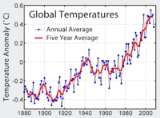
Temperature record
Encyclopedia
- For extreme records instead of records as a set of data, see Temperature extremes
- For instrument-derived temperature records, see Instrumental temperature recordInstrumental temperature recordThe instrumental temperature record shows fluctuations of the temperature of the global land surface and oceans. This data is collected from several thousand meteorological stations, Antarctic research stations and satellite observations of sea-surface temperature. Currently, the longest-running...
The temperature record shows the fluctuations of the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of the atmosphere and the oceans through various spans of time. The most detailed information exists since 1850, when methodical thermometer-based records began. There are numerous estimates of temperatures since the end of the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
glaciation, particularly during the current Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
epoch. Older time periods are studied by paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology is the study of changes in climate taken on the scale of the entire history of Earth. It uses a variety of proxy methods from the Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells and microfossils; it then...
.
The Instrumental Period: from 1850
Detailed information exists since 1850, when methodical thermometer-based records began.Tropospheric temperature (the satellite and balloon temperature records)
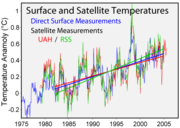
Several groups have analyzed the satellite data to calculate temperature trends in the troposphere. Both the University of Alabama in Huntsville
UAH satellite temperature dataset
The UAH satellite temperature dataset, developed at the University of Alabama in Huntsville, attempts to infer the temperature of the atmosphere at various levels from satellite measurements of radiance....
(UAH) and the private, NASA funded, corporation Remote Sensing Systems
Remote Sensing Systems
Remote Sensing Systems is a private research company founded in 1974 by Frank Wentz. It processes microwave data from a variety of NASA satellites. Most of their research is supported by the Earth Science Enterprise program. The company is based in Santa Rosa, California.They are a widely cited...
RSS
Remote Sensing Systems
Remote Sensing Systems is a private research company founded in 1974 by Frank Wentz. It processes microwave data from a variety of NASA satellites. Most of their research is supported by the Earth Science Enterprise program. The company is based in Santa Rosa, California.They are a widely cited...
(RSS) find an upward trend.
For the lower troposphere (TLT), UAH find a global average trend since 1978 of +0.140 °C/decade, to January 2011.
RSS finds +0.148°C/decade, to January 2011.
In 2004 Fu et al. found trends of +0.19 °C/decade when applied to the RSS dataset. Vinnikov and Grody found +0.20°C/decade up between 1978 and 2005, since which the dataset has not been updated.
Proxies: tree rings, ice cores: the last 2000 years

Proxy (climate)
In the study of past climates is known as paleoclimatology, climate proxies are preserved physical characteristics of the past that stand in for direct measurements , to enable scientists to reconstruct the climatic conditions that prevailed during much of the Earth's history...
measurements can be used to reconstruct the temperature record before the historical period. Quantities such as tree ring widths, coral
Coral
Corals are marine animals in class Anthozoa of phylum Cnidaria typically living in compact colonies of many identical individual "polyps". The group includes the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.A coral "head" is a colony of...
growth, isotope variations in ice core
Ice core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet, most commonly from the polar ice caps of Antarctica, Greenland or from high mountain glaciers elsewhere. As the ice forms from the incremental build up of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper, and an ice...
s, ocean and lake sediments, cave deposits, fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s, ice core
Ice core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet, most commonly from the polar ice caps of Antarctica, Greenland or from high mountain glaciers elsewhere. As the ice forms from the incremental build up of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper, and an ice...
s, borehole temperatures, and glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
length records are correlated with climatic fluctuations. From these, proxy temperature reconstructions of the last 2000 years have been performed for the northern hemisphere, and over shorter time scales for the southern hemisphere and tropics.
Geographic coverage by these proxies is necessarily sparse, and various proxies are more sensitive to faster fluctuations. For example, tree rings, ice cores, and corals generally show variation on an annual time scale, but borehole reconstructions rely on rates of thermal diffusion, and small scale fluctuations are washed out. Even the best proxy records contain far fewer observations than the worst periods of the observational record, and the spatial and temporal resolution of the resulting reconstructions is correspondingly coarse. Connecting the measured proxies to the variable of interest, such as temperature or rainfall, is highly non-trivial. Data sets from multiple complementary proxies covering overlapping time periods and areas are reconciled to produce the final reconstructions.
