
Void ratio
Encyclopedia
Void ratio, in materials science
, is related to porosity
and defined as the ratio
:
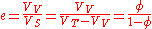
and
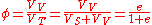
where is void ratio,
is void ratio, 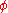 is porosity
is porosity
, VV is the volume of void-space (such as fluids), VS is the volume of solids, and VT is the total or bulk volume. This figure is relevant in composites
, in mining
(particular with regard to the properties of tailings
), and in soil science
. In geotechnical engineering
, it is considered as one of the state variables of soils and represented by the symbol e.
Materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
, is related to porosity
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
and defined as the ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
:
and
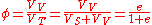
where
 is void ratio,
is void ratio,  is porosity
is porosityPorosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
, VV is the volume of void-space (such as fluids), VS is the volume of solids, and VT is the total or bulk volume. This figure is relevant in composites
Composite material
Composite materials, often shortened to composites or called composition materials, are engineered or naturally occurring materials made from two or more constituent materials with significantly different physical or chemical properties which remain separate and distinct at the macroscopic or...
, in mining
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
(particular with regard to the properties of tailings
Tailings
Tailings, also called mine dumps, slimes, tails, leach residue, or slickens, are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction of an ore...
), and in soil science
Soil science
Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and management of soils.Sometimes terms which...
. In geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering
Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of earth materials. Geotechnical engineering is important in civil engineering, but is also used by military, mining, petroleum, or any other engineering concerned with construction on or in the ground...
, it is considered as one of the state variables of soils and represented by the symbol e.
Engineering applications
- Volume change tendency control. If void ratio is high (loose soils) voids in a soil skeleton tend to minimize under loading - adjacent particles contract. The opposite situation, i.e. when void ratio is relatively small (dense soils), indicates that the volume of the soil is vulnerable to increase under loading - particles dilate.
- Fluid conductivity control (ability of water movement through the soil). Loose soils show high conductivity, while dense soils are not so permeable.
- Particles movement. In a loose soil particles can move quite easily, whereas in a dense one finer particles cannot pass through the voids, which leads to clogging.

