuate Thai territory. So Azaewunky's army left Siam, but the remnants of the Burmese forces continued the war until they were pushed out of the country in September of that year.
In King Taksin's opinion, so long as Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai sometimes written as "Chiengmai" or "Chiangmai", is the largest and most culturally significant city in northern Thailand. It is the capital of Chiang Mai Province , a former capital of the Kingdom of Lanna and was the tributary Kingdom of Chiang Mai from 1774 until 1939. It is...
was ruled by the Burmese, the north of Siam would be constantly subjected to their incursions. The prerequisite for the maintenance of peace in that region would therefore be the complete expulsion of the Burmese from Chiang Mai. In 1771, the Burmese Governor of that city moved his army southwards and laid siege to Phichai
Amphoe Phichai
Phichai is the southernmost district of Uttaradit Province, northern Thailand.-Geography:Neighboring districts are Tron, Thong Saen Khan of Uttaradit Province, Wat Bot, Phrom Phiram of Phitsanulok Province, Sawankhalok and Si Nakhon of Sukhothai Province-History:Mueang Phichai is believed to be...
, but he was driven out. Taksin followed the Burmese with a view to studying their strength, and his army was thus not prepared for a direct assault on their city fortress. After meeting with stubborn resistance, he retired, presumably believing in an ancient prophesy to the effect that two attempts were required for the capture of Chiang Mai. King Narairaja had tried twice to seize it before it fell into his hands.
The Burmese failure to take Phichai formed a prelude to Taksin's second-expedition to Chaing Mai. In 1773, a Burmese army which threatened Phichai was drawn into an ambush and was heavily routed. Phraya Phichai
Phraya Phichai
Phraya Phichai , or popularly known as Phraya Phichai Dap Hak was a historic Thai nobleman in the Ayutthaya period who fought with a sword in each hand until one was broken.-History:Phraya Phichai was a Siamese general...
, the Phichai Governor, engaged the Burmese in a hand to hand fight until his two long swords were broken, and thus won the name of "Broken Sword." When a Thai army under the command of Chao Phraya Chakri and Chao Phraya Surasih reached Lampang, Phraya Chaban and Phraya Kawila, the two leading officials who had deserted the Burmese joined him in laying siege to Chaing Mai and soon King Taksin arrived on the spot. The city fell to the Thai armies in January 1775, but the Burmese Governor and the commander managed to escape with their families. Before his departure for Thonburi, the King conferred honours and distinction on those who had contributed to success of his campaign. Phraya Chaban was made Governor of Chaing Mai with the title of Phraya Wichienprakarn, while Phraya Kawila and Phraya Waiwongsa governed Lampang
Lampang
Lampang, also called Nakhon Lampang to differentiate from Lampang Province, is the third largest town in northern Thailand and capital of Lampang Province and the Lampang district. Traditional names for Lampang include Wiang Lakon and Khelang Nakhon. The city is still growing rapidly as trading...
and Lamphun
Lamphun
Lamphun is a town in northern Thailand, capital of Lamphun Province. It covers the whole tambon Nai Mueang of Mueang Lamphun district...
respectively. Chao Phraya Chakri was directed to prolong his stay in order to assist them in the pacification of the north, which included the Laotian states. However, the Burmese King considered that as the Laotian states constituted his base for the maintenance of Burmese power in the territory further east, namely, Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang, or Louangphrabang , is a city located in north central Laos, where the Nam Khan river meets the Mekong River about north of Vientiane. It is the capital of Luang Prabang Province...
and Vientiane
Vientiane
-Geography:Vientiane is situated on a bend of the Mekong river, which forms the border with Thailand at this point.-Climate:Vientiane features a tropical wet and dry climate with a distinct monsoon season and a dry season. Vientiane’s dry season spans from November through March. April marks the...
, Chiang Mai must be taken back, and so a Burmese army of 6,000 men was sent there to carry out its mission in 1776. The Burmese entered the city, but were forced out by a Thai army under Chao Phraya Surasih which had marched to its relief. Chaing Mai had suffered from the recent campaigns so badly that its population was greatly reduced and impoverished, and in the event of a new Burmese attack, it could not defend itself. For these reasons, King Taksin abandoned the city and its remaining inhabitants were transplanted to Lampang. Chiang Mai thus became a deserted city and remained so for fifteen years. Over the next few years, Taksin managed to gain control over Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai sometimes written as "Chiengmai" or "Chiangmai", is the largest and most culturally significant city in northern Thailand. It is the capital of Chiang Mai Province , a former capital of the Kingdom of Lanna and was the tributary Kingdom of Chiang Mai from 1774 until 1939. It is...