Proxy reconstructions extending back 2,000 years have been performed, but reconstructions for the last 1,000 years are supported by more and higher quality independent data sets. These reconstructions indicate:
- global mean surface temperatures over the last 25 years have been higher than any comparable period since AD 1600, and probably since AD 900
- there was a Little Ice AgeLittle Ice AgeThe Little Ice Age was a period of cooling that occurred after the Medieval Warm Period . While not a true ice age, the term was introduced into the scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939...
centered around AD 1700 - there was a Medieval Warm PeriodMedieval Warm PeriodThe Medieval Warm Period , Medieval Climate Optimum, or Medieval Climatic Anomaly was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region, that may also have been related to other climate events around the world during that time, including in China, New Zealand, and other countries lasting from...
centered around AD 1000, though the exact timing and magnitude are uncertain and may have shown regional variation.
Indirect historical proxies
As well as natural, numerical proxies (tree-ring widths, for example) thereexist records from the human historical period that can be used to infer
climate variations, including: reports of frost fairs on the Thames; records of good and bad harvests; dates of spring blossom or lambing; extraordinary falls of rain and snow; and unusual floods or droughts. Such records can be used to infer historical temperatures, but generally in a more qualitative manner than natural proxies.
Recent evidence suggests that a sudden and short-lived climatic shift between 2200 and 2100 BCE
4.2 kiloyear event
The 4.2 kiloyear BP aridification event was one of the most severe climatic events of the Holocene period in terms of impact on cultural upheaval. Starting in ≈2200 BC, it probably lasted the entire 22nd century BC. It is very likely to have caused the collapse of the Old Kingdom in Egypt as...
occurred in the region between Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
and Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, with some evidence suggesting a global change. The result was a cooling and reduction in precipitation. This is believed to be a primary cause of the collapse of the Old Kingdom
Old Kingdom
Old Kingdom is the name given to the period in the 3rd millennium BC when Egypt attained its first continuous peak of civilization in complexity and achievement – the first of three so-called "Kingdom" periods, which mark the high points of civilization in the lower Nile Valley .The term itself was...
of Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
.
Paleoclimate

Many estimates of past temperatures have been made over Earth's history
History of Earth
The history of the Earth describes the most important events and fundamental stages in the development of the planet Earth from its formation 4.578 billion years ago to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to the understanding of the main events of the Earth's...
. The field of paleoclimatology includes ancient temperature records. As the present article is oriented toward recent temperatures, there is a focus here on events since the retreat of the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
glaciers. The 10,000 years of the Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
epoch covers most of this period, since the end of the Northern Hemisphere's Younger Dryas
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas stadial, also referred to as the Big Freeze, was a geologically brief period of cold climatic conditions and drought between approximately 12.8 and 11.5 ka BP, or 12,800 and 11,500 years before present...
millennium-long cooling. The Holocene Climatic Optimum
Holocene climatic optimum
The Holocene Climate Optimum was a warm period during roughly the interval 9,000 to 5,000 years B.P.. This event has also been known by many other names, including: Hypsithermal, Altithermal, Climatic Optimum, Holocene Optimum, Holocene Thermal Maximum, and Holocene Megathermal.This warm period...
was generally warmer than the 20th century, but numerous regional variations have been noted since the start of the Younger Dryas.
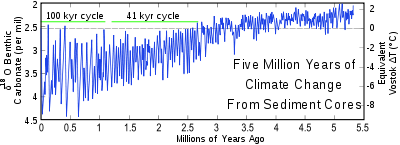
The long term ice coreIce coreAn ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet, most commonly from the polar ice caps of Antarctica, Greenland or from high mountain glaciers elsewhere. As the ice forms from the incremental build up of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper, and an ice...
record: the last 800,000 years
Even longer term records exist for few sites: the recent Antarctic EPICA core reaches 800 kyr; many others reach more than 100,000 years. The EPICA core covers eight glacial/interglacial cycles. The NGRIP core from Greenland stretchs back more than 100 kyr, with 5 kyr in the Eemian interglacialEemian interglacial
The Eemian was an interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago and ended about 114,000 years ago. It was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day. The prevailing Eemian climate is believed to...
. Whilst the large-scale signals from the cores are clear, there are problems interpreting the detail, and connecting the isotopic variation to the temperature signal.
Geologic evidence of past temperature changes
See also
- CLIWOCCliwocThe Climatological database for the world's oceans was a research project to convert ships' logbooks into a computerised database. It was funded by the European Union, and the bulk of the work was done between 2001 and 2003...
(climatological database for the world's oceans) - Temperature record of the past 1000 yearsTemperature record of the past 1000 yearsThe temperature record of the 2nd millennium describes the reconstruction of temperatures since 1000 CE on the Northern Hemisphere, later extended back to 1 CE and also to cover the southern hemisphere. A reconstruction is needed because a reliable surface temperature record exists only since about...
- DendroclimatologyDendroclimatologyDendroclimatology is the science of determining past climates from trees . Tree rings are wider when conditions favor growth, narrower when times are difficult. Other properties of the annual rings, such as maximum latewood density have been shown to be better proxies than simple ring width...

