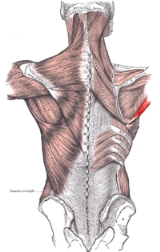
Teres major muscle
Encyclopedia
The teres major muscle is a muscle of the upper limb
and one of six scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle, innervated by the lower subscapular nerve
(c5,c6).
, and from the fibrous septa
interposed between this muscle and the rotor cuff lateral rotator pair of the teres minor and infraspinatus.
The fibers of teres major insert into the medial lip of the bicipital groove of the humerus
.
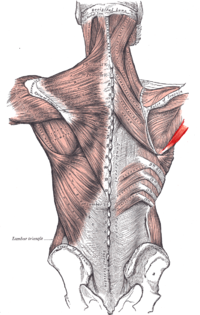 The tendon, at its insertion, lies behind that of the latissimus dorsi, from which it is separated by a bursa
The tendon, at its insertion, lies behind that of the latissimus dorsi, from which it is separated by a bursa
, the two tendons being, however, united along their lower borders for a short distance.
Together with teres minor muscle
, teres major muscle forms the axillary space
, through which several important arteries and veins pass. Teres major is not part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder, but it does combine with the deltoideus to make the six scapulohumeral muscles.
The teres major muscle is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve of the brachial plexus.
.
Upper limb
The upper limb or upper extremity is the region in an animal extending from the deltoid region to the hand, including the arm, axilla and shoulder.-Definition:...
and one of six scapulohumeral muscles. It is a thick but somewhat flattened muscle, innervated by the lower subscapular nerve
Lower subscapular nerve
The lower subscapular nerve is a nerve that supplies the lower part of the subscapularis muscle, and also supplies the teres major muscle....
(c5,c6).
Origin and insertion
It arises from the oval area on the dorsal surface of the inferior angle of the scapulaInferior angle of the scapula
The inferior angle of the scapula , thick and rough, is formed by the union of the vertebral and axillary borders; its dorsal surface affords attachment to the Teres major and frequently to a few fibers of the Latissimus dorsi....
, and from the fibrous septa
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
interposed between this muscle and the rotor cuff lateral rotator pair of the teres minor and infraspinatus.
The fibers of teres major insert into the medial lip of the bicipital groove of the humerus
Humerus
The humerus is a long bone in the arm or forelimb that runs from the shoulder to the elbow....
.
Relations

Bursa (anatomy)
A bursa is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of slimy fluid . It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement...
, the two tendons being, however, united along their lower borders for a short distance.
Together with teres minor muscle
Teres minor muscle
The teres minor is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff.-Origin:It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminæ, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the...
, teres major muscle forms the axillary space
Axillary space
The axillary space is an anatomic space, bounded by teres major muscle, teres minor muscle and humerus. Furthermore, it is split into two parts, the lateral and medial, by the long head of triceps brachii muscle.-Medial axillary space:...
, through which several important arteries and veins pass. Teres major is not part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder, but it does combine with the deltoideus to make the six scapulohumeral muscles.
The teres major muscle is innervated by the lower subscapular nerve of the brachial plexus.
Action
The teres major is a medial rotator and adductor of the humerus and assists the latissimus dorsi in drawing the previously raised humerus downward and backward (extension, but not hyper extension). It also helps stabilize the humeral head in the glenoid cavityGlenoid cavity
The glenoid cavity is a shallow pyriform, articular surface, which is located on the lateral angle of the scapula. It is directed laterally and forward and articulates with the head of the humerus; it is broader below than above and its vertical diameter is the longest.This cavity forms the...
.