, and put Cambodia under the vassalage of Siam by 1779 after repeated military campaigns.
Expansion to the Outer Zone

Amphoe Nang Rong
Nang Rong is a district of Buriram Province, northeastern Thailand.-Geography:Neighboring districts are Chamni, Mueang Buriram, Prakhon Chai, Chaloem Phra Kiat, Lahan Sai, Pakham, Non Suwan and Nong Ki of Buriram Province.It is the closest major town to the Phanom Rung Historical Park, and 11th...
, who had rebelled against the Thai king. A Thai army under Chao Phraya Chakri was ordered to move against the rebel, who was caught and executed, and having received reinforcements under Chao Phraya Surasih, he advanced to Champasak, where the ruler, Chao O and his deputy, were captured and were summarily beheaded. Champasak was added to the Kingdom of Siam, and King Taksin was so pleased with Chao Phraya Chakri's conduct of the campaign that he promoted him to be Somdej Chao Phraya Mahakasatsuek Piluekmahima Tuknakara Ra-adet (Thai
Thai language
Thai , also known as Central Thai and Siamese, is the national and official language of Thailand and the native language of the Thai people, Thailand's dominant ethnic group. Thai is a member of the Tai group of the Tai–Kadai language family. Historical linguists have been unable to definitively...
:สมเด็จเจ้าพระยามหากษัตริย์ศึก พิลึกมหึมาทุกนคราระอาเดช) (meaning the supreme Chao Phraya, Great Warrior-King who was so remarkably powerful that every city was afraid of his might)—being the highest title of nobility that a commoner could reach. It would be equivalent to the rank of a Royal Duke
Royal Dukedoms in the United Kingdom
A Royal Duke is a duke who is a member of the British Royal Family, entitled to the style of "His Royal Highness". The current Royal Dukedoms are, in order of precedence:*Lancaster , held by queen Elizabeth II...
.
In Vientiane
Vientiane
-Geography:Vientiane is situated on a bend of the Mekong river, which forms the border with Thailand at this point.-Climate:Vientiane features a tropical wet and dry climate with a distinct monsoon season and a dry season. Vientiane’s dry season spans from November through March. April marks the...
, a Minister of State, Pra Woh, had rebelled against the ruling prince and fled to the Champasak territory, where he set himself up at Donmotdang near the present city of Ubon. He made formal submission to Siam, when he annexed Champasak, but after the withdrawal of the Thai army, he was attacked and killed by troops from Vientiane. This action was instantly regarded by King Taksin as a great insult to him, and at his command, Somdej Chao Phya Mahakasatsuek invaded Vientiane with an army of 20,000 men in 1778. It would be useful here to briefly summarise the history of Laos which had been separated into two principalities of Luang Prabang and Vientiane since the beginning of the eighteenth century. The Prince of Luang Prabang, who was in enmity with the Prince of Vientiane, submitted to Siam for his own safety, bringing his men to join Somdej Chao Phya Mahakasatsuek in besieging the city. After a siege of Vientiane which took about four months, the Thais took Vientiane and carried off the image of the Emerald Buddha
Emerald Buddha
The Emerald Buddha is the palladium of the Kingdom of Thailand, a figurine of the sitting Buddha, made of green jadeite , clothed in gold, and about 45 cm tall...
to Thonburi. The Prince of Vientiane managed to escape and went into exile. Thus Luang Prabang and Vientiane became Thai dependencies. Nothing definite is known about the origin of the celebrated Emerald Buddha. It is believed that this image was carved from green jasper by an artist or artists in northern India about two thousand years ago. It was taken to Ceylon and then to Chiang Rai
Chiang Rai
-Demographics:Official Population count: According to the Thailand National Statistical Office, as of September 2010, Chiang Rai municipal district has a population of 199,699...
, a town in the north of Siam where it was, in 1434, found intact in a chedi which had been struck by lightning. As an object of great veneration among Thai Buddhists. it has been deposited in monasteries in Lampang
Lampang
Lampang, also called Nakhon Lampang to differentiate from Lampang Province, is the third largest town in northern Thailand and capital of Lampang Province and the Lampang district. Traditional names for Lampang include Wiang Lakon and Khelang Nakhon. The city is still growing rapidly as trading...
, Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai
Chiang Mai sometimes written as "Chiengmai" or "Chiangmai", is the largest and most culturally significant city in northern Thailand. It is the capital of Chiang Mai Province , a former capital of the Kingdom of Lanna and was the tributary Kingdom of Chiang Mai from 1774 until 1939. It is...
, Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang
Luang Prabang, or Louangphrabang , is a city located in north central Laos, where the Nam Khan river meets the Mekong River about north of Vientiane. It is the capital of Luang Prabang Province...
