Theophylline
Encyclopedia
Respiratory disease
Respiratory disease is a medical term that encompasses pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange possible in higher organisms, and includes conditions of the upper respiratory tract, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleura and pleural cavity, and the...
s such as COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
and asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
under a variety of brand names. Because of its numerous side-effects, the drug is now rarely administered for clinical use. As a member of the xanthine
Xanthine
Xanthine , is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids and in other organisms. A number of stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine and theobromine....
family, it bears structural and pharmacological similarity to caffeine
Caffeine
Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline xanthine alkaloid that acts as a stimulant drug. Caffeine is found in varying quantities in the seeds, leaves, and fruit of some plants, where it acts as a natural pesticide that paralyzes and kills certain insects feeding on the plants...
. It is naturally found in tea
Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by adding cured leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant to hot water. The term also refers to the plant itself. After water, tea is the most widely consumed beverage in the world...
, although in trace amounts (~1 mg/L), significantly less than therapeutic doses. It is found also in cocoa beans. Amounts as high as 3.7 mg/g have been reported in Criollo cocoa beans.
The main actions of theophylline involve:
- relaxing bronchial smooth muscleSmooth muscleSmooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two sub-groups; the single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit smooth muscle tissues, the autonomic nervous system innervates a single cell within a sheet or bundle and the action potential is propagated by...
- increasing heart muscle contractility and efficiency; as a positive inotropic
- increasing heart rate: positive chronotropicChronotropicChronotropic effects are those that change the heart rate.Chronotropic drugs may change the heart rate by affecting the nerves controlling the heart, or by changing the rhythm produced by the sinoatrial node...
- increasing blood pressureBlood pressureBlood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
- increasing renalKidneyThe kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
blood flow - some anti-inflammatoryInflammationInflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
effects - central nervous systemCentral nervous systemThe central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
stimulatory effect mainly on the medullary respiratory centerRespiratory centerThe respiratory center is located in the medulla oblongata, which is the lowermost part of the brain stem. The RC receives controlling signals of neural, chemical and hormonal nature and controls the rate and depth of respiratory movements of the diaphragm and other respiratory muscles...
.
Medical uses
The main therapeutic uses of theophylline are aimed at:- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPDChronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseChronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
) - asthmaAsthmaAsthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
- infant apneaApnea of prematurityApnea of prematurity is defined as cessation of breathing by a premature infant that lasts for more than 15 seconds and/or is accompanied by hypoxia or bradycardia. Apnea is traditionally classified as either obstructive, central, or mixed. Obstructive apnea may occur when the infant's neck is...
Uses Under Investigation
A clinical study reported in 2008 that theophylline was helpful in improving the sense of smell in study subjects with anosmiaAnosmia
Anosmia is a lack of functioning olfaction, or in other words, an inability to perceive odors. Anosmia may be either temporary or permanent. A related term, hyposmia, refers to a decreased ability to smell, while hyperosmia refers to an increased ability to smell. Some people may be anosmic for one...
.
Adverse effects
The use of theophylline is complicated by its interaction with various drugs, chiefly cimetidineCimetidine
Cimetidine INN is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that inhibits the production of acid in the stomach. It is largely used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline under the trade name Tagamet...
and phenytoin
Phenytoin
Phenytoin sodium is a commonly used antiepileptic. Phenytoin acts to suppress the abnormal brain activity seen in seizure by reducing electrical conductance among brain cells by stabilizing the inactive state of voltage-gated sodium channels...
, and that it has a narrow therapeutic index
Therapeutic index
The therapeutic index is a comparison of the amount of a therapeutic agent that causes the therapeutic effect to the amount that causes death or toxicity ....
, so its use must be monitored to avoid toxicity
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage a living or non-living organisms. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell or an organ , such as the liver...
. It can also cause nausea, diarrhea, increase in heart rate, arrhythmias, and CNS excitation (headaches, insomnia
Insomnia
Insomnia is most often defined by an individual's report of sleeping difficulties. While the term is sometimes used in sleep literature to describe a disorder demonstrated by polysomnographic evidence of disturbed sleep, insomnia is often defined as a positive response to either of two questions:...
, irritability, dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness refers to an impairment in spatial perception and stability. The term is somewhat imprecise. It can be used to mean vertigo, presyncope, disequilibrium, or a non-specific feeling such as giddiness or foolishness....
and lightheadedness
Lightheadedness
Light-headedness is a common and often unpleasant sensation of dizziness and/or feeling that one may be about to faint, which may be transient, recurrent, or occasionally chronic. In some cases, the individual may feel as though his or her head is weightless. The individual may also feel as...
