
Terzaghi's Principle
Encyclopedia
Terzaghi's Principle states that when a rock is subjected to a stress, it is opposed by the fluid pressure of pores in the rock.
More specifically, Karl von Terzaghi's Principle, also known as Terzaghi's theory of one-dimensional consolidation, states that all quantifiable changes in stress
to a soil [compression, deformation, shear resistance] are a direct result of a change in effective stress. The effective stress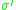 is related to total stress
is related to total stress  and the pore pressure
and the pore pressure  by the relationship;
by the relationship;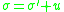
reading that total stress is equal to the sum of effective stress and pore water pressure.
More specifically, Karl von Terzaghi's Principle, also known as Terzaghi's theory of one-dimensional consolidation, states that all quantifiable changes in stress
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
to a soil [compression, deformation, shear resistance] are a direct result of a change in effective stress. The effective stress
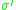 is related to total stress
is related to total stress  and the pore pressure
and the pore pressure  by the relationship;
by the relationship;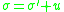
reading that total stress is equal to the sum of effective stress and pore water pressure.
Assumptions of Terzaghi's Principle
- The soil is homogenous (uniform in composition throughout).
- The soil is fully saturated (zero air voids due to water content being so high).
- The solid particles and water are incompressible.
- Compression and flow are one-dimensional (vertical axis being the one of interest).
- Strains in the soil are relatively small.
- Darcy's LawDarcy's lawDarcy's law is a phenomenologically derived constitutive equation that describes the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. The law was formulated by Henry Darcy based on the results of experiments on the flow of water through beds of sand...
is valid for all hydraulic gradients. - The coefficient of permeability and the coefficient of volume compressibility remain constant throughout the process.
- There is a unique relationship, independent of time, between the void ratio and effective stress.