, Vientiane
Vientiane
-Geography:Vientiane is situated on a bend of the Mekong river, which forms the border with Thailand at this point.-Climate:Vientiane features a tropical wet and dry climate with a distinct monsoon season and a dry season. Vientiane’s dry season spans from November through March. April marks the...
, Thonburi
Thonburi
Thon Buri is an area of modern Bangkok. It was capital of Thailand from 1767 to 1782, during the reign of King Taksin, after the previous capital Ayutthaya was sacked by the Burmese. It is located on the opposite bank of Chao Phraya River to Bangkok...
, and eventually in Bangkok
Bangkok
Bangkok is the capital and largest urban area city in Thailand. It is known in Thai as Krung Thep Maha Nakhon or simply Krung Thep , meaning "city of angels." The full name of Bangkok is Krung Thep Mahanakhon Amon Rattanakosin Mahintharayutthaya Mahadilok Phop Noppharat Ratchathani Burirom...
.
In 1770, King Taksin launched a war against the Nguyễn Lords over their control of Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
. After some initial defeats, the joint Siamese-Cambodian army defeated the Nguyễn army in 1771 and 1772. These defeats helped provoke an internal rebellion (the Tây Sơn rebellion) which would soon sweep the Nguyễn out of power. In 1773, the Nguyễn made peace with King Taksin, giving back some land they controlled in Cambodia.
In 1769, Cambodia was in turmoil again, due to the rivalry for the throne by two royal brothers, the elder of who was King Ramraja (Non). Having suffered defeat at the hands of his brother (Ton) who was aided by Annamite troops, he sought shelter in Siam. Prince Ton proclaimed himself as King Narairaja. This struggle afforded an opportunity to King Taksin to resuscitate Thai suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
over Cambodia as in the days of Ayutthaya. An army was dispatched to assist the ex-King Ramraja to regain his power, but met with no success.
In 1771, however, the Thai forces won back the Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
throne for him, but Narairaja retreated to the east of the country. In the end, Ramraja and Narairaja came to a compromise, whereby the former became the first King and the latter was the second King or Maha Uparayoj
Uparaja
Uparaja or Ouparath, also Ouparaja , was a royal title reserved for the vice royal in the Buddhist dynasties in Burma, Cambodia, and Laos and Thailand as well as some of their minor tributary kingdoms.-Burma:...
, and Prince Tam was Maha Uparat or Deputy to the first and the second King. This arrangement proved to be unsatisfactory. Prince Tam was murdered, while the second King died suddenly. Believing that King Ramraja was responsible for their deaths, many prominent officials under the leadership of Prince Talaha (Mu) revolted, caught him and drowned him in the river in 1780. Prince Talaha put Prince Ang Eng, the four year old son of the ex-King Narairaja, on the throne with himself acting as Regent
Regent
A regent, from the Latin regens "one who reigns", is a person selected to act as head of state because the ruler is a minor, not present, or debilitated. Currently there are only two ruling Regencies in the world, sovereign Liechtenstein and the Malaysian constitutive state of Terengganu...
, but he soon leaned too much Annam, thus coming into conflict with King Taksin’s policy to support a pro-Thai prince on the Cambodian throne. The Thai King therefore decided on an invasion of Cambodia. A Thai army of 20,000 under Somdej Chao Phraya Mahakasatsuek moved into Cambodia, and in the event of his success in subduing the country, he was to assist in crowning Taksin’s son, Prince Intarapitak, as King of Cambodia. With the aid of an Annamite army, Prince Talana was prepared to take his stand against the Thai forces at Phnom Penh, but before any fighting started, serious disturbances which had broken out in Siam made Somdej Chao Phraya Mahakasatsuek decide on a hasty return to Thonburi, after handing the command of the army to Chao Phraya Surasih.
Relation with Chinese Empire: 'Underlined'
When Ayutthaya fell to the Burmese in 1767, Thai and Chinese sources mentioned that Taksin, then the lord of Tak, broke the Burmese siege and led his troops to Chantaburi. During those years, Chinese Empire was into border conflicts with Konbaung Burma. The Burmese invasion into Siam became the warning for Chinese Empire. Taksin, then, sent tributaty mission to require the royal seal, claiming that the throne of Ayutthaya Kingdom came to an end. Vietnamese and Chinese sources reported that the aim of Taksin in attacking Cambodia was to uproot the remnants of Ayutthaya royal 'remnants' taking refuge in that kingdom.Chinese Court could not help but seized the chance by asking Taksin, as a 'new vassal', to be her ally in the war against the Burmese barbarians. Eventually Chinese Court approved the royal status of Taksin, as the new king of Siam.