). Seizures can also occur in severe cases of toxicity and is considered to be a neurological emergency. Its toxicity is increased by erythromycin
Erythromycin
Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic that has an antimicrobial spectrum similar to or slightly wider than that of penicillin, and is often used for people who have an allergy to penicillins. For respiratory tract infections, it has better coverage of atypical organisms, including mycoplasma and...
, cimetidine
Cimetidine
Cimetidine INN is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that inhibits the production of acid in the stomach. It is largely used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers. It is marketed by GlaxoSmithKline under the trade name Tagamet...
, and fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a synthetic chemotherapeutic antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone drug class.It is a second-generation fluoroquinolone antibacterial. It kills bacteria by interfering with the enzymes that cause DNA to rewind after being copied, which stops synthesis of DNA and of...
. It can reach toxic levels when taken with fatty meals, an effect called dose dumping
Dose dumping
Dose dumping is a phenomenon of drug metabolism in which environmental factors can cause the premature and exaggerated release of a drug. This can greatly increase the concentration of a drug in the body and thereby produce adverse effects or even drug-induced toxicity.Dose dumping is most commonly...
.
Mechanisms of action
Like other methylated xanthine derivativesXanthine
Xanthine , is a purine base found in most human body tissues and fluids and in other organisms. A number of stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine and theobromine....
, theophylline is both a
- competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitorPhosphodiesterase inhibitorA phosphodiesterase inhibitor is a drug that blocks one or more of the five subtypes of the enzyme phosphodiesterase , therefore preventing the inactivation of the intracellular second messengers cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine monophosphate by the respective PDE...
, which raises intracellular cAMPCyclic adenosine monophosphateCyclic adenosine monophosphate is a second messenger important in many biological processes...
, activates PKACAMP-dependent protein kinaseIn cell biology, Protein kinase A refers to a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP . PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase...
, inhibits TNF-alphaTNF inhibitorTumor necrosis factor promotes the inflammatory response, which in turn causes many of the clinical problems associated with autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn's disease, psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa and refractory asthma. These disorders are...
and inhibits leukotrieneLeukotrieneLeukotrienes are fatty signaling molecules. They were first found in leukocytes . One of their roles is to trigger contractions in the smooth muscles lining the trachea; their overproduction is a major cause of inflammation in asthma and allergic rhinitis...
synthesis, and reduces inflammationAnti-inflammatoryAnti-inflammatory refers to the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation. Anti-inflammatory drugs make up about half of analgesics, remedying pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system....
and innate immunity - nonselective adenosine receptorAdenosine receptorThe adenosine receptors are a class of purinergic receptors, G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as endogenous ligand.-Pharmacology:...
antagonist, antagonizing A1, A2, and A3 receptors almost equally, which explains many of its cardiac effects
Theophylline has been shown to inhibit TGF-beta-mediated conversion of pulmonary fibroblasts into myofibroblasts in COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
and asthma
Asthma
Asthma is the common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath...
via cAMP-PKA pathway and suppresses COL1 mRNA, which codes for the protein collagen
Collagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
.
It has been shown that theophylline may reverse the clinical observations of steroid insensitivity in patients with COPD and asthmatics that are active smokers (a condition resulting in oxidative stress
Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress represents an imbalance between the production and manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage...
) via a distinctly separate mechanism. Theophylline in vitro can restore the reduced HDAC (histone deacetylase) activity that is induced by oxidative stress (i.e., in smokers), returning steroid responsiveness toward normal. Furthermore, theophylline has been shown to directly activate HDAC2. (Corticosteroid
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex. Corticosteroids are involved in a wide range of physiologic systems such as stress response, immune response and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte...
s switch off the inflammatory response by blocking the expression of inflammatory mediators through deacetylation of histones, an effect mediated via histone deacetylase-2 (HDAC2). Once deacetylated, DNA is repackaged so that the promoter regions of inflammatory genes are unavailable for binding of transcription factors such as NF-κB that act to turn on inflammatory activity. It has recently been shown that the oxidative stress associated with cigarette smoke can inhibit the activity of HDAC2, thereby blocking the anti-inflammatory effects of corticosteroids.) Thus theophylline could prove to be a novel form of adjunct therapy in improving the clinical response to steroids in smoking asthmatics.
Absorption
When theophylline is administered intravenously, bioavailabilityBioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
is 100%. However, if taken orally, taking the drug late in the evening may slow the absorption process, without affecting the bioavailability. Taking the drug after a meal high in fat content will also slow down the absorption process, without affecting the bioavailability.