Territory

Ayutthaya (city)
Ayutthaya city is the capital of Ayutthaya province in Thailand. Located in the valley of the Chao Phraya River. The city was founded in 1350 by King U Thong, who went there to escape a smallpox outbreak in Lop Buri and proclaimed it the capital of his kingdom, often referred to as the Ayutthaya...
, Ang Thong
Ang Thong
Ang Thong ) is a town in Thailand, capital of the Ang Thong Province. The town covers the whole tambon Talat Luang and Bang Kaeo as well as parts of the tambon Sala Daeng, Ban Hae, Ban It, Pho Sa and Yansue, all of Mueang Ang Thong district, and as of 2006 has a population of 13,738...
, Singburi, Lopburi
Lopburi
Lopburi ) is the capital city of Lopburi Province in Thailand. It is located about 150 km north-east of Bangkok. As of 2006 it has a population of 26,500...
, Uthai Thani
Uthai Thani
Uthai Thani is a town in Thailand, capital of the Uthai Thani province, in the Lower North of the country. It covers the whole tambon Uthai Mai of Mueang Uthai Thani district. The town is situated on the right bank of the Sakae Krang River, a few kilometers upstream from where it flows into the...
, Nakhon Sawan
Nakhon Sawan
Nakhon Sawan is a city in Thailand, the name literally means "Heavenly City". The city is the capital of Nakhon Sawan Province, and covers the complete subdistrict Pak Nam Pho and parts of Khwae Yai, Nakhon Sawan Tok, Nakhon Sawan Ok and Wat Sai, all of Mueang Nakhon Sawan district...
, Chachoengsao
Chachoengsao
Chachoengsao ) is a town in central Thailand, capital of the Chachoengsao Province. It is located on the bank of the Bang Pakong River. It occupies the tambon Na Mueang and parts of Ban Mai, Bang Tin Pet, Wang Takhian and Sothon of Mueang Chachoengsao district...
, Prachinburi
Prachinburi
Prachinburi is a town in Thailand, capital of the Prachinburi Province....
, Nakhon Nayok, Chonburi
Chonburi (city)
Chonburi is the capital of Chonburi Province in Thailand. It is located about 100km east of Bangkok, on the coast to the Gulf of Thailand. The name means city of water.Chonburi has had town status since 1935.-External links:...
, Rayong
Rayong
Rayong is a city located on the shore of the Gulf of Thailand, in the east coast region of Thailand. It is the capital of Rayong Province, and covers the tambon Tha Pradu and Pak Nam and parts of tambon Choeng Noen and Noen Phra, all within Mueang Rayong district...
, Chantaburi, Trat
Trat
Trat is a town in Thailand, capital of Trat Province and the Mueang Trat district. The town is located in the east of Thailand, at the mouth of the Trat River, near the border with Cambodia.-Travel and Accommodation:...
, Nakhon Chai Si
Amphoe Nakhon Chai Si
Nakhon Chai Si is a district of Nakhon Pathom Province, central Thailand.-History:It was established in the reign of King Maha Chakkraphat of Ayutthaya kingdom....
, Nakhon Pathom
Nakhon Pathom
Nakhon Pathom is a city in central Thailand, capital of the Nakhon Pathom Province. One of the most important landmarks is the giant Phra Pathom Chedi...
, Suphanburi
Suphanburi
Suphan Buri is a town in central Thailand, capital of the Suphan Buri Province. It covers the whole tambon Tha Philiang and parts of the tambon Rua Yai and Tha Rahat, all within the Mueang Suphan Buri district...
, Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi
Ratchaburi ) is a town in western Thailand, capital of the Ratchaburi Province. It covers the whole tambon Nai Mueang of Mueang Ratchaburi district. As of 2006 it has a population of 38,208.-External links:*...
, Samut Sakhon
Samut Sakhon
Samut Sakhon is a town in Thailand, capital of the Samut Sakhon province....
, Samut Songkhram
Samut Songkhram
Samut Songkhram ) is a town in Thailand, capital of the Samut Songkhram Province and the Samut Songkhram district. It covers the area of the tambon Mae Klong, which is also the old name of the town as well as the Mae Klong River, which enters the Gulf of Thailand near the town....
, Phetchaburi
Phetchaburi
Phetchaburi , also known as Phetburi, is a town in central Thailand, capital of the Phetchaburi Province. In Thai, Phetchaburi means city of diamonds . It is approximately 160km south of Bangkok, at the northern end of the Thai Peninsula...
, Kanchanaburi
Kanchanaburi
Kanchanaburi ) is a town in the west of Thailand and the capital of Kanchanaburi province. In 2006 it had a population of 31,327...
, and Prachuap Khiri Khan
Prachuap Khiri Khan
Prachuap Khiri Khan is a town in southern Thailand. It is the capital of Prachuap Khiri Khan province and is on the coast at one of the narrowest stretches in Thailand, only 10 km from the Burmese border at Dansingkhorn. The town can reached from Bangkok by train from Hualampong Station or by...
.
Throughout his reign, King Taksin carried out his policy of expansion.
In the north, including the whole of Lanna
Lanna
The Kingdom of Lanna was a kingdom centered in present-day northern Thailand from the 13th to 18th centuries. The cultural development of the people of Lanna, the Tai Yuan people, had begun long before as successive Tai Yuan kingdoms preceded Lanna...
. Burmese was driven out. local allies became Thonburi's subjugation.
In the south, including Syburi
Syburi
Saiburi is the name for the Malay state of Kedah returned to Thailand when the Japanese occupied British Malaya during World War II....
(today is Kedah
Kedah
Kedah is a state of Malaysia, located in the northwestern part of Peninsular Malaysia. The state covers a total area of over 9,000 km², and it consists of the mainland and Langkawi. The mainland has a relatively flat terrain, which is used to grow rice...
) and Trengganu in Malaysia.
In the east, Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
was subjugated. His forces even attacked South Vietnam
South Vietnam
South Vietnam was a state which governed southern Vietnam until 1975. It received international recognition in 1950 as the "State of Vietnam" and later as the "Republic of Vietnam" . Its capital was Saigon...
In the northeast, including Vientiane
Vientiane
-Geography:Vientiane is situated on a bend of the Mekong river, which forms the border with Thailand at this point.-Climate:Vientiane features a tropical wet and dry climate with a distinct monsoon season and a dry season. Vientiane’s dry season spans from November through March. April marks the...
, Phuan
Phuan
The Phuan , also known as Tai Phuan, Thai Puan or Lao Phuan, are a Theravada Buddhist Tai people spread out in small pockets over most of the northeastern Isan region with other groups scattered in central Thailand and Laos . According to the Ethnologue Report, the Phuan number 204,704 and that is...
, Luang Phrabang, and Hua Phan Ha Thang Hok.
In the southeast, including Phutthaimat (Hà Tiên
Hà Tiên
Hà Tiên or Ha Tien is a town in Kien Giang Province, Tay Nam Bo of Vietnam. Area: 8,851.5 ha, population : 39,957. The town borders Cambodia to the west....
in Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
today).
In the west, as far as Mergui
Mergui
Myeik is a city in Tanintharyi Division in Myanmar , located in the extreme south of the country on the coast of an island on the Andaman Sea. the estimated population was over 209,000. The area inland from the city is a major smuggling corridor into Thailand.-History:Myeik was the southernmost...
and Tenasserim in Myanmar
Myanmar
Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south....
today leading to the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
.
Economy, culture and religion
After King Taksin established Thonburi as his capital, people were living in abject poverty, and food and clothing were scarce. The king was well aware of the plight of his subjects, so in order to legitimize his claim for the Kingdom, he considered solving economic problems as the main priority. He paid high prices for rice from his own money to induce foreign traders to bring in adequate amounts of basic necessities to satisfy the need of the people. He then distributed rice and clothing to all his starving subjects without exception. People who had been dispersed came back to their homes. NormalcyNormalcy
"A return to normalcy" was United States presidential candidate Warren G. Harding’s campaign promise in the election of 1920...
was restored. The economy of the country gradually recovered. King Taksin sent three diplomatic envoys to China in 1767, which then was under the reign of Qianlong Emperor
Qianlong Emperor
The Qianlong Emperor was the sixth emperor of the Manchu-led Qing Dynasty, and the fourth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. The fourth son of the Yongzheng Emperor, he reigned officially from 11 October 1735 to 8 February 1796...
. Six years later, in 1772, China recognized Taksin as the legitimate ruler of Siam.
The record dating from 1777 states: "Important goods from Thailand are amber, gold, colored rocks, good nuggets, gold dust, semi-precious stones, and hard lead." During this time the king actively encouraged the Chinese to settle in Siam, principally those from Chaozhou
Chaozhou
Chaozhou is a city in eastern Guangdong province of the People's Republic of China. It borders Shantou to the south, Jieyang to the southwest, Meizhou to the northwest, the province of Fujian to the east, and the South China Sea to the southeast...