Distribution
Theophylline is distributed in the extracellular fluid, in the placenta, in the mother's milk and in the central nervous system. The volume of distribution is 0.5 L/kg. The protein binding is 40%. The volume of distribution may increase in neonates and those suffering from cirrhosis or malnutrition, whereas the volume of distribution may decrease in those who are obese.Metabolism
Theophylline is metabolized extensively in the liver (up to 70%). It undergoes N-demethylation via cytochromeCytochrome
Cytochromes are, in general, membrane-bound hemoproteins that contain heme groups and carry out electron transport.They are found either as monomeric proteins or as subunits of bigger enzymatic complexes that catalyze redox reactions....
P450 1A2. It is metabolized by parallel first order and Michaelis-Menten
Michaelis-Menten kinetics
In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics is one of the simplest and best-known models of enzyme kinetics. It is named after German biochemist Leonor Michaelis and Canadian physician Maud Menten. The model takes the form of an equation describing the rate of enzymatic reactions, by relating...
pathways. Metabolism may become saturated (non-linear), even within the therapeutic range. Small dose increases may result in disproportionately large increases in serum concentration. Methylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
in caffeine is also important in the infant population. Smokers and people with hepatic (liver) impairment metabolize it differently.
Elimination
Theophylline is excreted unchanged in the urine (up to 10%). Clearance of the drug is increased in these conditions: children 1 to 12, teenagers 12 to 16, adult smokers, elderly smokers, cystic fibrosisCystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease affecting most critically the lungs, and also the pancreas, liver, and intestine...
, hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the term for overactive tissue within the thyroid gland causing an overproduction of thyroid hormones . Hyperthyroidism is thus a cause of thyrotoxicosis, the clinical condition of increased thyroid hormones in the blood. Hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis are not synonymous...
. Clearance of the drug is decreased in these conditions: elderly, acute congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, hypothyroidism and febrile viral illness.
The elimination half-life
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
varies: 30 hours for premature neonates, 24 hours for neonates, 3.5 hours for children ages 1 to 9, 8 hours for adult non-smokers, 5 hours for adult smokers, 24 hours for those with hepatic impairment, 12 hours for those with congestive heart failure NYHA class I-II, 24 hours for those with congestive heart failure NYHA class III-IV, 12 hours for the elderly.
History
Theophylline was first extracted from tea leaves and chemically identified around 1888 by the German biologist Albrecht KosselAlbrecht Kossel
Ludwig Karl Martin Leonhard Albrecht Kossel was a German biochemist and pioneer in the study of genetics. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1910 for his work in determining the chemical composition of nucleic acids, the genetic substance of biological cells.Kossel...
. Just seven years after its discovery, a chemical synthesis
Chemical synthesis
In chemistry, chemical synthesis is purposeful execution of chemical reactions to get a product, or several products. This happens by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions...
starting with 1,3-dimethyluric acid was described by Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer
Emil Fischer may refer to:* Emil Fischer , German dramatic basso* Franz Joseph Emil Fischer , German chemist, worked with oil and coal* Hermann Emil Fischer , German Nobel laureate in chemistry...
and Lorenz Ach. The Traube synthesis, an alternative method to synthesize theophylline, was introduced in 1900 by another German scientist, Wilhelm Traube
Wilhelm Traube
Wilhelm Traube was a German chemist.- Biography :Traube was born at Ratibor in Prussian Silesia, a son of the famous private scholar Moritz Traube....
. Theophylline's first clinical use came in 1902 as diuretic
Diuretic
A diuretic provides a means of forced diuresis which elevates the rate of urination. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from bodies, although each class does so in a distinct way.- Medical uses :...
. It took an additional 20 years until its first description in asthma treatment.
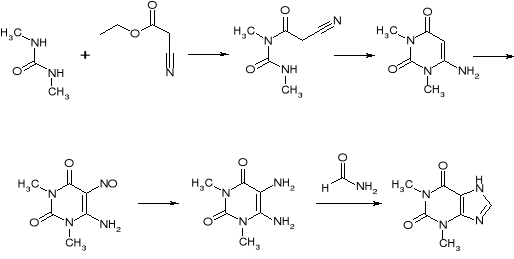
Synthesis
Theophylline can be prepared synthetically starting from dimethylureaDimethylurea
Dimethylurea is a urea derivative and used as an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is a colorless crystalline powder with little toxicity.-Uses:...
and ethyl 2-cyanoacetate.