, partly with the intention to revive the stagnating economy and upgrading the local workforce at that time. He had to fight almost constantly for most of his reign to maintain the independence of his country. As the economic influence of the immigrant Chinese community grew with time, many aristocrats, which he took in from the Ayutthaya nobility, began to turn against him for having allied with the Chinese merchants. According to a scholar, the opposition was led mainly by the Bunnag
Bunnag
The House of Bunnag was a powerful Siamese noble family of the Persian descent of the early Rattanakosin. By the nineteenth century, its power and influence reached its zenith. The family was favored by Chakri monarchs and monopolized high-ranking titles. Three Somdet Chao Phrayas came from the...
s, a merchant-aristocrat family of Persian
Persian people
The Persian people are part of the Iranian peoples who speak the modern Persian language and closely akin Iranian dialects and languages. The origin of the ethnic Iranian/Persian peoples are traced to the Ancient Iranian peoples, who were part of the ancient Indo-Iranians and themselves part of...
origins, successors of Ayutthaya's minister of Port&Finance, or Phra Klang Coupled with the tax revenues that these activities provided—helped restore the kingdom's devastated economy.
Thai galleon
Galleon
A galleon was a large, multi-decked sailing ship used primarily by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries. Whether used for war or commerce, they were generally armed with the demi-culverin type of cannon.-Etymology:...
s travelled to Portuguese colony of Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
, in Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, India. However, formal diplomatic relations were not formed. In 1776, Francis Light
Francis Light
Captain Francis Light was the founder of the British colony of Penang and its capital George Town in 1786.-Early years:...
sent 1,400 flintlock
Flintlock
Flintlock is the general term for any firearm based on the flintlock mechanism. The term may also apply to the mechanism itself. Introduced at the beginning of the 17th century, the flintlock rapidly replaced earlier firearm-ignition technologies, such as the doglock, matchlock and wheellock...
s along with other goods as gifts to King Taksin. Later, Thonburi ordered some guns from England. Royal letters were exchanged and in 1777, George Stratton, the Viceroy of Madras, sent a gold scabbard
Scabbard
A scabbard is a sheath for holding a sword, knife, or other large blade. Scabbards have been made of many materials over the millennia, including leather, wood, and metals such as brass or steel.-Types of scabbards:...
decorated with gems to King Taksin.
In 1770, natives of Terengganu
Terengganu
Terengganu is a sultanate and constitutive state of federal Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, Darul Iman...
and Jakarta
Jakarta
Jakarta is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Officially known as the Special Capital Territory of Jakarta, it is located on the northwest coast of Java, has an area of , and a population of 9,580,000. Jakarta is the country's economic, cultural and political centre...
presented King Taksin with 2,200 shotguns. At that time, Holland controlled the Java
Java
Java is an island of Indonesia. With a population of 135 million , it is the world's most populous island, and one of the most densely populated regions in the world. It is home to 60% of Indonesia's population. The Indonesian capital city, Jakarta, is in west Java...
Islands.
Simultaneously King Taksin was deeply engaged in restoring law and order in the Kingdom and in administering a programme of public welfare to his people. Abuses in the Buddhist establishment, and among the public, were duly rectified, and food and clothes as well as other necessities of life were hastily distributed to those who needed them, thus bringing respect and affection to him.
King Taksin was also interested in other branches of art, including dance and drama. There is evidence that when he went to suppress the Chao Nakhon Si Thammarat faction in 1769, he brought back Chao Nakhon's female dancers. Together with dancers that he had assembled from other places, they trained and set up a royal troupe in Thonburi on the Ayutthaya model. The King wrote four episodes from the Ramakian for the royal troupe to rehearse and perform.
When he went north to suppress the Phra Fang faction, he could see that monks in the north were lax and undisciplined. He invited ecclesiastical dignitaries from the capital to teach those monks and brought them back in line with the main teachings of Buddhism. Even though King Taksin had applied himself to reforming the Buddhist religion after its period of decline following the loss of Ayutthaya to Burma, gradually bringing it back to the normalcy it enjoyed during the Ayutthaya kingdom, since his reign was so brief he was not able to do very much.
The administration of the Sangha
Sangha
Sangha is a word in Pali or Sanskrit that can be translated roughly as "association" or "assembly," "company" or "community" with common goal, vision or purpose...
during the Thonburi period followed the model established in Ayutthaya, and he allowed French missionaries to enter Thailand, and like a previous Thai king, helped them build a church in 1780.
Final years and death
Thai historians indicate that the strain on him took its toll, and the king started to become a religious fanatic. In 1781 Taksin showed increasing signs of mental trouble. He believed himself to be a future Buddha, expecting to change the colour of his blood from red to white. As he started practising meditation, he even gave lecture to the monks. Sometimes he flogged monks who refused to worship him as such.Economic tension caused by war was serious. As famine spread, looting and crimes were widespread. Corrupt officials were reportedly abundant. Taksin himself executed several officials harshly. Discontent among officials could be expected.
Several historians have suggested that the tale of his 'insanity' may have been reconstructed as an excuse for his overthrow. However, the letters of a French priest who was in Thonburi at the time support the accounts of the monarch's peculiar behavior. Thus the terms 'insanity' or 'madness' possibly were the contemporary definition describing the monarch's actions. With the Burmese threat still prevalent, a strong ruler was needed on the throne. According to some sources, many oppressions and abuses made by officials were reported. King Taksin punished them harshly, torturing and executing high officials. Finally a faction led by Phraya San seized the capital and forced the king to step down.
According to the following Rattanakosin era accounts, King Taksin was described as 'insane.' The disturbance in Thonburi widely spread, with killing and looting prevalent. A coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
removing Taksin from the throne consequently took place, although Taksin requested to be allowed to join the monkhood. When the coup occurred, General Chao Phraya Chakri
Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke
Phra Bat Somdet Phra Poramintharamaha Chakri Borommanat Phra Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke , posthumously titled "the Great", or Rama I , was the founder and the first monarch of the reigning House of Chakri of Siam . He ascended the throne in 1782, after defeating a rebellion which had deposed King...
was away fighting in Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, but he quickly returned to the Thai capital following being informed of the coup. Upon having arrived at the capital, the General extinguished the coup through arrests, investigations and punishments. Peace was then restored in the capital.
According to the Royal Thai Chronicles, General Chao Phraya Chakri decided to put the deposed Taksin to death. The Chronicles stated that, while being taken to the executing venue, Taksin asked for an audience with General Chao Phraya Chakri but was turned down by the General. Taksin was beheaded in front of Wichai Prasit fortress on Wednesday, April 10, 1782, and his body was buried at Wat Bang Yi Ruea Tai. General Chao Phraya Chakri then seized control of the capital and declared himself king together with establishing the House of Chakri.
The Official Annamese Chronicles states that Taksin was ordered to be executed by General Chao Phraya Chakri at Wat Chaeng by being sealed in a velvet sack and was beaten to death with a scented sandalwood club. There was an account claiming that Taksin was secretly sent to a palace located in the remote mountains of Nakhon Si Thammarat
Nakhon Si Thammarat
Nakhon Si Thammarat is a town in southern Thailand, capital of the Nakhon Si Thammarat Province and the Nakhon Si Thammarat district. It is about south of Bangkok, on the east coast of the Malay Peninsula. The city was the administrative center of southern Thailand during most of its history. ...
where he lived until 1825, and that a substitute was beaten to death in his place. King Taksin ashes and that of his wife are located at Wat Intharam (located in Thonburi). They have been placed in two lotus bud shaped stupas which stand before the old hall.
Critics over the coup
Another contradicting view of the events is that General Chakri actually wanted to be King and had accused King Taksin of being Chinese. The late history was aimed at legitimizing the new monarch, Phraya Chakri or Rama I of Rattanakosin. According to Nidhi EoseewongNidhi Eoseewong
Nidhi Eoseewong is a prominent Thai historian, writer, and political commentator.- Biography :Nidhi Eoseewong was born on May 8, 1940, to an ethnic Chinese family in Chiang Mai, Thailand...
,a prominent Thai historian, writer, and political commentator, Taksin could be seen as the originator, new style of leader, promoting the 'decentralized' kingdom and new generation of the nobles, of Chinese merchants-origin, his major helpers in the wars. On the other hand, Phraya Chakri and his supporters were of 'old' generation of the Ayutthaya nobles, discontent with the previously said changes.
However, this overlooks the fact that Chao Phraya Chakri was himself of partly Chinese origin as well as he himself being married to one of Taksin's daughters. No previous conflicts between them were mentioned in histories. Reports on the conflicts between the king and the Chinese merchants were seen caused by the control of the rice price in the time of famine. However, prior to returning to Thonburi, Chao Phraya Chakri had Taksin's son summoned to Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
and executed. All in all, Phraya Chakri was, in fact, the highest noble in the kingdom, charging the state affairs as the Chancellor. Therefore he was of the greatest potential to be the new leader.
Another view of the events is that Thailand owed China for millions of baht. In order to cancel the agreement between China and Thailand, King Taksin decided to ordain and pretend to die in an execution.
Legacy
King Taksin was seen by some radical historians as a King who differed from the Kings of Ayutthaya, in his origins, his policies, and his leadership style, as a representative of a new class. During the Bangkok Period right up till the Siamese Revolution of 1932Siamese Revolution of 1932
The Siamese Revolution of 1932 or the Siamese Coup d'état of 1932 was a crucial turning point in Thai history in the 20th century...
King Taksin was, said, not as highly honoured as other Siamese Kings because the leaders in the Chakri Dynasty were still concerned about their own political legitimacy. After 1932, when the absolute monarchy gave way to the democratic period, King Taksin become more honoured than ever before. Instead, King Taksin became one of the national heroes. This was because the leaders of that time such as Plaek Pibulsonggram
Plaek Pibulsonggram
Field Marshal Plaek Pibunsongkhram , often known as Phibun Songkhram or simply Phibun in English, was Prime Minister and virtual military dictator of Thailand from 1938 to 1944 and 1948 to 1957.- Early years :...
and even later military junta, on the other hand, wanted to glorify and publicise the stories of certain historical figures in the past in order to support their own policy of nationalism
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
, expansionism
Expansionism
In general, expansionism consists of expansionist policies of governments and states. While some have linked the term to promoting economic growth , more commonly expansionism refers to the doctrine of a state expanding its territorial base usually, though not necessarily, by means of military...
and patriotism
Patriotism
Patriotism is a devotion to one's country, excluding differences caused by the dependencies of the term's meaning upon context, geography and philosophy...
.
King Taksin statue was unveiled in the middle of Wongwian Yai
Wongwian Yai
Wongwian Yai, also spelled "Wong Wian Yai" or "Wongwien Yai" , is a large roundabout in Thon Buri, western bank of the Chao Phraya River in Bangkok, Thailand, where the Statue of King Taksin is situated...
(the Big Traffic Circle) in Thonburi, at the intersection of Prajadhipok/Inthara Phithak/Lat Ya/Somdet Phra Chao Taksin Roads. The king is portrayed with his right hand holding a sword, measuring approximately 9 metres in height from his horse's feet to the spire of his hat, rests on a reinforced concrete pedestal of 8.90 x 1.80 x 3.90 metres. There are four frames of stucco relief on the two sides of the pedestal. The opening ceremony of this monument was held on April 17, 1954 and the royal homage-paying fair takes place annually on 28 December. The king today officially comes to pay respect to king Taksin statue.
The monument featuring King Taksin riding on a horseback surrounded by his four trusted soldiers; Pra Chiang-ngen (later Phraya Sukhothai), Luang Pichai-asa (later Phraya Phichai
Phraya Phichai
Phraya Phichai , or popularly known as Phraya Phichai Dap Hak was a historic Thai nobleman in the Ayutthaya period who fought with a sword in each hand until one was broken.-History:Phraya Phichai was a Siamese general...
), Luang Prom-sena, Luang Raj-saneha. It is placed on the groung of Toong na-chey public park on Leab muang road, just opposite the City Hall, Chantaburi.
In 1981 the Thai cabinet passed a resolution to bestow on King Taksin the honorary title of the Great. The date of his coronation, December 28, is the official day of homage to King Taksin, although it is not designated as a public holiday. The Maw Sukha Association on January 31, 1999 cast the King Taksin Savior of the Nation Amulet, which sought to honour the contributions of King Taksin to Siam during his reign.
The Na Nagara (also spelled Na Nakorn) family is descended in the direct male line from King Taksin.
A tomb containing King Taksin's clothes and a family shrine were found at Chenghai district in Guangdong province in China in 1921. It is believed that a descendant of King Taksin the Great must have sent his clothes to be buried there to conform to Chinese practice. This supports the claim that the place was his father's hometown.
King Taksin the Great Shrine is located on Tha Luang Road in front of Camp Taksin. It is an important place of Chantaburi in order to demonstrate binding of People in Chanthaburi to King Taksin. It is a nine-sided building. The roof is a pointed helmet. Inside of this place enshrined the statue of King Taksin.
- HTMS TaksinHTMS TaksinHTMS Taksin , hull number 622, commissioned in 1995, is a modified version of the Chinese-made Type 053 frigate, designed and built by the China State Shipbuilding Corporation in Shanghai...
, Royal Thai NavyRoyal Thai NavyThe Royal Thai Navy is the navy of Thailand and part of the Royal Thai Armed Forces, it was established in the late 19th century. Admiral Prince Abhakara Kiartiwongse is "The Father of Royal Thai Navy". Similar to the organizational structure of the United States, the Royal Thai Navy includes the...
frigateFrigateA frigate is any of several types of warship, the term having been used for ships of various sizes and roles over the last few centuries.In the 17th century, the term was used for any warship built for speed and maneuverability, the description often used being "frigate-built"...
.
Issue
King Taksin had 21 sons and 9 daughters named
|
|
|
|

